Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0102 - A Rare Case of IgG4 Related Disease Masquerading as Pancreatic Cancer
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- SP
Sailaja Pisipati, MBBS
Mayo Clinic Arizona
Rochester, MN
Presenting Author(s)
Sailaja Pisipati, MBBS1, Sean Sileno, MD2, Rahul Pannala, MD2, Michelle Anderson, MD2
1Mayo Clinic Arizona, Scottsdale, AZ; 2Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ
Introduction: Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a rare, distinct form of pancreatitis, characterized by lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, fibrosis, frequent elevations of serum IgG4, and dramatic response to steroids. It can manifest as obstructive jaundice, pancreatic mass and should be distinguished from pancreatic adenocarcinoma, although this can be challenging.
Case Description/Methods: 66-year-old male with microscopic colitis, was admitted with 6-months of abdominal pain, weight loss and fatigue. He developed erythematous, pruritic rash refractory to several therapies for possible lupus. Biopsy of rash showed features of interface dermatitis and scattered eosinophils. Labs suggested elevated lipase 512, deranged liver enzymes with ALP 341, ALT/AST 257/128, bilirubin 0.2. Abdominal CT revealed 4.1cm pancreatic head mass, with abrupt cut off of distal bile duct with proximal dilation, mild pancreatic ductal dilation and peripancreatic stranding in keeping with mild pancreatitis. Endoscopic ultrasound demonstrated indistinct 31 x 29mm mass in the head and uncinate, core biopsies obtained and metal biliary stent deployed. Pathology demonstrated lymphoplasmacytic and neutrophilic infiltration and areas of dense fibrosis. IgG4 staining showed increase in IgG4-positive cells; pathology was suggestive of AIP-1. Autoimmune panel showed elevated IgG4 205, and negative for other autoimmune conditions. Diagnosis of AIP-1 was made and patient was initiated on prednisone 40mg daily. Symptoms though improved initially, relapsed with elevation in IgG4 levels with prednisone taper needing escalation of steroid dose. Sequential MRCPs at 4 and 16 weeks demonstrated resolution of the pancreatic changes, but persistent multifocal biliary ductal stricturing and periductal enhancement in keeping with autoimmune IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. Based on 2019 ACR criteria, diagnosis of IgG4 Related Disease (IgG4-RD) was made. He was subsequently initiated on anti-CD 20 monoclonal antibody–rituximab, with clinical and radiographic improvement.
Discussion: IgG4-RD is an immune mediated fibrosclerosing disease characterized by infiltration with IgG4 plasma cells, associated with AIP-1. Common extra-pancreatic sites include biliary tree, salivary gland, periorbital tissue, lung, kidney, nodes, aorta, retroperitoneum, thyroid. Symptom relapse is common after initial therapy with corticosteroids. Rituximab is safe and effective for maintenance; it causes B-cell depletion resulting in depletion of IgG-4 plasma cells.

Disclosures:
Sailaja Pisipati, MBBS1, Sean Sileno, MD2, Rahul Pannala, MD2, Michelle Anderson, MD2. P0102 - A Rare Case of IgG4 Related Disease Masquerading as Pancreatic Cancer, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mayo Clinic Arizona, Scottsdale, AZ; 2Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ
Introduction: Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a rare, distinct form of pancreatitis, characterized by lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, fibrosis, frequent elevations of serum IgG4, and dramatic response to steroids. It can manifest as obstructive jaundice, pancreatic mass and should be distinguished from pancreatic adenocarcinoma, although this can be challenging.
Case Description/Methods: 66-year-old male with microscopic colitis, was admitted with 6-months of abdominal pain, weight loss and fatigue. He developed erythematous, pruritic rash refractory to several therapies for possible lupus. Biopsy of rash showed features of interface dermatitis and scattered eosinophils. Labs suggested elevated lipase 512, deranged liver enzymes with ALP 341, ALT/AST 257/128, bilirubin 0.2. Abdominal CT revealed 4.1cm pancreatic head mass, with abrupt cut off of distal bile duct with proximal dilation, mild pancreatic ductal dilation and peripancreatic stranding in keeping with mild pancreatitis. Endoscopic ultrasound demonstrated indistinct 31 x 29mm mass in the head and uncinate, core biopsies obtained and metal biliary stent deployed. Pathology demonstrated lymphoplasmacytic and neutrophilic infiltration and areas of dense fibrosis. IgG4 staining showed increase in IgG4-positive cells; pathology was suggestive of AIP-1. Autoimmune panel showed elevated IgG4 205, and negative for other autoimmune conditions. Diagnosis of AIP-1 was made and patient was initiated on prednisone 40mg daily. Symptoms though improved initially, relapsed with elevation in IgG4 levels with prednisone taper needing escalation of steroid dose. Sequential MRCPs at 4 and 16 weeks demonstrated resolution of the pancreatic changes, but persistent multifocal biliary ductal stricturing and periductal enhancement in keeping with autoimmune IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. Based on 2019 ACR criteria, diagnosis of IgG4 Related Disease (IgG4-RD) was made. He was subsequently initiated on anti-CD 20 monoclonal antibody–rituximab, with clinical and radiographic improvement.
Discussion: IgG4-RD is an immune mediated fibrosclerosing disease characterized by infiltration with IgG4 plasma cells, associated with AIP-1. Common extra-pancreatic sites include biliary tree, salivary gland, periorbital tissue, lung, kidney, nodes, aorta, retroperitoneum, thyroid. Symptom relapse is common after initial therapy with corticosteroids. Rituximab is safe and effective for maintenance; it causes B-cell depletion resulting in depletion of IgG-4 plasma cells.

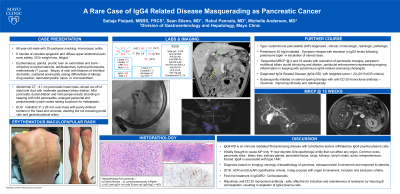
Figure: a) Erythematous, pruritic, maculopapular rash
b) Coronal view of CT abdomen showing pancreatic head mass (yellow arrow) and proximal biliary dilation
c) Cholangiogram demonstrating proximal biliary dilation and distal biliary stricture
d) Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and fibrosis
e) Immunohistochemistry with IgG4 positive plasma cells
f) MRI showing resolution of pancreatic head mass and multi-focal pancreatic duct strictures
g) MRCP demonstrating biliary and pancreatic ductal strictures
b) Coronal view of CT abdomen showing pancreatic head mass (yellow arrow) and proximal biliary dilation
c) Cholangiogram demonstrating proximal biliary dilation and distal biliary stricture
d) Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and fibrosis
e) Immunohistochemistry with IgG4 positive plasma cells
f) MRI showing resolution of pancreatic head mass and multi-focal pancreatic duct strictures
g) MRCP demonstrating biliary and pancreatic ductal strictures
Disclosures:
Sailaja Pisipati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sean Sileno indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rahul Pannala: Aimmune Therapeutics, a Nestlé Health Science company – Consultant. blue star genomics – Advisor or Review Panel Member. HCL technologies – Consultant.
Michelle Anderson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sailaja Pisipati, MBBS1, Sean Sileno, MD2, Rahul Pannala, MD2, Michelle Anderson, MD2. P0102 - A Rare Case of IgG4 Related Disease Masquerading as Pancreatic Cancer, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
