Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0223 - Not so Microscopic Colitis: Abnormal Endoscopic Findings in a Patient With Lymphocytic Colitis
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- NS
Nitin K. Sardana, MD
Gastro Health
Annandale, VA
Presenting Author(s)
Dipam Shah, MD1, Reem Al Shabeeb, MD1, Christie Zheng, BS2, Monica Passi, MD3, Nitin K. Sardana, MD4
1Inova Fairfax Medical Campus, Fairfax, VA; 2Inova, Fairfax, VA; 3Gastro Health, Fairfax, VA; 4Gastro Health, Annandale, VA
Introduction: Lymphocytic colitis and collagenous colitis are subtypes of microscopic colitis diagnosed by histological findings and are characterized by normal mucosa on colonoscopy. Recent advances in endoscopic technology have revealed certain macroscopic findings associated with MC, predominately with collagenous colitis. We report a case of lymphocytic colitis with abnormal endoscopic findings.
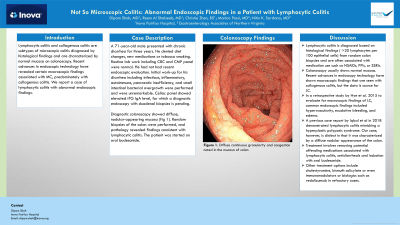
Case Description/Methods: A 71 year-old male presented with chronic diarrhea for three years. He denied diet changes, new medications or tobacco smoking. Routine lab work including CBC and CMP panel were normal. He had not had recent endoscopic evaluation. Initial work-up for his diarrhea including infectious, inflammatory, autoimmune, pancreatic insufficiency, and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth were performed and were unremarkable. Celiac panel showed elevated tTG IgA level, for which a diagnostic endoscopy with duodenal biopsies is pending. Diagnostic colonoscopy showed diffuse, nodular-appearing mucosa (fig 1). Random biopsies of the colon were performed and pathology revealed findings consistent with lymphocytic colitis. The patient was started on oral budesonide.
Discussion: Lymphocytic colitis is diagnosed based on histological findings ( >20 lymphocytes per 100 epithelial cells) from random colon biopsies and are often associated with medication use such as NSAIDs, PPIs, or SSRIs. Colonoscopy usually shows normal mucosa. Recent advances in endoscopy technology have shown macroscopic findings that are seen with collagenous colitis, but the data is scarce for LC. In a retrospective study by Hye et al. 2015 to evaluate for macroscopic findings of LC, common endoscopic findings included hypervascularity, exudative bleeding, and edema. A previous case report by Iqbal et al in 2018 demonstrated lymphocytic colitis mimicking a hyperplastic polyposis syndrome. Our case, however, is distinct in that it was characterized by a diffuse nodular appearance of the colon.
Treatment involves removing potential offending medications associated with lymphocytic colitis, antidiarrheals and induction with oral budesonide. Other treatment options include cholestyramine, bismuth salicylate or even immunomodulators or biologics such as vedolizumab in refractory cases.

Disclosures:
Dipam Shah, MD1, Reem Al Shabeeb, MD1, Christie Zheng, BS2, Monica Passi, MD3, Nitin K. Sardana, MD4. P0223 - Not so Microscopic Colitis: Abnormal Endoscopic Findings in a Patient With Lymphocytic Colitis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Inova Fairfax Medical Campus, Fairfax, VA; 2Inova, Fairfax, VA; 3Gastro Health, Fairfax, VA; 4Gastro Health, Annandale, VA
Introduction: Lymphocytic colitis and collagenous colitis are subtypes of microscopic colitis diagnosed by histological findings and are characterized by normal mucosa on colonoscopy. Recent advances in endoscopic technology have revealed certain macroscopic findings associated with MC, predominately with collagenous colitis. We report a case of lymphocytic colitis with abnormal endoscopic findings.
Case Description/Methods: A 71 year-old male presented with chronic diarrhea for three years. He denied diet changes, new medications or tobacco smoking. Routine lab work including CBC and CMP panel were normal. He had not had recent endoscopic evaluation. Initial work-up for his diarrhea including infectious, inflammatory, autoimmune, pancreatic insufficiency, and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth were performed and were unremarkable. Celiac panel showed elevated tTG IgA level, for which a diagnostic endoscopy with duodenal biopsies is pending. Diagnostic colonoscopy showed diffuse, nodular-appearing mucosa (fig 1). Random biopsies of the colon were performed and pathology revealed findings consistent with lymphocytic colitis. The patient was started on oral budesonide.
Discussion: Lymphocytic colitis is diagnosed based on histological findings ( >20 lymphocytes per 100 epithelial cells) from random colon biopsies and are often associated with medication use such as NSAIDs, PPIs, or SSRIs. Colonoscopy usually shows normal mucosa. Recent advances in endoscopy technology have shown macroscopic findings that are seen with collagenous colitis, but the data is scarce for LC. In a retrospective study by Hye et al. 2015 to evaluate for macroscopic findings of LC, common endoscopic findings included hypervascularity, exudative bleeding, and edema. A previous case report by Iqbal et al in 2018 demonstrated lymphocytic colitis mimicking a hyperplastic polyposis syndrome. Our case, however, is distinct in that it was characterized by a diffuse nodular appearance of the colon.
Treatment involves removing potential offending medications associated with lymphocytic colitis, antidiarrheals and induction with oral budesonide. Other treatment options include cholestyramine, bismuth salicylate or even immunomodulators or biologics such as vedolizumab in refractory cases.

Figure: Figure 1
Disclosures:
Dipam Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Reem Al Shabeeb indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christie Zheng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Monica Passi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nitin Sardana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dipam Shah, MD1, Reem Al Shabeeb, MD1, Christie Zheng, BS2, Monica Passi, MD3, Nitin K. Sardana, MD4. P0223 - Not so Microscopic Colitis: Abnormal Endoscopic Findings in a Patient With Lymphocytic Colitis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
