Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P0363 - Artificial Intelligence-Aided Colonoscopy in a Real World Setting
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- JA
Jayati Anand
Sidney Kimmel Medical School
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Presenting Author(s)
Jayati Anand, 1, Shiv Gandhi, MD2, Krunal Patel, MD3
1Sidney Kimmel Medical School, Philadelphia, PA; 2University of Massachusetts Medical Center, Worcester, MA; 3UMass Memorial Medical Center, Worcester, MA
Introduction: Artificial intelligence-aided colonoscopy (AIAC) is thought to increase adenoma detection rate (ADR) in colonoscopy. However, the impact on experienced endoscopists in community practice has not been established. Some studies have shown an improvement in ADR, whereas others have shown a decrease in ADR. Further, there is a concern that AIAC might prolong withdrawal time leading to longer procedure time. We performed a retrospective review of colonoscopies performed without and with computer-assisted detection (CADe) software in a community hospital with experienced endoscopists.
Methods: We reviewed screening and surveillance colonoscopies performed by 3 experienced endoscopists in a community hospital setting. Each endoscopist had at least 15+ years of experience with 25,000+ colonoscopies performed. We compared procedures performed over one month with computer-assisted polyp detection software (GI Genius, Medtronic) to those performed without it. We compared the adenoma detection rate and withdrawal time. AIAC data was obtained from the first complete month of implementation. Patients with incomplete colonoscopy and inadequate bowel preparation were excluded.
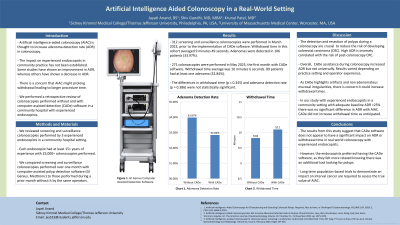
Results: Our study included 583 colonoscopies (312 pre-AIAC, 271 AIAC). Both groups were similar in age and gender distribution. 312 screening and surveillance colonoscopies were performed in March 2023, prior to the implementation of CADe software. Withdrawal time in this cohort averaged 9 minutes 49 seconds. Adenomas were detected in 106 patients (33.97%). 271 colonoscopies were performed in May 2023, the first month with CADe software. Withdrawal time average was 10 minutes 6 seconds. 89 patients had at least one adenoma (32.84%). The differences in withdrawal time (p = 0.345) and adenoma detection rate (p = 0.386) were not statistically significant.
Discussion: The results from this study suggest that CADe software does not appear to have a significant impact on ADR or withdrawal time in real world colonoscopy with experienced endoscopists. However, the endoscopists preferred having the CADe software, as they felt more relaxed knowing there was an additional tool looking for polyps. Long term population-based trials to demonstrate an impact on interval cancer are required to assess the true value of AIAC.
Disclosures:
Jayati Anand, 1, Shiv Gandhi, MD2, Krunal Patel, MD3. P0363 - Artificial Intelligence-Aided Colonoscopy in a Real World Setting, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Sidney Kimmel Medical School, Philadelphia, PA; 2University of Massachusetts Medical Center, Worcester, MA; 3UMass Memorial Medical Center, Worcester, MA
Introduction: Artificial intelligence-aided colonoscopy (AIAC) is thought to increase adenoma detection rate (ADR) in colonoscopy. However, the impact on experienced endoscopists in community practice has not been established. Some studies have shown an improvement in ADR, whereas others have shown a decrease in ADR. Further, there is a concern that AIAC might prolong withdrawal time leading to longer procedure time. We performed a retrospective review of colonoscopies performed without and with computer-assisted detection (CADe) software in a community hospital with experienced endoscopists.
Methods: We reviewed screening and surveillance colonoscopies performed by 3 experienced endoscopists in a community hospital setting. Each endoscopist had at least 15+ years of experience with 25,000+ colonoscopies performed. We compared procedures performed over one month with computer-assisted polyp detection software (GI Genius, Medtronic) to those performed without it. We compared the adenoma detection rate and withdrawal time. AIAC data was obtained from the first complete month of implementation. Patients with incomplete colonoscopy and inadequate bowel preparation were excluded.
Results: Our study included 583 colonoscopies (312 pre-AIAC, 271 AIAC). Both groups were similar in age and gender distribution. 312 screening and surveillance colonoscopies were performed in March 2023, prior to the implementation of CADe software. Withdrawal time in this cohort averaged 9 minutes 49 seconds. Adenomas were detected in 106 patients (33.97%). 271 colonoscopies were performed in May 2023, the first month with CADe software. Withdrawal time average was 10 minutes 6 seconds. 89 patients had at least one adenoma (32.84%). The differences in withdrawal time (p = 0.345) and adenoma detection rate (p = 0.386) were not statistically significant.
Discussion: The results from this study suggest that CADe software does not appear to have a significant impact on ADR or withdrawal time in real world colonoscopy with experienced endoscopists. However, the endoscopists preferred having the CADe software, as they felt more relaxed knowing there was an additional tool looking for polyps. Long term population-based trials to demonstrate an impact on interval cancer are required to assess the true value of AIAC.
Disclosures:
Jayati Anand indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shiv Gandhi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krunal Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jayati Anand, 1, Shiv Gandhi, MD2, Krunal Patel, MD3. P0363 - Artificial Intelligence-Aided Colonoscopy in a Real World Setting, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
