Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0206 - The Evolving Epidemiology of Colonic Ischemia: A Multi-Center Study
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Kanika Sehgal, MBBS
Yale-New Haven Hospital
New Haven, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Kanika Sehgal, MBBS1, Rabia Rizwan, MD2, Abdelkader Chaar, MD2, Ahmad Nawaz, MD2, Karthik Gnanapandithan, MD3, Abdul Bhutta, MD4, Marc Fenster, MD5, Savio John, MD6, Lawrence Brandt, MD, MACG7, Paul Feuerstadt, MD, FACG8
1Yale-New Haven Hospital, New Haven, CT; 2Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT; 3Mayo Clinic Florida, Jacksonville, FL; 4University Gastroenterology, Portsmouth, RI; 5Montefiore, Bronx, NY; 6SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY; 7Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx, NY; 8PACT Gastroenterology Center and Yale School of Medicine, Hamden, CT
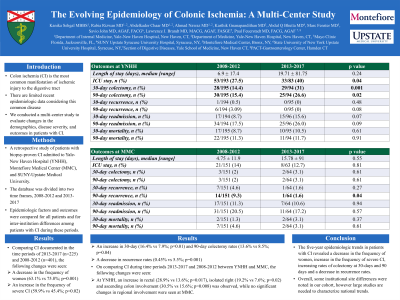
Introduction: Colon ischemia (CI) is the most common cause of ischemic injury to the GI tract but pertinent recent epidemiologic data are limited. We therefore conducted a multi-center study to evaluate changes in demographics, disease severity and outcomes in pts with CI.
Methods: A retrospective study of biopsy-proven CI pts admitted to Yale-New Haven Hospital (YNHH), Montefiore Medical Center (MMC), and SUNY-Upstate Medical University. The data base was divided into two time frames, 2008-2012 and 2013-2017, and epidemiologic factors and outcomes were compared for all pts and for inter-institution differences among CI pts during these periods.
Results: 401 and 225 pts were included in the 2008-2012 and 2013-2017 time periods respectively. Woman predominated but a decrease in female predominance was seen during 2013-2017 (75.8% in 2008-2012 vs 63.1% in 2013-2017; p=0.001). Comparing the older to the more recent time frame, CI severity decreased (45.4% vs 59.9%; p=0.023), rectal involvement increased (12.4% vs 20.8%; p=0.031), 30-day (8.0% vs 16.4%; p=0.001) and 90-day colectomy rates increased (8.5% vs 13.6%; p=0.043), and 90-day recurrence rate decreased (5.5% vs 0.4%; p=0.001).
Most CI patients were from YNHH (n=295) and MMC (n=215). Both sites held a female predominance, however this was not significant within the 5-year time frames. At YNHH, disease severity increased (47.2% vs 64.9%; p=0.012), while at MMC there was no difference in disease severity (45.0% vs 52.5%;p=0.327). A greater proportion of pts received antibiotics recently (p=0.008) at YNHH, though this was not significant change at MMC (p=0.251). At YNHH, the more recent time period had increases in rectal (13.6% vs 28.9%; p=0.017), isolated right-CI (7.6% vs 19.2%; p=0.027) and ascending colon involvement (15.6% vs 30.5%; p=0.008). There were no significant changes in regional involvement at MMC. At YNHH, there were increasing rates of ICU stay (27.5% vs 40.0%; p=0.043), 30-day (14.4% v 31%; p=0.001) and 90-day colectomy (15.4% vs 26.6%; p=0.023) in the more modern time frame. At MMC, 30-day colectomy rate increased though this was not significant (2% vs. 3.12%;p=0.613) while 90-day recurrence decreased (9.3% vs 1.6%; p=0.042).
Discussion: 5-year epidemiologic trends in pts with CI showed a decrease in the disease severity, with an increase in rectal involvement, with increasing rates of colectomy at 30 and 90 days. Some institutional site differences were noted but large studies are needed to characterize national trends.
