Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P0913 - Comparative Analysis of Noninvasive Tests of Hepatic Fibrosis With Liver Histopathology in a Large Clinical Cohort
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
.jpg)
Mahdi Taye, BA
Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Mahdi Taye, BA1, Ian Dinsmore, MS2, Tooraj Mirshahi, PhD2
1Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine, Scranton, PA; 2Geisinger Department of Genomic Health, Danville, PA
Introduction: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and liver fibrosis are progressive conditions. Advanced fibrosis is mostly irreversible, a major driver of hepatocellular carcinoma, and a leading cause of liver transplant. It is therefore important to monitor fibrosis progression in high-risk individuals; however, the gold-standard histopathologic assessment is invasive and carries risk. FIB-4 index, NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS), and vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) using FibroScan™ are non-invasive alternatives to assess liver fibrosis. We set out to compare outcomes from these non-invasive assessments with existing biopsy-proven liver pathology from perioperative as well as outpatient biopsied samples in a large clinic cohort.
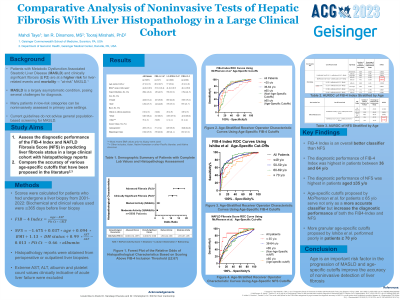
Methods: FIB-4 index, NFS, and liver stiffness measures (LSM) values were calculated for patients who had undergone a liver biopsy from 2001-2022. We used existing formulae for each score including age, platelet count, AST, ALT levels, BMI, diabetes status, and albumin. LSM values were obtained from VCTE. Histopathology staging from perioperative or outpatient biopsies was used. Biochemical and clinical values within 365 days prior to biopsy were used for calculations. VCTE values obtained closest to the time of biopsy were included. Established advanced fibrosis cutoffs were used to calculate sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and positive and negative likelihood ratios. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves were created and areas under the ROC (AUROC) were calculated.
Results: Among 7,547 patients who had undergone a liver biopsy with pathologic assessment; 7,360 have non-missing steatosis and fibrosis grading per histopathology, 5,569 had undergone bariatric surgery, with 75.27% having NAFLD. FIB-4, NFS, and VCTE values were calculated on 4836, 4265, and 269 patients, respectively. Using the gold standard histopathology for comparison, AUROC values for non-invasive assessment ranged from 0.708-0.839. AUROC for FIB-4 decreased in patients who were < 35 years old and >65 years old. FIB-4 and NFS performed best in identifying those at extremes—with no liver disease or most severe liver disease.
Discussion: Using a large liver biopsy dataset enabled us to assess noninvasive tests in staging hepatic fibrosis. Our findings highlight the utility of non-invasive tests in clinical settings where a biopsy is not available and for population-level assessment of chronic liver disease.
Disclosures:
Mahdi Taye, BA1, Ian Dinsmore, MS2, Tooraj Mirshahi, PhD2. P0913 - Comparative Analysis of Noninvasive Tests of Hepatic Fibrosis With Liver Histopathology in a Large Clinical Cohort, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Mahdi Taye, BA1, Ian Dinsmore, MS2, Tooraj Mirshahi, PhD2
1Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine, Scranton, PA; 2Geisinger Department of Genomic Health, Danville, PA
Introduction: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and liver fibrosis are progressive conditions. Advanced fibrosis is mostly irreversible, a major driver of hepatocellular carcinoma, and a leading cause of liver transplant. It is therefore important to monitor fibrosis progression in high-risk individuals; however, the gold-standard histopathologic assessment is invasive and carries risk. FIB-4 index, NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS), and vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) using FibroScan™ are non-invasive alternatives to assess liver fibrosis. We set out to compare outcomes from these non-invasive assessments with existing biopsy-proven liver pathology from perioperative as well as outpatient biopsied samples in a large clinic cohort.
Methods: FIB-4 index, NFS, and liver stiffness measures (LSM) values were calculated for patients who had undergone a liver biopsy from 2001-2022. We used existing formulae for each score including age, platelet count, AST, ALT levels, BMI, diabetes status, and albumin. LSM values were obtained from VCTE. Histopathology staging from perioperative or outpatient biopsies was used. Biochemical and clinical values within 365 days prior to biopsy were used for calculations. VCTE values obtained closest to the time of biopsy were included. Established advanced fibrosis cutoffs were used to calculate sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and positive and negative likelihood ratios. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves were created and areas under the ROC (AUROC) were calculated.
Results: Among 7,547 patients who had undergone a liver biopsy with pathologic assessment; 7,360 have non-missing steatosis and fibrosis grading per histopathology, 5,569 had undergone bariatric surgery, with 75.27% having NAFLD. FIB-4, NFS, and VCTE values were calculated on 4836, 4265, and 269 patients, respectively. Using the gold standard histopathology for comparison, AUROC values for non-invasive assessment ranged from 0.708-0.839. AUROC for FIB-4 decreased in patients who were < 35 years old and >65 years old. FIB-4 and NFS performed best in identifying those at extremes—with no liver disease or most severe liver disease.
Discussion: Using a large liver biopsy dataset enabled us to assess noninvasive tests in staging hepatic fibrosis. Our findings highlight the utility of non-invasive tests in clinical settings where a biopsy is not available and for population-level assessment of chronic liver disease.
Disclosures:
Mahdi Taye indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ian Dinsmore indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tooraj Mirshahi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahdi Taye, BA1, Ian Dinsmore, MS2, Tooraj Mirshahi, PhD2. P0913 - Comparative Analysis of Noninvasive Tests of Hepatic Fibrosis With Liver Histopathology in a Large Clinical Cohort, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

