Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0391 - Dupilumab Efficacy in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Persists for Histologic, Symptomatic, and Endoscopic Outcomes Regardless of Concomitant High-Dose Proton Pump Inhibitor Use
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- ED
Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH
University of North Carolina School of Medicine
Chapel Hill, North Carolina
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Marc E. Rothenberg, MD, PhD1, Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH2, Albert J. Bredenoord, MD3, Xian Sun, PhD4, Elizabeth Laws, PhD5, Eric Mortensen, MD, PhD6, Jennifer Maloney, MD6, Lila Glotfelty, MD, PhD5, Arsalan Shabbir, MD, PhD6
1Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati, OH; 2University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 3Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Noord-Holland, Netherlands; 4Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Bridgewater, NJ; 5Sanofi, Bridgewater, NJ; 6Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Tarrytown, NY
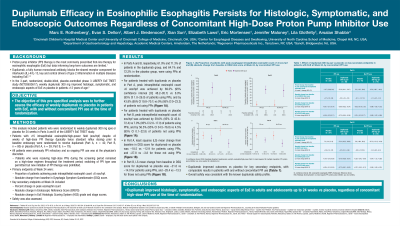
Introduction: Proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy is the most commonly prescribed first-line therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) but data informing long-term outcomes are limited. In the 3-part, phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET study (NCT03633617) weekly dupilumab 300 mg improved histologic, symptomatic, and endoscopic aspects of EoE in patients ≥12 years. This pre-specified analysis assessed the efficacy of weekly dupilumab vs placebo in patients with and without concomitant PPI use.
Methods: Patients with intraepithelial eosinophil (eos) infiltration (peak cell count ≥15 eos/high-power field [hpf]) after ≥8 weeks high-dose PPI (typically twice standard reflux dosing) were randomized to dupilumab (Part A, n=42; Part B, n=80) or placebo (Part A, n=39; Part B, n=79). Patients using high-dose PPIs at screening remained on a high-dose regimen throughout the treatment period; switching of PPI types was permitted but new initiation of PPIs was prohibited. Endpoints at Week 24 were: proportion of patients achieving peak eos count ≤6 eos/hpf, absolute change from baseline in Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire (DSQ) score, % change in peak eos count, absolute change in Endoscopic Reference Score and Histologic Scoring System grade/stage scores.
Results: In Parts A and B, respectively, 61.9% and 71.3% of patients in the dupilumab group and 64.1% and 72.2% in the placebo group were using PPIs at randomization. For patients treated with dupilumab vs placebo in Parts A and B, respectively, peak eos count ≤6 eos/hpf was achieved by 69.2% (95% confidence interval [CI] 48.2–85.7) vs 8.0% (95% CI 1.0–26.0) and 59.6% (95% CI 45.8–72.4) vs 7.0% (95% CI 2.0–17.0) of patients using PPIs, and by 43.8% (95% CI 19.8–70.1) vs 0% (95% CI 0–23.2) and 56.5% (95% CI 34.5-76.8) vs 4.5% (95% CI 0.1–22.8) of patients not using PPIs. Least squares mean change from baseline in DSQ score for dupilumab vs placebo was –18.5 vs –12.9 and –21.8 vs –14.0 for patients using PPIs in Parts A and B, respectively, and –27.8 vs –3.8 and –28.4 vs –13.3 for those not using PPIs (Figure). Dupilumab improved outcomes vs placebo for secondary endpoints, with comparable results in patients with and without concomitant PPI use. Dupilumab was generally well tolerated.
Discussion: Dupilumab improved histologic, symptomatic, and endoscopic aspects of EoE in adults and adolescents, up to 24 weeks, regardless of concomitant high-dose PPI use.

Disclosures:
Marc E. Rothenberg, MD, PhD1, Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH2, Albert J. Bredenoord, MD3, Xian Sun, PhD4, Elizabeth Laws, PhD5, Eric Mortensen, MD, PhD6, Jennifer Maloney, MD6, Lila Glotfelty, MD, PhD5, Arsalan Shabbir, MD, PhD6. P0391 - Dupilumab Efficacy in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Persists for Histologic, Symptomatic, and Endoscopic Outcomes Regardless of Concomitant High-Dose Proton Pump Inhibitor Use, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Marc E. Rothenberg, MD, PhD1, Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH2, Albert J. Bredenoord, MD3, Xian Sun, PhD4, Elizabeth Laws, PhD5, Eric Mortensen, MD, PhD6, Jennifer Maloney, MD6, Lila Glotfelty, MD, PhD5, Arsalan Shabbir, MD, PhD6
1Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati, OH; 2University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 3Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Noord-Holland, Netherlands; 4Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Bridgewater, NJ; 5Sanofi, Bridgewater, NJ; 6Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Tarrytown, NY
Introduction: Proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy is the most commonly prescribed first-line therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) but data informing long-term outcomes are limited. In the 3-part, phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET study (NCT03633617) weekly dupilumab 300 mg improved histologic, symptomatic, and endoscopic aspects of EoE in patients ≥12 years. This pre-specified analysis assessed the efficacy of weekly dupilumab vs placebo in patients with and without concomitant PPI use.
