Sunday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P0607 - Analysis of Gastrointestinal Bleeding in COVID-19 Pneumonia Hospitalizations in the U.S. During 2020
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Aboud Kaliounji, MD
SUNY Downstate Health Sciences University
Brooklyn, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Aboud Kaliounji, MD1, Anwar Uddin, MD1, Peter Lymberopoulos, MD1, Ese Uwagbale, MD2, Chidiebele Omaliko, MD3, Sharanya Nemakallu, MD4, Junxin Shi, MD, PhD5, Tamta Chkhikvadze, MD1
1SUNY Downstate Health Sciences University, Brooklyn, NY; 2Rochester General Hospital, Rochester, NY; 3One Brooklyn Health-Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4One Brooklyn Health, Brooklyn, NY; 5Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, OH
Introduction: COVID-19 hospitalization surge significantly impacted care delivery across different specialties. We aimed to analyze the endoscopic management of upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) during 2020 from the largest administrative database, Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS).
Methods: Adult patients were extracted from NIS 2020 with ICD-10 diagnosis and procedure codes of COVID-19 (C19P) (J12.81, J12.82, J12.8), UGIB (K92.0, K92.1, K92.2) and esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) on same hospitalization (0DJ08ZZ, 0W3P8ZZ). Hospitalizations were separately analyzed for those on mechanical ventilation (MV) >96 hours (5A1955Z) and those who were not and for patients on long-term anticoagulation (AC) (Z79. 01). Demographics and mortality were analyzed.
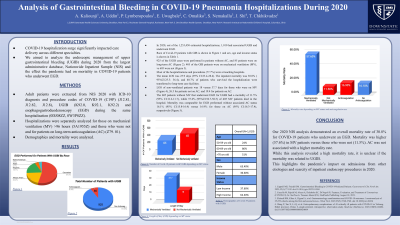
Results: In 2020, out of the 1,253,450 estimated hospitalizations, 1,010 had associated UGIB and underwent EGD. 405/125,960 were on MV, while 605/1,127,490 were not. 925 of the cases were performed in patients without AC, and 85 patients were on long-term AC. 63.4% of patients were male and 51% were above age 70, 35.5% were 60-69, and 24.5% were 50-59. 53.9% were White, 20.2% Black, 18.1% Hispanic, 4.1% Asian/Pacific Islander, and 3.6% Native American/Others. 37.6% of patients were residents of low-income areas. Most of the hospitalizations and procedures (77.7%) were at teaching hospitals. The mean LOS was 25.9 days (95% CI:23.4-28.4). The inpatient mortality was 30.8% ( 95%CI:25.3- 36.4), and 40.7% of patients who survived the hospitalization were transferred to long-term care facilities. The 605 patients without MV that underwent EGD for UGIB had a mortality of 11.5% (95% CI:11.2-11.7), while 57.6% (95%CI:56.7-58.5) of 405 MV patients died in the hospital. LOS of nonventilated patients was 18 versus 37.7 days for those who were on MV, 26.5 for patients not on AC, and 19.4 for patients on AC. Mortality was comparable for EGD performed without associated AC status 16.1% (95% CI:15.8-16.4) versus 16.9% for those on AC (95% CI:16.3-17.4), respectively.
Discussion: Our 2020 NIS analysis demonstrated an overall mortality rate of 30.8% for COVID-19 patients who underwent an EGD. Mortality was higher (57.6%) in MV patients versus those who were not (11.5%). AC was not associated with a higher mortality rate. While this analysis revealed a high mortality rate, it is unclear if the mortality was related to UGIB. This highlights the pandemic’s impact on admissions from other etiologies and scarcity of inpatient endoscopy procedures in 2020.
Disclosures:
Aboud Kaliounji, MD1, Anwar Uddin, MD1, Peter Lymberopoulos, MD1, Ese Uwagbale, MD2, Chidiebele Omaliko, MD3, Sharanya Nemakallu, MD4, Junxin Shi, MD, PhD5, Tamta Chkhikvadze, MD1. P0607 - Analysis of Gastrointestinal Bleeding in COVID-19 Pneumonia Hospitalizations in the U.S. During 2020, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1SUNY Downstate Health Sciences University, Brooklyn, NY; 2Rochester General Hospital, Rochester, NY; 3One Brooklyn Health-Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4One Brooklyn Health, Brooklyn, NY; 5Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, OH
Introduction: COVID-19 hospitalization surge significantly impacted care delivery across different specialties. We aimed to analyze the endoscopic management of upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) during 2020 from the largest administrative database, Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS).
Methods: Adult patients were extracted from NIS 2020 with ICD-10 diagnosis and procedure codes of COVID-19 (C19P) (J12.81, J12.82, J12.8), UGIB (K92.0, K92.1, K92.2) and esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) on same hospitalization (0DJ08ZZ, 0W3P8ZZ). Hospitalizations were separately analyzed for those on mechanical ventilation (MV) >96 hours (5A1955Z) and those who were not and for patients on long-term anticoagulation (AC) (Z79. 01). Demographics and mortality were analyzed.
Results: In 2020, out of the 1,253,450 estimated hospitalizations, 1,010 had associated UGIB and underwent EGD. 405/125,960 were on MV, while 605/1,127,490 were not. 925 of the cases were performed in patients without AC, and 85 patients were on long-term AC. 63.4% of patients were male and 51% were above age 70, 35.5% were 60-69, and 24.5% were 50-59. 53.9% were White, 20.2% Black, 18.1% Hispanic, 4.1% Asian/Pacific Islander, and 3.6% Native American/Others. 37.6% of patients were residents of low-income areas. Most of the hospitalizations and procedures (77.7%) were at teaching hospitals. The mean LOS was 25.9 days (95% CI:23.4-28.4). The inpatient mortality was 30.8% ( 95%CI:25.3- 36.4), and 40.7% of patients who survived the hospitalization were transferred to long-term care facilities. The 605 patients without MV that underwent EGD for UGIB had a mortality of 11.5% (95% CI:11.2-11.7), while 57.6% (95%CI:56.7-58.5) of 405 MV patients died in the hospital. LOS of nonventilated patients was 18 versus 37.7 days for those who were on MV, 26.5 for patients not on AC, and 19.4 for patients on AC. Mortality was comparable for EGD performed without associated AC status 16.1% (95% CI:15.8-16.4) versus 16.9% for those on AC (95% CI:16.3-17.4), respectively.
Discussion: Our 2020 NIS analysis demonstrated an overall mortality rate of 30.8% for COVID-19 patients who underwent an EGD. Mortality was higher (57.6%) in MV patients versus those who were not (11.5%). AC was not associated with a higher mortality rate. While this analysis revealed a high mortality rate, it is unclear if the mortality was related to UGIB. This highlights the pandemic’s impact on admissions from other etiologies and scarcity of inpatient endoscopy procedures in 2020.
Disclosures:
Aboud Kaliounji indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anwar Uddin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Peter Lymberopoulos indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ese Uwagbale indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chidiebele Omaliko indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sharanya Nemakallu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Junxin Shi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tamta Chkhikvadze indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aboud Kaliounji, MD1, Anwar Uddin, MD1, Peter Lymberopoulos, MD1, Ese Uwagbale, MD2, Chidiebele Omaliko, MD3, Sharanya Nemakallu, MD4, Junxin Shi, MD, PhD5, Tamta Chkhikvadze, MD1. P0607 - Analysis of Gastrointestinal Bleeding in COVID-19 Pneumonia Hospitalizations in the U.S. During 2020, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
