Sunday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P0847 - Common Bile Duct Size, Gender, and Hispanic Origin Are Not Predictive of Incidental Choledocholithiasis in Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Ultrasound
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Adrian Pona, MD
Prisma Health-Upstate
Greenville, SC
Presenting Author(s)
Varun Moktan, MD1, Adrian Pona, MD1, Mina Rismani, MD2, Hayden Shuster, PharmD3, Yianni Protopapadakis, MS, DO4, Sean Fitzgerald, DO3, Pranav Patel, MD3, Diego Lim, MD, MPH1, Veeral M. Oza, MD3
1Prisma Health-Upstate, Greenville, SC; 2Medical College of Georgia, Greenville, SC; 3Prisma Health, Greenville, SC; 4Prisma Health System, Greenville, SC
Introduction: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a widely recognized diagnostic tool for detecting biliary stones and sludge. Despite its high sensitivity, the frequency of detecting incidental choledocholithiasis (CD) on EUS remains unclear. We performed a retrospective chart review to evaluate the finding of incidental CD in patients undergoing an EUS for reasons other than biliary stones and sludge.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted evaluating all EUS studies performed between 2019 and 2022 at a single tertiary academic medical center. Clinical data including demographics, indications, presence of stones and sludge, and diagnosis were recorded. Averages for numerical data were reported calculating the mean. Differences were analyzed using a two-sample t-test.
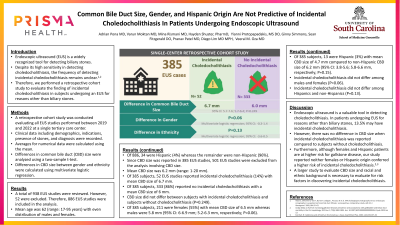
Results: A total of 938 EUS studies were reviewed. Of these, 52 patients had EUS for suspected CD and were excluded. A total of 886 patients were therefore analyzed. Average age of the cohort was 62.3 years and ranged from 17-95 years. 49.8% were males and 50.2% females. Approximately 34 patients (3.8%) were of Hispanic origin. The remainder were non-Hispanic (96.2%). The average CBD size was 6.2mm(range 1-20). 13.5% of patients had findings of incidental stone. In these patients with finding of incidental stone, the average CBD size increased to 6.7mm. This however was not statistically significant in our cohort (p = 0.249). Interestingly, female gender seems to be predictive of a slightly larger CBD size although this was not statistically significant (6.5mm vs 5.8mm ; p= 0.059). Hispanic patient population appears to have a smaller CBD size in our cohort than one would expect (4.7mm vs 5.8mm). This also was not statistically significant (p =0.15)
Discussion: Endoscopic ultrasound is a valuable tool in detecting biliary stones. In patients undergoing EUS for reasons other than biliary stones or sludge, 13.5% may have incidental CD. Interestingly, there was no difference in CBD size when incidental CD patients were compared to those patients who did not have stones. Furthermore, although Hispanic patient population and females patients are higher risk for gallstone disease, in our cohort, this did not seem to be the case, and being a female or a Hispanic origin patient did not confer a higher risk for finding of incidental CD. A larger study to evaluate CBD size and racial background is necessary to evaluate for risk factors of discovering incidental CD.
Disclosures:
Varun Moktan, MD1, Adrian Pona, MD1, Mina Rismani, MD2, Hayden Shuster, PharmD3, Yianni Protopapadakis, MS, DO4, Sean Fitzgerald, DO3, Pranav Patel, MD3, Diego Lim, MD, MPH1, Veeral M. Oza, MD3. P0847 - Common Bile Duct Size, Gender, and Hispanic Origin Are Not Predictive of Incidental Choledocholithiasis in Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Ultrasound, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Prisma Health-Upstate, Greenville, SC; 2Medical College of Georgia, Greenville, SC; 3Prisma Health, Greenville, SC; 4Prisma Health System, Greenville, SC
Introduction: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a widely recognized diagnostic tool for detecting biliary stones and sludge. Despite its high sensitivity, the frequency of detecting incidental choledocholithiasis (CD) on EUS remains unclear. We performed a retrospective chart review to evaluate the finding of incidental CD in patients undergoing an EUS for reasons other than biliary stones and sludge.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted evaluating all EUS studies performed between 2019 and 2022 at a single tertiary academic medical center. Clinical data including demographics, indications, presence of stones and sludge, and diagnosis were recorded. Averages for numerical data were reported calculating the mean. Differences were analyzed using a two-sample t-test.
Results: A total of 938 EUS studies were reviewed. Of these, 52 patients had EUS for suspected CD and were excluded. A total of 886 patients were therefore analyzed. Average age of the cohort was 62.3 years and ranged from 17-95 years. 49.8% were males and 50.2% females. Approximately 34 patients (3.8%) were of Hispanic origin. The remainder were non-Hispanic (96.2%). The average CBD size was 6.2mm(range 1-20). 13.5% of patients had findings of incidental stone. In these patients with finding of incidental stone, the average CBD size increased to 6.7mm. This however was not statistically significant in our cohort (p = 0.249). Interestingly, female gender seems to be predictive of a slightly larger CBD size although this was not statistically significant (6.5mm vs 5.8mm ; p= 0.059). Hispanic patient population appears to have a smaller CBD size in our cohort than one would expect (4.7mm vs 5.8mm). This also was not statistically significant (p =0.15)
Discussion: Endoscopic ultrasound is a valuable tool in detecting biliary stones. In patients undergoing EUS for reasons other than biliary stones or sludge, 13.5% may have incidental CD. Interestingly, there was no difference in CBD size when incidental CD patients were compared to those patients who did not have stones. Furthermore, although Hispanic patient population and females patients are higher risk for gallstone disease, in our cohort, this did not seem to be the case, and being a female or a Hispanic origin patient did not confer a higher risk for finding of incidental CD. A larger study to evaluate CBD size and racial background is necessary to evaluate for risk factors of discovering incidental CD.
Disclosures:
Varun Moktan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adrian Pona indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mina Rismani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hayden Shuster indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yianni Protopapadakis indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sean Fitzgerald indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pranav Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Diego Lim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Veeral Oza: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Varun Moktan, MD1, Adrian Pona, MD1, Mina Rismani, MD2, Hayden Shuster, PharmD3, Yianni Protopapadakis, MS, DO4, Sean Fitzgerald, DO3, Pranav Patel, MD3, Diego Lim, MD, MPH1, Veeral M. Oza, MD3. P0847 - Common Bile Duct Size, Gender, and Hispanic Origin Are Not Predictive of Incidental Choledocholithiasis in Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Ultrasound, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
