Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P0905 - A Systematic Time-Trend Analysis of the Global Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality of Primary Liver Cancer From 1990 to 2019 Using the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2019
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Fouad Jaber, MD
University of Missouri-Kansas City
Kansas City, MO
Presenting Author(s)
Fouad Jaber, MD1, Saqr Alsakarneh, MD1, Anika Mittal, MS1, Hamza Alzghoul, MD2, Mohammad Aldiabat, MD3, Mohamed Ahmed, MD1, Azizullah Beran, MD4, Nikki duong, MD5, Mohammad Jaber, MD6, Laith Numan, MD, MS7, Mohamed Abdallah, MD8, Mohammad Almeqdadi, MD9, Babu Mohan, MD, MS10, Ala Abdel-Jalil, MD11, Hassan Ghoz, MD1
1University of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, MO; 2University of Central Florida, Gainesville, FL; 3NYU Langone, New York, NY; 4Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN; 5Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA; 6Al-Azhar University, Gaza, Palestinian Territories; 7Saint Louis University, St. Louis, MO; 8University of Minnesota Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN; 9Lahey Medical Center, Boston, MA; 10University of Utah Health School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT; 11Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Liver cancer incidence and mortality rates have displayed divergent trends in various regions worldwide. While some Eastern Asian countries have experienced a decline in liver cancer rates, many previously low-incidence countries, such as the United States, Australia, and several European nations, have seen a concerning increase. Assessing global trends in liver cancer is crucial in addressing healthcare disparities and guiding effective policy-making and resource allocation. This study aims to evaluate the incidence, prevalence, and mortality of liver cancer worldwide from 1990 to 2019 using data from the Global Burden of Diseases (GBD), Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2019.
Methods: Liver cancer data, including incidence, prevalence, and mortality, were extracted from the GBD study 2019. Global liver cancer rates were assessed in 2019, and cause-specific analysis was conducted to evaluate the burden of liver cancer based on etiology. These parameters were also analyzed based on the sociodemographic index (SDI). Temporal trends in liver cancer incidence, prevalence, and mortality were examined across six regions (Americas, Africa, Europe, Eastern Mediterranean, Southeast Asia, and Western Pacific) from 1990 to 2019.
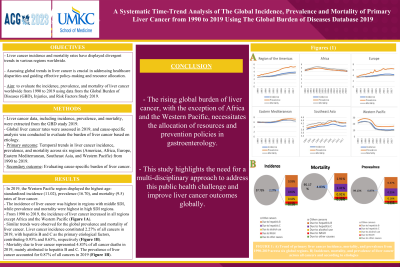
Results: In 2019, the Western Pacific region displayed the highest age-standardized incidence (11.02), prevalence (16.70), and mortality (9.5) rates of liver cancer. The incidence of liver cancer was highest in regions with middle SDI, while prevalence and mortality were highest in high SDI regions. From 1990 to 2019, the incidence of liver cancer increased in all regions except Africa and the Western Pacific (Figure 1A). Similar trends were observed for the global prevalence and mortality of liver cancer. Liver cancer incidence
constituted 2.27% of all cancers in 2019, with hepatitis B and C as the primary etiological factors, contributing 0.93% and 0.65%, respectively. Mortality due to liver cancer represented 4.83% of all cancer deaths in 2019, mainly attributed to hepatitis B and C. The prevalence of liver cancer accounted for 0.87% of all cancers in 2019 (Figure 1B).
Discussion: The rising global burden of liver cancer, with the exception of Africa and the Western Pacific, necessitates the allocation of resources and prevention policies in gastroenterology. This study highlights the need for a multi-disciplinary approach to address this public health challenge and improve liver cancer outcomes globally.