Disclosures:
Kanika Sehgal, MBBS1, Rabia Rizwan, MD2, Abdelkader Chaar, MD2, Ahmad Nawaz, MD2, Karthik Gnanapandithan, MD3, Abdul Bhutta, MD4, Marc Fenster, MD5, Savio John, MD6, Lawrence Brandt, MD, MACG7, Paul Feuerstadt, MD, FACG8. P0206 - The Evolving Epidemiology of Colonic Ischemia: A Multi-Center Study, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Yale-New Haven Hospital, New Haven, CT; 2Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT; 3Mayo Clinic Florida, Jacksonville, FL; 4University Gastroenterology, Portsmouth, RI; 5Montefiore, Bronx, NY; 6SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY; 7Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx, NY; 8PACT Gastroenterology Center and Yale School of Medicine, Hamden, CT
Introduction: Colon ischemia (CI) is the most common cause of ischemic injury to the GI tract but pertinent recent epidemiologic data are limited. We therefore conducted a multi-center study to evaluate changes in demographics, disease severity and outcomes in pts with CI.
Methods: A retrospective study of biopsy-proven CI pts admitted to Yale-New Haven Hospital (YNHH), Montefiore Medical Center (MMC), and SUNY-Upstate Medical University. The data base was divided into two time frames, 2008-2012 and 2013-2017, and epidemiologic factors and outcomes were compared for all pts and for inter-institution differences among CI pts during these periods.
Results: 401 and 225 pts were included in the 2008-2012 and 2013-2017 time periods respectively. Woman predominated but a decrease in female predominance was seen during 2013-2017 (75.8% in 2008-2012 vs 63.1% in 2013-2017; p=0.001). Comparing the older to the more recent time frame, CI severity decreased (45.4% vs 59.9%; p=0.023), rectal involvement increased (12.4% vs 20.8%; p=0.031), 30-day (8.0% vs 16.4%; p=0.001) and 90-day colectomy rates increased (8.5% vs 13.6%; p=0.043), and 90-day recurrence rate decreased (5.5% vs 0.4%; p=0.001).
Most CI patients were from YNHH (n=295) and MMC (n=215). Both sites held a female predominance, however this was not significant within the 5-year time frames. At YNHH, disease severity increased (47.2% vs 64.9%; p=0.012), while at MMC there was no difference in disease severity (45.0% vs 52.5%;p=0.327). A greater proportion of pts received antibiotics recently (p=0.008) at YNHH, though this was not significant change at MMC (p=0.251). At YNHH, the more recent time period had increases in rectal (13.6% vs 28.9%; p=0.017), isolated right-CI (7.6% vs 19.2%; p=0.027) and ascending colon involvement (15.6% vs 30.5%; p=0.008). There were no significant changes in regional involvement at MMC. At YNHH, there were increasing rates of ICU stay (27.5% vs 40.0%; p=0.043), 30-day (14.4% v 31%; p=0.001) and 90-day colectomy (15.4% vs 26.6%; p=0.023) in the more modern time frame. At MMC, 30-day colectomy rate increased though this was not significant (2% vs. 3.12%;p=0.613) while 90-day recurrence decreased (9.3% vs 1.6%; p=0.042).
Discussion: 5-year epidemiologic trends in pts with CI showed a decrease in the disease severity, with an increase in rectal involvement, with increasing rates of colectomy at 30 and 90 days. Some institutional site differences were noted but large studies are needed to characterize national trends.
Disclosures:
Kanika Sehgal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rabia Rizwan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelkader Chaar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Nawaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karthik Gnanapandithan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Bhutta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marc Fenster indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Savio John indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lawrence Brandt: Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant.
Paul Feuerstadt: Ferring/Rebiotix, Inc. – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Merck & Co. – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Seres Therapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Takeda Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Kanika Sehgal, MBBS1, Rabia Rizwan, MD2, Abdelkader Chaar, MD2, Ahmad Nawaz, MD2, Karthik Gnanapandithan, MD3, Abdul Bhutta, MD4, Marc Fenster, MD5, Savio John, MD6, Lawrence Brandt, MD, MACG7, Paul Feuerstadt, MD, FACG8. P0206 - The Evolving Epidemiology of Colonic Ischemia: A Multi-Center Study, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
