Monday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P1784 - HIV & Non-HIV Patients Have Similar Rates of Neoplastic Findings at Index Screening Colonoscopy Within a Predominant African-American Cohort
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- PM
Pooja Mude, DO
Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University
North Augusta, SC
Presenting Author(s)
Pooja Mude, DO1, Lavannya Atri, MD2, Samantha Newman, 2, Carlos Palacio, MD3, John Erikson Yap, MD, MBA2, Christian Jackson, MD4, Kenneth J. Vega, MD, FACG2
1Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, North Augusta, SC; 2Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, Augusta, GA; 3University of Florida Health Science Center, Jacksonville, FL; 4VA Loma Linda Healthcare System, Loma Linda, CA
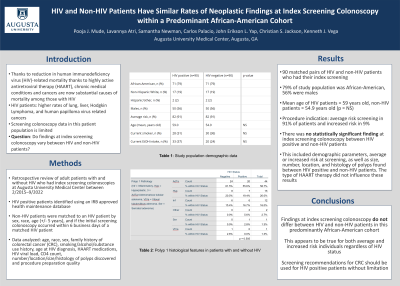
Introduction: Due to the reduction in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) related mortality due to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), chronic medical conditions and cancers are now substantial causes of mortality among those with HIV. HIV patients have higher rates of lung, liver, Hodgkin Lymphoma, and human papilloma virus related cancers, but screening colonoscopy data in this patient population is limited. The primary aim of our study was to determine if findings at index screening colonoscopy varied between HIV and non-HIV patients.
Methods: A retrospective review of adult patients with and without HIV who had index screening colonoscopies at Augusta University Medical Center between 2/2015–9/2022 was performed. HIV positive patients were identified using an IRB approved health maintenance database. Non-HIV patients were then matched to an HIV patient by sex, race, age (+/- 5 years), and if the initial screening colonoscopy occurred within 6 business days of a matched HIV patient. Data analyzed included: age, race, sex, family history of colorectal cancer (CRC), smoking/alcohol/substance use history, age at HIV diagnosis, HAART medications, HIV viral load, CD4 count, number/location/size/histology of polyps discovered and procedure preparation quality.
Results: 90 matched pairs of HIV and non-HIV patients who had their index screening colonoscopy were found within the inclusion period and comprised the study group. 79% of the study population was African-American and 56% were males. The mean age of HIV patients was 59 years old, while non-HIV patients was 54.9 years old (p = NS). Procedure indication was average risk screening in 91% of patients and increased risk in 9%. There was no statistically significant finding at index screening colonoscopy between HIV positive and non-HIV patients. This included demographic parameters, average or increased risk at screening, as well as size, number, location, and histology of polyps found between HIV positive and non-HIV patients. The type of HAART therapy did not influence these results.
Discussion: Findings at index screening colonoscopy do not differ between HIV and non-HIV patients in this predominantly African-American cohort. This appears to be true for both average and increased risk individuals regardless of HIV status. Screening recommendations for CRC should be used for HIV positive patients without limitation.
Disclosures:
Pooja Mude, DO1, Lavannya Atri, MD2, Samantha Newman, 2, Carlos Palacio, MD3, John Erikson Yap, MD, MBA2, Christian Jackson, MD4, Kenneth J. Vega, MD, FACG2. P1784 - HIV & Non-HIV Patients Have Similar Rates of Neoplastic Findings at Index Screening Colonoscopy Within a Predominant African-American Cohort, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, North Augusta, SC; 2Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, Augusta, GA; 3University of Florida Health Science Center, Jacksonville, FL; 4VA Loma Linda Healthcare System, Loma Linda, CA
Introduction: Due to the reduction in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) related mortality due to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), chronic medical conditions and cancers are now substantial causes of mortality among those with HIV. HIV patients have higher rates of lung, liver, Hodgkin Lymphoma, and human papilloma virus related cancers, but screening colonoscopy data in this patient population is limited. The primary aim of our study was to determine if findings at index screening colonoscopy varied between HIV and non-HIV patients.
Methods: A retrospective review of adult patients with and without HIV who had index screening colonoscopies at Augusta University Medical Center between 2/2015–9/2022 was performed. HIV positive patients were identified using an IRB approved health maintenance database. Non-HIV patients were then matched to an HIV patient by sex, race, age (+/- 5 years), and if the initial screening colonoscopy occurred within 6 business days of a matched HIV patient. Data analyzed included: age, race, sex, family history of colorectal cancer (CRC), smoking/alcohol/substance use history, age at HIV diagnosis, HAART medications, HIV viral load, CD4 count, number/location/size/histology of polyps discovered and procedure preparation quality.
Results: 90 matched pairs of HIV and non-HIV patients who had their index screening colonoscopy were found within the inclusion period and comprised the study group. 79% of the study population was African-American and 56% were males. The mean age of HIV patients was 59 years old, while non-HIV patients was 54.9 years old (p = NS). Procedure indication was average risk screening in 91% of patients and increased risk in 9%. There was no statistically significant finding at index screening colonoscopy between HIV positive and non-HIV patients. This included demographic parameters, average or increased risk at screening, as well as size, number, location, and histology of polyps found between HIV positive and non-HIV patients. The type of HAART therapy did not influence these results.
Discussion: Findings at index screening colonoscopy do not differ between HIV and non-HIV patients in this predominantly African-American cohort. This appears to be true for both average and increased risk individuals regardless of HIV status. Screening recommendations for CRC should be used for HIV positive patients without limitation.
Disclosures:
Pooja Mude indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lavannya Atri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samantha Newman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carlos Palacio indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Erikson Yap indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christian Jackson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kenneth Vega indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pooja Mude, DO1, Lavannya Atri, MD2, Samantha Newman, 2, Carlos Palacio, MD3, John Erikson Yap, MD, MBA2, Christian Jackson, MD4, Kenneth J. Vega, MD, FACG2. P1784 - HIV & Non-HIV Patients Have Similar Rates of Neoplastic Findings at Index Screening Colonoscopy Within a Predominant African-American Cohort, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
