Sunday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P0529 - Dietary Management of Patients with Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders - A Provider Needs Assessment Survey
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- SB
Shaili Babbar, MD
New York University Langone
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Shaili Babbar, MD1, Emily Johnston, BA1, Ashish Malhotra, MD1, Judith Kim, MD1, Aasma Shaukat, MD2, Lisa Malter, MD3
1New York University Langone, New York, NY; 2NYU Langone Health, New York, NY; 3NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY
Introduction: Patients with functional GI disorders (FGID) commonly ask providers for diet and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms. Few physicians have been trained in nutrition interventions specific to FGID, and many barriers to counseling have been identified. We surveyed clinicians on knowledge, attitudes and barriers related to nutrition in their care of patients with FGID.
Methods: A nutrition researcher and a group of gastroenterologists developed a 22-item survey in REDCap and distributed it via email to NYU Grossman School of Medicine faculty (n=800). Providers were given 1 month to complete the survey, and a reminder email was sent the day before the survey closed. No incentives were provided. No identifying data was collected, and this project met the criteria for quality improvement.
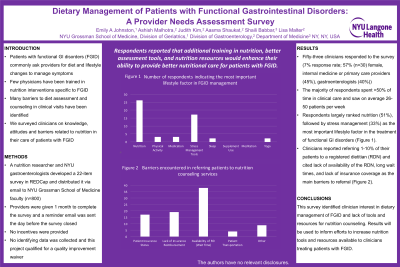
Results: Fifty-three clinicians responded to the survey (7% response rate). Respondents were 57% (n=30) female, mostly internal medicine or primary care providers (45%) or gastroenterologists (40%). 89% of respondents were physicians. The majority of respondents spent >50% of time in clinical care and saw on average 26-50 patients per week. Respondents largely ranked nutrition as the most important lifestyle factor in the management of FGID (51%), followed by stress management (33%). Clinicians reported referring 1-10% of their patients to a registered dietitian (RDN) and cited lack of availability of the RDN, long wait times, and lack of insurance coverage as the main barriers to referral. Respondents reported that additional training in nutrition, better assessment tools and nutrition resources would enhance their ability to provide better nutritional care for patients with FGID.
Discussion: This survey identified clinician interest in dietary management of FGID and lack of tools and resources for nutrition counseling. Results will be used to inform efforts to increase nutrition tools and resources available to clinicians treating patients with FGID.
Disclosures:
Shaili Babbar, MD1, Emily Johnston, BA1, Ashish Malhotra, MD1, Judith Kim, MD1, Aasma Shaukat, MD2, Lisa Malter, MD3. P0529 - Dietary Management of Patients with Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders - A Provider Needs Assessment Survey, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1New York University Langone, New York, NY; 2NYU Langone Health, New York, NY; 3NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY
Introduction: Patients with functional GI disorders (FGID) commonly ask providers for diet and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms. Few physicians have been trained in nutrition interventions specific to FGID, and many barriers to counseling have been identified. We surveyed clinicians on knowledge, attitudes and barriers related to nutrition in their care of patients with FGID.
Methods: A nutrition researcher and a group of gastroenterologists developed a 22-item survey in REDCap and distributed it via email to NYU Grossman School of Medicine faculty (n=800). Providers were given 1 month to complete the survey, and a reminder email was sent the day before the survey closed. No incentives were provided. No identifying data was collected, and this project met the criteria for quality improvement.
Results: Fifty-three clinicians responded to the survey (7% response rate). Respondents were 57% (n=30) female, mostly internal medicine or primary care providers (45%) or gastroenterologists (40%). 89% of respondents were physicians. The majority of respondents spent >50% of time in clinical care and saw on average 26-50 patients per week. Respondents largely ranked nutrition as the most important lifestyle factor in the management of FGID (51%), followed by stress management (33%). Clinicians reported referring 1-10% of their patients to a registered dietitian (RDN) and cited lack of availability of the RDN, long wait times, and lack of insurance coverage as the main barriers to referral. Respondents reported that additional training in nutrition, better assessment tools and nutrition resources would enhance their ability to provide better nutritional care for patients with FGID.
Discussion: This survey identified clinician interest in dietary management of FGID and lack of tools and resources for nutrition counseling. Results will be used to inform efforts to increase nutrition tools and resources available to clinicians treating patients with FGID.
Disclosures:
Shaili Babbar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Emily Johnston indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashish Malhotra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Judith Kim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aasma Shaukat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lisa Malter: Abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Celltrion – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Merck – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support.
Shaili Babbar, MD1, Emily Johnston, BA1, Ashish Malhotra, MD1, Judith Kim, MD1, Aasma Shaukat, MD2, Lisa Malter, MD3. P0529 - Dietary Management of Patients with Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders - A Provider Needs Assessment Survey, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