Disclosures:
Fouad Jaber, MD1, Saqr Alsakarneh, MD1, Anika Mittal, MS1, Hamza Alzghoul, MD2, Mohammad Aldiabat, MD3, Mohamed Ahmed, MD1, Azizullah Beran, MD4, Nikki duong, MD5, Mohammad Jaber, MD6, Laith Numan, MD, MS7, Mohamed Abdallah, MD8, Mohammad Almeqdadi, MD9, Babu Mohan, MD, MS10, Ala Abdel-Jalil, MD11, Hassan Ghoz, MD1. P0905 - A Systematic Time-Trend Analysis of the Global Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality of Primary Liver Cancer From 1990 to 2019 Using the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2019, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, MO; 2University of Central Florida, Gainesville, FL; 3NYU Langone, New York, NY; 4Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN; 5Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA; 6Al-Azhar University, Gaza, Palestinian Territories; 7Saint Louis University, St. Louis, MO; 8University of Minnesota Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN; 9Lahey Medical Center, Boston, MA; 10University of Utah Health School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT; 11Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Liver cancer incidence and mortality rates have displayed divergent trends in various regions worldwide. While some Eastern Asian countries have experienced a decline in liver cancer rates, many previously low-incidence countries, such as the United States, Australia, and several European nations, have seen a concerning increase. Assessing global trends in liver cancer is crucial in addressing healthcare disparities and guiding effective policy-making and resource allocation. This study aims to evaluate the incidence, prevalence, and mortality of liver cancer worldwide from 1990 to 2019 using data from the Global Burden of Diseases (GBD), Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2019.
Methods: Liver cancer data, including incidence, prevalence, and mortality, were extracted from the GBD study 2019. Global liver cancer rates were assessed in 2019, and cause-specific analysis was conducted to evaluate the burden of liver cancer based on etiology. These parameters were also analyzed based on the sociodemographic index (SDI). Temporal trends in liver cancer incidence, prevalence, and mortality were examined across six regions (Americas, Africa, Europe, Eastern Mediterranean, Southeast Asia, and Western Pacific) from 1990 to 2019.
Results: In 2019, the Western Pacific region displayed the highest age-standardized incidence (11.02), prevalence (16.70), and mortality (9.5) rates of liver cancer. The incidence of liver cancer was highest in regions with middle SDI, while prevalence and mortality were highest in high SDI regions. From 1990 to 2019, the incidence of liver cancer increased in all regions except Africa and the Western Pacific (Figure 1A). Similar trends were observed for the global prevalence and mortality of liver cancer. Liver cancer incidence
constituted 2.27% of all cancers in 2019, with hepatitis B and C as the primary etiological factors, contributing 0.93% and 0.65%, respectively. Mortality due to liver cancer represented 4.83% of all cancer deaths in 2019, mainly attributed to hepatitis B and C. The prevalence of liver cancer accounted for 0.87% of all cancers in 2019 (Figure 1B).
Discussion: The rising global burden of liver cancer, with the exception of Africa and the Western Pacific, necessitates the allocation of resources and prevention policies in gastroenterology. This study highlights the need for a multi-disciplinary approach to address this public health challenge and improve liver cancer outcomes globally.

Figure: Figure 1-A: Trend of liver cancer incidence, prevalence, and mortality worldwide divided by six regions from 1990 to 2019. Figure 1-B: Global liver cancer incidence, prevalence, and mortality by cause.
Disclosures:
Fouad Jaber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saqr Alsakarneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anika Mittal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Alzghoul indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Aldiabat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Azizullah Beran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nikki duong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Jaber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laith Numan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Abdallah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Almeqdadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Babu Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ala Abdel-Jalil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hassan Ghoz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fouad Jaber, MD1, Saqr Alsakarneh, MD1, Anika Mittal, MS1, Hamza Alzghoul, MD2, Mohammad Aldiabat, MD3, Mohamed Ahmed, MD1, Azizullah Beran, MD4, Nikki duong, MD5, Mohammad Jaber, MD6, Laith Numan, MD, MS7, Mohamed Abdallah, MD8, Mohammad Almeqdadi, MD9, Babu Mohan, MD, MS10, Ala Abdel-Jalil, MD11, Hassan Ghoz, MD1. P0905 - A Systematic Time-Trend Analysis of the Global Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality of Primary Liver Cancer From 1990 to 2019 Using the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2019, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
