Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1011 - Multiple Pyogenic Liver Abscesses Secondary to Streptococcus Intermedius Due to Sigmoid Diverticulitis
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Sirmad B. Chaudhary, MD
University of Tennessee Health Science Center
Memphis, TN
Presenting Author(s)
Sirmad B. Chaudhary, MD1, Andres Rene. Diaz, MD2
1University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN; 2East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN
Introduction: Pyogenic liver abscesses are rare in immunocompetent patients but can be highly fatal. Common causes for the development of these abscesses include dissemination from underlying biliary, systemic, or diverticular infections. With respect to diverticular infections, disruption in the colonic lining can lead to seeding of the liver via the portal venous system.
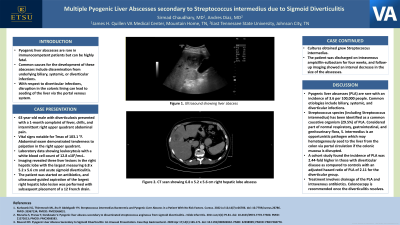
Case Description/Methods: A 63 year-old male with a history of diverticulosis presented to the emergency department with a 1-month complaint of fever, chills, and intermittent right upper quadrant abdominal pain. He was afebrile on admission but developed a fever on hospital day two with a Tmax of 103.1 °F. Abdominal exam demonstrated tenderness to palpation in the right upper quadrant. Laboratory data was notable for leukocytosis with a white blood cell count of 12.8 x103/mcL. Imaging revealed three liver lesions in the right hepatic lobe with the largest measuring 6.8 x 5.2 x 5.6 cm and acute sigmoid diverticulitis. The patient was started on empiric antibiotics, and ultrasound-guided aspiration of the largest right hepatic lobe lesion was performed with subsequent placement of a 12 French drain. Cultures obtained grew Streptococcus intermedius. The patient was discharged on intravenous ampicillin-sulbactam for four weeks, and follow-up imaging showed an interval decrease in the size of the abscesses.
Discussion: Pyogenic liver abscesses (PLA) are rare with an incidence of 3.6 per 100,000 people. Common etiologies include biliary, systemic, and diverticular infections. Streptococcus species (including Streptococcus intermedius) has been identified as a common causative organism (29.5%) of PLA. Considered part of normal respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary flora, S. intermedius is an opportunistic pathogen which may hematogenously seed to the liver from the colon via portal circulation if the colonic mucosa is disrupted. A cohort study found the incidence of PLA was 2.44-fold higher in those with diverticular disease as compared to controls with an adjusted hazard ratio of PLA of 2.11 for the diverticular group. Treatment involves drainage of the PLA and intravenous antibiotics. Colonoscopy is recommended once the diverticulitis resolves.

Disclosures:
Sirmad B. Chaudhary, MD1, Andres Rene. Diaz, MD2. P1011 - Multiple Pyogenic Liver Abscesses Secondary to Streptococcus Intermedius Due to Sigmoid Diverticulitis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN; 2East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN
Introduction: Pyogenic liver abscesses are rare in immunocompetent patients but can be highly fatal. Common causes for the development of these abscesses include dissemination from underlying biliary, systemic, or diverticular infections. With respect to diverticular infections, disruption in the colonic lining can lead to seeding of the liver via the portal venous system.
Case Description/Methods: A 63 year-old male with a history of diverticulosis presented to the emergency department with a 1-month complaint of fever, chills, and intermittent right upper quadrant abdominal pain. He was afebrile on admission but developed a fever on hospital day two with a Tmax of 103.1 °F. Abdominal exam demonstrated tenderness to palpation in the right upper quadrant. Laboratory data was notable for leukocytosis with a white blood cell count of 12.8 x103/mcL. Imaging revealed three liver lesions in the right hepatic lobe with the largest measuring 6.8 x 5.2 x 5.6 cm and acute sigmoid diverticulitis. The patient was started on empiric antibiotics, and ultrasound-guided aspiration of the largest right hepatic lobe lesion was performed with subsequent placement of a 12 French drain. Cultures obtained grew Streptococcus intermedius. The patient was discharged on intravenous ampicillin-sulbactam for four weeks, and follow-up imaging showed an interval decrease in the size of the abscesses.
Discussion: Pyogenic liver abscesses (PLA) are rare with an incidence of 3.6 per 100,000 people. Common etiologies include biliary, systemic, and diverticular infections. Streptococcus species (including Streptococcus intermedius) has been identified as a common causative organism (29.5%) of PLA. Considered part of normal respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary flora, S. intermedius is an opportunistic pathogen which may hematogenously seed to the liver from the colon via portal circulation if the colonic mucosa is disrupted. A cohort study found the incidence of PLA was 2.44-fold higher in those with diverticular disease as compared to controls with an adjusted hazard ratio of PLA of 2.11 for the diverticular group. Treatment involves drainage of the PLA and intravenous antibiotics. Colonoscopy is recommended once the diverticulitis resolves.

Figure: 6.8 x 5.2 x 5.6 cm right hepatic lobe abscess
Disclosures:
Sirmad Chaudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andres Diaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sirmad B. Chaudhary, MD1, Andres Rene. Diaz, MD2. P1011 - Multiple Pyogenic Liver Abscesses Secondary to Streptococcus Intermedius Due to Sigmoid Diverticulitis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
