Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0044 - Utilization of Analytic Morphomics to Differentiate Mucinous From Nonmucinous Pancreatic Cysts
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- SM
Stacy B. Menees, MD, MS
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Stacy B. Menees, MD, MS1, Derstine Brian, PhD2, Grace Su, MD2
1University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI; 2Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI
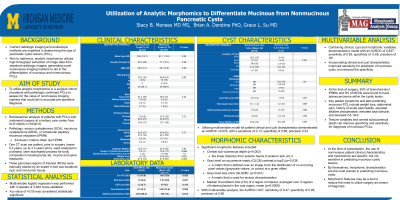
Introduction: Current radiologic imaging and endoscopic methods are imperfect in determining the type of pancreatic cystic lesions (PCL). Akin to radiomics, analytic morphomics utilizes high throughput extraction of image data from standard radiologic images, generating novel noninvasive imaging markers to aid in the differentiation of mucinous and nonmucinous PCLs. The aim of this study is to utilize analytic morphomics in a surgical cohort of patients with pathologic confirmed PCLs to assess for the value of noninvasive imaging markers that could aid in accurate pre-operative diagnosis.
Methods: We performed a retrospective review from 01/01/2000 - 11/18/2019 using Data Direct to query for patients with pancreatic cystic lesions who underwent surgery. Chart review was performed to confirm pathologic diagnosis of serous cystadenoma (SCA), mucinous cystadenoma (MCN), or intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) and extract patient demographic and clinical characteristics. Main-duct IPMNs were excluded from this cohort. Analysis of CT scans was performed in blinded, semi-automated process. Univariate analysis and multivariable analysis was performed utilizing 3-fold cross-validation of variables with a p < .05 or a priori selected or excluded based on clinical relevance, ‘noise’ and/or highly collinear variables.
Results: 170 patients were included in this analysis. On univariate analysis, the clinical factors associated with mucinous PCLs included presence of abdominal pain or weight loss, elevated alkaline phosphatase (109 vs. 83), elevated total bilirubin (3.0 vs. 0.52), cyst size (5.09 cm vs. 3.78 cm) and elevated serum CA 19-9 (188 vs 13). On multivariable model, the AUROC =0.63, with sensitivity of 0.03, and specificity of 0.98. The morphomic features on univariate analysis included the linear distance from anterior fascia to anterior skin at L3 (23.18 vs. 30.31), grey level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM contrast.tc.top3) (8.58 vs. 7.48), gray level size zone (GLSZM) and median Hounsfield Units (HU) of a region of interest, averaged over 3 regions of interest placed in the cyst region, mean (19.16 vs. 49.08). On multivariable analysis, the AUROC=.805, with a sensitivity of 0.35 and specificity of 0.97.
Discussion: Conclusion: At the time of presentation, the use of noninvasive patient clinical characteristics and radiomics are specific, but not sensitive in predicting mucinous cystic lesions. Morphomic features may be a tool to reduce the need to utilize surgery as means of diagnosis.
Disclosures:
Stacy B. Menees, MD, MS1, Derstine Brian, PhD2, Grace Su, MD2. P0044 - Utilization of Analytic Morphomics to Differentiate Mucinous From Nonmucinous Pancreatic Cysts, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI; 2Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI
Introduction: Current radiologic imaging and endoscopic methods are imperfect in determining the type of pancreatic cystic lesions (PCL). Akin to radiomics, analytic morphomics utilizes high throughput extraction of image data from standard radiologic images, generating novel noninvasive imaging markers to aid in the differentiation of mucinous and nonmucinous PCLs. The aim of this study is to utilize analytic morphomics in a surgical cohort of patients with pathologic confirmed PCLs to assess for the value of noninvasive imaging markers that could aid in accurate pre-operative diagnosis.
Methods: We performed a retrospective review from 01/01/2000 - 11/18/2019 using Data Direct to query for patients with pancreatic cystic lesions who underwent surgery. Chart review was performed to confirm pathologic diagnosis of serous cystadenoma (SCA), mucinous cystadenoma (MCN), or intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) and extract patient demographic and clinical characteristics. Main-duct IPMNs were excluded from this cohort. Analysis of CT scans was performed in blinded, semi-automated process. Univariate analysis and multivariable analysis was performed utilizing 3-fold cross-validation of variables with a p < .05 or a priori selected or excluded based on clinical relevance, ‘noise’ and/or highly collinear variables.
Results: 170 patients were included in this analysis. On univariate analysis, the clinical factors associated with mucinous PCLs included presence of abdominal pain or weight loss, elevated alkaline phosphatase (109 vs. 83), elevated total bilirubin (3.0 vs. 0.52), cyst size (5.09 cm vs. 3.78 cm) and elevated serum CA 19-9 (188 vs 13). On multivariable model, the AUROC =0.63, with sensitivity of 0.03, and specificity of 0.98. The morphomic features on univariate analysis included the linear distance from anterior fascia to anterior skin at L3 (23.18 vs. 30.31), grey level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM contrast.tc.top3) (8.58 vs. 7.48), gray level size zone (GLSZM) and median Hounsfield Units (HU) of a region of interest, averaged over 3 regions of interest placed in the cyst region, mean (19.16 vs. 49.08). On multivariable analysis, the AUROC=.805, with a sensitivity of 0.35 and specificity of 0.97.
Discussion: Conclusion: At the time of presentation, the use of noninvasive patient clinical characteristics and radiomics are specific, but not sensitive in predicting mucinous cystic lesions. Morphomic features may be a tool to reduce the need to utilize surgery as means of diagnosis.
| Variable | |
| cyst type IPMN MCN SCA | 48% 27% 25% |
| Gender Female | 70.6% |
| Mean Age yrs | 60.7 (+13.9) |
| Mean Cyst size (cm) | 4.8 (+5.3) |
Table: Patient demographics
Disclosures:
Stacy Menees indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Derstine Brian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Grace Su: Applied Morphomics – equity interest.
Stacy B. Menees, MD, MS1, Derstine Brian, PhD2, Grace Su, MD2. P0044 - Utilization of Analytic Morphomics to Differentiate Mucinous From Nonmucinous Pancreatic Cysts, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
