Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P1810 - Efficacy of Recurrence Prevention by Adjuvant Radiotherapy After Endoscopic Resection for Early Esophagus Cancer
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- HF
Hirofumi Fukushima, PhD
Juntendo University School of Medicine
Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan
Presenting Author(s)
Hirofumi Fukushima, PhD, Nobuko Serizawa, PhD, Takahito Awatsu, MD, Mayu Yada, MD, Takashi Murakami, PhD, Hiroya Ueyama, PhD, Dai Ishikawa, PhD, Tomoyoshi Shibuya, PhD, Mariko Hojo, PhD, Akihito Nagahara, PhD
Juntendo University School of Medicine, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan
Introduction:
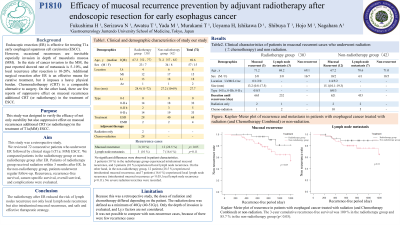
Endoscopic resection (ER) is effective for treating T1a early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). However, occasional recurrences are inevitable especially invasion in depth of muscularis mucosa (MM). In the state of cancer invasion to the MM, the past reported showed rate of metastasis is 5–10%, and local recurrence is 10-20%. Additional surgical resection after ER is an effective means for curative treatment, but it imposes a heavy physical burden. Radiotherapy is a comparable alternative to surgery. This study was designed to verify the efficacy of not only curability but also suppressive effect on recurrences additional radiotherapy in the treatment of T1a(MM) ESCC.
Methods: This study was a retrospective study. We reviewed 72 consecutive patients who underwent ER followed by clinical stage I (T1a: MM) ESCC. We compared patients in the radiotherapy group or non-radiotherapy group after ER. Patients of radiotherapy group received radiation within 3 months after ER. In the non-radiotherapy group, patients underwent regular follow-up. Recurrence, recurrence-free survival, cancer-specific survival, overall survival, and complications were evaluated.
Results:
There were 30 cases of radiotherapy group and 42 cases of non-radiotherapy group among 72 patients. 3 patients (10 %) in the radiotherapy group experienced intraluminal mucosal recurrence, and 3 patients (10 %) experienced local lymph node recurrence. On the other hand, in the non-radiotherapy group, 10 patients (23.8 %) experienced intraluminal mucosal recurrence, and 7 patients (16.6 %) experienced local lymph node recurrence (intraluminal mucosal recurrence: p< 0.05, local lymph node recurrence p=0.11). The 3-year cumulative recurrence-free survival was 100 % in the radiotherapy group and 85.7 % in the non-radiotherapy group (p< 0.05). No severe radiation toxicities were recorded.
Discussion: The radiotherapy after ESD reduced the risk of lymph nodes recurrence not only local lymph node recurrence but also intraluminal mucosal recurrence, and safe and effective therapeutic strategy. Report including representative cases.
Disclosures:
Hirofumi Fukushima, PhD, Nobuko Serizawa, PhD, Takahito Awatsu, MD, Mayu Yada, MD, Takashi Murakami, PhD, Hiroya Ueyama, PhD, Dai Ishikawa, PhD, Tomoyoshi Shibuya, PhD, Mariko Hojo, PhD, Akihito Nagahara, PhD. P1810 - Efficacy of Recurrence Prevention by Adjuvant Radiotherapy After Endoscopic Resection for Early Esophagus Cancer, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Juntendo University School of Medicine, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan
Introduction:
Endoscopic resection (ER) is effective for treating T1a early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). However, occasional recurrences are inevitable especially invasion in depth of muscularis mucosa (MM). In the state of cancer invasion to the MM, the past reported showed rate of metastasis is 5–10%, and local recurrence is 10-20%. Additional surgical resection after ER is an effective means for curative treatment, but it imposes a heavy physical burden. Radiotherapy is a comparable alternative to surgery. This study was designed to verify the efficacy of not only curability but also suppressive effect on recurrences additional radiotherapy in the treatment of T1a(MM) ESCC.
Methods: This study was a retrospective study. We reviewed 72 consecutive patients who underwent ER followed by clinical stage I (T1a: MM) ESCC. We compared patients in the radiotherapy group or non-radiotherapy group after ER. Patients of radiotherapy group received radiation within 3 months after ER. In the non-radiotherapy group, patients underwent regular follow-up. Recurrence, recurrence-free survival, cancer-specific survival, overall survival, and complications were evaluated.
Results:
There were 30 cases of radiotherapy group and 42 cases of non-radiotherapy group among 72 patients. 3 patients (10 %) in the radiotherapy group experienced intraluminal mucosal recurrence, and 3 patients (10 %) experienced local lymph node recurrence. On the other hand, in the non-radiotherapy group, 10 patients (23.8 %) experienced intraluminal mucosal recurrence, and 7 patients (16.6 %) experienced local lymph node recurrence (intraluminal mucosal recurrence: p< 0.05, local lymph node recurrence p=0.11). The 3-year cumulative recurrence-free survival was 100 % in the radiotherapy group and 85.7 % in the non-radiotherapy group (p< 0.05). No severe radiation toxicities were recorded.
Discussion: The radiotherapy after ESD reduced the risk of lymph nodes recurrence not only local lymph node recurrence but also intraluminal mucosal recurrence, and safe and effective therapeutic strategy. Report including representative cases.
Disclosures:
Hirofumi Fukushima indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nobuko Serizawa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Takahito Awatsu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mayu Yada indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Takashi Murakami indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hiroya Ueyama indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dai Ishikawa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tomoyoshi Shibuya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mariko Hojo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akihito Nagahara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hirofumi Fukushima, PhD, Nobuko Serizawa, PhD, Takahito Awatsu, MD, Mayu Yada, MD, Takashi Murakami, PhD, Hiroya Ueyama, PhD, Dai Ishikawa, PhD, Tomoyoshi Shibuya, PhD, Mariko Hojo, PhD, Akihito Nagahara, PhD. P1810 - Efficacy of Recurrence Prevention by Adjuvant Radiotherapy After Endoscopic Resection for Early Esophagus Cancer, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