Methods: Patients with intraepithelial eosinophil (eos) infiltration (peak cell count ≥15 eos/high-power field [hpf]) after ≥8 weeks high-dose PPI (typically twice standard reflux dosing) were randomized to dupilumab (Part A, n=42; Part B, n=80) or placebo (Part A, n=39; Part B, n=79). Patients using high-dose PPIs at screening remained on a high-dose regimen throughout the treatment period; switching of PPI types was permitted but new initiation of PPIs was prohibited. Endpoints at Week 24 were: proportion of patients achieving peak eos count ≤6 eos/hpf, absolute change from baseline in Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire (DSQ) score, % change in peak eos count, absolute change in Endoscopic Reference Score and Histologic Scoring System grade/stage scores.
Results: In Parts A and B, respectively, 61.9% and 71.3% of patients in the dupilumab group and 64.1% and 72.2% in the placebo group were using PPIs at randomization. For patients treated with dupilumab vs placebo in Parts A and B, respectively, peak eos count ≤6 eos/hpf was achieved by 69.2% (95% confidence interval [CI] 48.2–85.7) vs 8.0% (95% CI 1.0–26.0) and 59.6% (95% CI 45.8–72.4) vs 7.0% (95% CI 2.0–17.0) of patients using PPIs, and by 43.8% (95% CI 19.8–70.1) vs 0% (95% CI 0–23.2) and 56.5% (95% CI 34.5-76.8) vs 4.5% (95% CI 0.1–22.8) of patients not using PPIs. Least squares mean change from baseline in DSQ score for dupilumab vs placebo was –18.5 vs –12.9 and –21.8 vs –14.0 for patients using PPIs in Parts A and B, respectively, and –27.8 vs –3.8 and –28.4 vs –13.3 for those not using PPIs (Figure). Dupilumab improved outcomes vs placebo for secondary endpoints, with comparable results in patients with and without concomitant PPI use. Dupilumab was generally well tolerated.
Discussion: Dupilumab improved histologic, symptomatic, and endoscopic aspects of EoE in adults and adolescents, up to 24 weeks, regardless of concomitant high-dose PPI use.

Figure: Figure. Effect of dupilumab qw on primary endpoints (A) proportion of patients with peak esophageal intraepithelial eosinophil count of ≤6 eos/hpf and (B) absolute change from baseline in DSQ total score at Week 24, by concomitant PPI use
CI, confidence interval; DSQ, Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire; eos, eosinophils; hpf, high-power field; LS, least squares; PPI, proton pump inhibitor; qw, once weekly; SE, standard error.
CI, confidence interval; DSQ, Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire; eos, eosinophils; hpf, high-power field; LS, least squares; PPI, proton pump inhibitor; qw, once weekly; SE, standard error.
Disclosures:
Marc Rothenberg: Allakos – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant. BMS – Consultant. Celldex – Consultant, Equity interest. ClostraBio – Consultant, Equity interest. Ellodi Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. GSK – Consultant. Guidepoint – Consultant. Mapi Research Trust – Royalties. Nextstone One – Consultant, Equity interest. PulmOne – Consultant, Equity interest. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant. Revolo – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Santa Ana Bio – Consultant, Equity interest. Serpin Pharma – Consultant, Equity interest. Spoon Guru – Consultant, Equity interest. Teva Pharmaceuticals – Royalties. UpToDate – Royalties.
Evan Dellon: Abbott – Consultant. Abbvie – Consultant. Adare/Ellodi – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Aimmune – Consultant. Akesobio – Consultant. Alfasigma – Consultant. ALK – Consultant. Allakos – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Amgen – Consultant. Aqilion – Consultant. Arena/Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Aslan – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Avir – Consultant. Banner Pharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support. Biorasi – Consultant. Calypso – Consultant. Celgene/Receptos/BMS – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Celldex – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. EsoCap – Consultant. Eupraxia – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant. Gossamer Bio – Consultant. GSK – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Holoclara – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Invea – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Knightpoint – Consultant. Landos – Consultant. LucidDx – Consultant. Meritage – Grant/Research Support. Miraca – Grant/Research Support. Morphic – Consultant. Nexstone Immunology – Consultant. Nutricia – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Parexel/Calyx – Consultant. Phathom – Consultant. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Revolo Biotherapeutics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Robarts/Alimentiv – Consultant. Salix – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Shire/Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Target RWE – Consultant. Upstream Bio – Consultant.
Albert Bredenoord: Alimentiv – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Aqilion – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Dr. Falk Pharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Eupraxia – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Laborie – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant. Norgine – Grant/Research Support. Nutricia – Grant/Research Support. Reckitt – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. SST – Grant/Research Support. Thelial – Grant/Research Support.
Xian Sun: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee, Shareholder.
Elizabeth Laws: Sanofi – Employee, Stock Options.
Eric Mortensen: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee, Shareholder.
Jennifer Maloney: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee, Shareholder.
Lila Glotfelty: Sanofi – Employee, Stock Options.
Arsalan Shabbir: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Marc E. Rothenberg, MD, PhD1, Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH2, Albert J. Bredenoord, MD3, Xian Sun, PhD4, Elizabeth Laws, PhD5, Eric Mortensen, MD, PhD6, Jennifer Maloney, MD6, Lila Glotfelty, MD, PhD5, Arsalan Shabbir, MD, PhD6. P0391 - Dupilumab Efficacy in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Persists for Histologic, Symptomatic, and Endoscopic Outcomes Regardless of Concomitant High-Dose Proton Pump Inhibitor Use, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

