Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0473 - Bringing Awareness to BRCA1 Associated Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Anastasia Novikov, MD
Elmhurst Hospital Center/ Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Elmhurst, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Anastasia Novikov, MD1, Vennis Lourdusamy, MD2, Nirali Sheth, MD2, Genanew Bedanie, MD3, Natalie Balassiano, MD4, Maliyat Matin, MD2, Aaron Walfish, MD2
1Elmhurst Hospital Center/ Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Elmhurst, NY; 2Elmhurst Hospital Center/ Icahn School of Medicine, Elmhurst, NY; 3Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 4Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai / NYC Health and Hospitals, Queens, NY
Introduction: BRCA1 and BRCA2 are tumor suppressor genes involved in DNA repair. Mutations of those genes are known to be strongly associated with breast and ovarian cancer, other gynecologic malignancies such as endometrial and fallopian tube, as well as less commonly gastric and biliary cancers. Esophageal cancer harboring BRCA1 mutation is exceedingly rare and only reported in the literature handful of times.
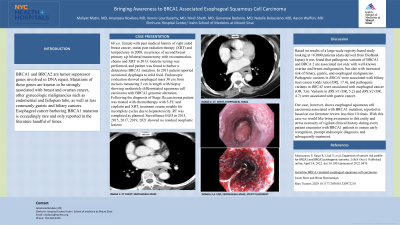
Case Description/Methods: 68 y.o. female with past medical history of right sided breast cancer, status post radiation therapy (XRT) and lumpectomy in 2008, recurrence of second breast primary s/p bilateral mastectomy with reconstruction, chemo and XRT in 2013. Genetic testing was performed, and patient was found to harbor a deleterious BRCA1 mutation. In 2013 patient reported occasional dysphagia to solid food. Endoscopic evaluation showed esophageal mass 30 cm from incisors measuring 5 cm in length with biopsy showing moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with BRCA1 genomic alteration. Following the diagnosis of Stage IIa carcinoma patient was treated with chemotherapy with 5-FU and cisplatin and XRT, treatment course notable for incomplete cycles due to hepatotoxicity. RT was completed as planned. Surveillance EGD in 2012, 2015, 2017, 2019, 2021 showed no residual neoplastic lesions.
Discussion: Based on results of a large-scale registry-based study looking at >63000 patients (data derived from BioBank Japan) it was found that pathogenic variants of BRCA1 and BRCA 2 are associated not only with well-known ovarian and breast malignancies, but also with increased risk of biliary, gastric, and esophageal malignancies. Pathogenic variants in BRCA1 were associated with biliary tract cancer (odds ratio [OR], 17.4), and pathogenic variants in BRCA2 were associated with esophageal cancer (OR, 5.6). Variants in BRCA1 (OR, 5.2) and BRCA2 (OR, 4.7) were associated with gastric cancer.
Our case, however, shows esophageal squamous cell carcinoma associated with BRCA1 mutation, reported in based on our literature review less then 10 times. With this case we would like bring awareness to this entity and stress necessity of vigilant clinical history during every patient encounter with BRCA1 patients to ensure early recognition, prompt endoscopic diagnosis, and subsequently treatment.
References:
Momozawa Y, Sasai R, Usui Y, et al. Expansion of cancer risk profile for BRCA1 and BRCA2 pathogenic variants. JAMA Oncol. Published online April 14, 2022. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.0476

Disclosures:
Anastasia Novikov, MD1, Vennis Lourdusamy, MD2, Nirali Sheth, MD2, Genanew Bedanie, MD3, Natalie Balassiano, MD4, Maliyat Matin, MD2, Aaron Walfish, MD2. P0473 - Bringing Awareness to BRCA1 Associated Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Elmhurst Hospital Center/ Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Elmhurst, NY; 2Elmhurst Hospital Center/ Icahn School of Medicine, Elmhurst, NY; 3Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 4Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai / NYC Health and Hospitals, Queens, NY
Introduction: BRCA1 and BRCA2 are tumor suppressor genes involved in DNA repair. Mutations of those genes are known to be strongly associated with breast and ovarian cancer, other gynecologic malignancies such as endometrial and fallopian tube, as well as less commonly gastric and biliary cancers. Esophageal cancer harboring BRCA1 mutation is exceedingly rare and only reported in the literature handful of times.
Case Description/Methods: 68 y.o. female with past medical history of right sided breast cancer, status post radiation therapy (XRT) and lumpectomy in 2008, recurrence of second breast primary s/p bilateral mastectomy with reconstruction, chemo and XRT in 2013. Genetic testing was performed, and patient was found to harbor a deleterious BRCA1 mutation. In 2013 patient reported occasional dysphagia to solid food. Endoscopic evaluation showed esophageal mass 30 cm from incisors measuring 5 cm in length with biopsy showing moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with BRCA1 genomic alteration. Following the diagnosis of Stage IIa carcinoma patient was treated with chemotherapy with 5-FU and cisplatin and XRT, treatment course notable for incomplete cycles due to hepatotoxicity. RT was completed as planned. Surveillance EGD in 2012, 2015, 2017, 2019, 2021 showed no residual neoplastic lesions.
Discussion: Based on results of a large-scale registry-based study looking at >63000 patients (data derived from BioBank Japan) it was found that pathogenic variants of BRCA1 and BRCA 2 are associated not only with well-known ovarian and breast malignancies, but also with increased risk of biliary, gastric, and esophageal malignancies. Pathogenic variants in BRCA1 were associated with biliary tract cancer (odds ratio [OR], 17.4), and pathogenic variants in BRCA2 were associated with esophageal cancer (OR, 5.6). Variants in BRCA1 (OR, 5.2) and BRCA2 (OR, 4.7) were associated with gastric cancer.
Our case, however, shows esophageal squamous cell carcinoma associated with BRCA1 mutation, reported in based on our literature review less then 10 times. With this case we would like bring awareness to this entity and stress necessity of vigilant clinical history during every patient encounter with BRCA1 patients to ensure early recognition, prompt endoscopic diagnosis, and subsequently treatment.
References:
Momozawa Y, Sasai R, Usui Y, et al. Expansion of cancer risk profile for BRCA1 and BRCA2 pathogenic variants. JAMA Oncol. Published online April 14, 2022. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.0476

Figure: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Disclosures:
Anastasia Novikov indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vennis Lourdusamy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nirali Sheth indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Genanew Bedanie indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Natalie Balassiano indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maliyat Matin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aaron Walfish indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anastasia Novikov, MD1, Vennis Lourdusamy, MD2, Nirali Sheth, MD2, Genanew Bedanie, MD3, Natalie Balassiano, MD4, Maliyat Matin, MD2, Aaron Walfish, MD2. P0473 - Bringing Awareness to BRCA1 Associated Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
