Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P0781 - Impact of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors Use on the Outcomes of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A US Cohort Propensity-Matched Study
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Khaled Alsabbagh Alchirazi, MD
Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Khaled Alsabbagh Alchirazi, MD1, Osama Hamid, MD, MRCPI1, Thabet Qapaja, MD1, Abel Joseph, MD1, Muaz Alsabbagh, MD1, Almaza Albakri, MD2, Miguel Regueiro, MD3
1Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 2King Hussein Medical Center, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 3Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have an anti-inflammatory effect in atherosclerotic disease, renal injury and neuroinflammation. The aim of this study is to assess Crohn’s disease (CD) related outcomes in diabetic patients treated with SGLT2.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was performed using TriNetX (Cambridge, MA) which provides real-time access to deidentified electronic health records of more than 101 million patients. Patients with CD were identified using ICD-10 codes. We identified diabetic patients with concomitant CD who received SGLT2 inhibitors. The CD control cohort included patients with CD and diabetes who did not receive SGLT2 inhibitors. 1:1 propensity-score matching (PSM) was performed for age, gender, race, ethnicity, IBD subtype & phenotype, prior IBD related surgery and known co-morbid conditions. IBD-related outcomes were evaluated. We excluded patients on glucagon-like peptide GLP-1 and dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors patients. Adjusted odds ratios (aOR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated.
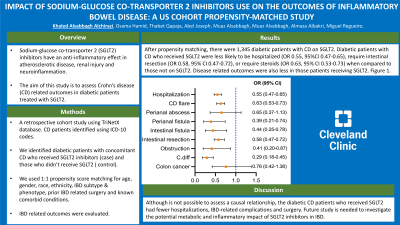
Results: After propensity matching, there were 1,345 diabetic patients with CD on SGLT2. Diabetic patients with CD who received SGLT2 were less likely to be hospitalized (OR 0.55, 95%CI 0.47-0.65), require intestinal resection (OR 0.58, 95% CI 0.47-0.72), or require steroids (OR 0.63, 95% CI 0.53-0.73) when compared to those not on SGLT2. Disease related outcomes were also less in those patients receiving SGLT2; perianal fistula (OR 0.39, 95% CI 0.21-0.74), intestinal fistula (OR 0.44, 95% CI 0.21-0.74), or bowel obstruction (OR 0.41, 95% CI 0.20-0.87).
Discussion: Although is not possible to assess a causal relationship, the diabetic CD patients who received SGLT2 had fewer hospitalizations, IBD-related complications and surgery. Future study is needed to investigate the potential metabolic and inflammatory impact of SGLT2 inhibitors in IBD.

Disclosures:
Khaled Alsabbagh Alchirazi, MD1, Osama Hamid, MD, MRCPI1, Thabet Qapaja, MD1, Abel Joseph, MD1, Muaz Alsabbagh, MD1, Almaza Albakri, MD2, Miguel Regueiro, MD3. P0781 - Impact of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors Use on the Outcomes of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A US Cohort Propensity-Matched Study, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 2King Hussein Medical Center, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 3Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have an anti-inflammatory effect in atherosclerotic disease, renal injury and neuroinflammation. The aim of this study is to assess Crohn’s disease (CD) related outcomes in diabetic patients treated with SGLT2.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was performed using TriNetX (Cambridge, MA) which provides real-time access to deidentified electronic health records of more than 101 million patients. Patients with CD were identified using ICD-10 codes. We identified diabetic patients with concomitant CD who received SGLT2 inhibitors. The CD control cohort included patients with CD and diabetes who did not receive SGLT2 inhibitors. 1:1 propensity-score matching (PSM) was performed for age, gender, race, ethnicity, IBD subtype & phenotype, prior IBD related surgery and known co-morbid conditions. IBD-related outcomes were evaluated. We excluded patients on glucagon-like peptide GLP-1 and dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors patients. Adjusted odds ratios (aOR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated.
Results: After propensity matching, there were 1,345 diabetic patients with CD on SGLT2. Diabetic patients with CD who received SGLT2 were less likely to be hospitalized (OR 0.55, 95%CI 0.47-0.65), require intestinal resection (OR 0.58, 95% CI 0.47-0.72), or require steroids (OR 0.63, 95% CI 0.53-0.73) when compared to those not on SGLT2. Disease related outcomes were also less in those patients receiving SGLT2; perianal fistula (OR 0.39, 95% CI 0.21-0.74), intestinal fistula (OR 0.44, 95% CI 0.21-0.74), or bowel obstruction (OR 0.41, 95% CI 0.20-0.87).
Discussion: Although is not possible to assess a causal relationship, the diabetic CD patients who received SGLT2 had fewer hospitalizations, IBD-related complications and surgery. Future study is needed to investigate the potential metabolic and inflammatory impact of SGLT2 inhibitors in IBD.

Figure: Figure 1: adjusted odds ratio of outcomes of Crohn's disease (CD) among SGLT2 users. abbreviations: OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval; C.diff: Clostridium difficile.
Disclosures:
Khaled Alsabbagh Alchirazi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Osama Hamid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thabet Qapaja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abel Joseph indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muaz Alsabbagh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Almaza Albakri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miguel Regueiro: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Alfasigma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Allergan – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Celgene – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Eli Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Gilead Sciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Miraca Labs – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Prometheus – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Salix – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Seres – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Target RWE – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. UCB – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Wolters Kluwer Health – Royalties.
Khaled Alsabbagh Alchirazi, MD1, Osama Hamid, MD, MRCPI1, Thabet Qapaja, MD1, Abel Joseph, MD1, Muaz Alsabbagh, MD1, Almaza Albakri, MD2, Miguel Regueiro, MD3. P0781 - Impact of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors Use on the Outcomes of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A US Cohort Propensity-Matched Study, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
