Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1048 - IgG-4 Related Disease: The HIT and Run of a Dormant Disease
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- WD
Wilfor J. Diaz Fernandez, MD
BIDMC
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Wilfor J. Diaz Fernandez, MD
BIDMC, Boston, MA
Introduction: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a chronic, systemic, and autoimmune disease. It may involve various organs and the affected tissues are infiltrated by a large number of lymphocytes, in particular, IgG4-positive plasma cells. The involvement of the hepatobiliary and gastrointestinal tract has been described in prior reports but it is rarely affected. We herein report an interesting case of IgG4-RD manifesting as a duodenal ulcer and decompensated liver disease.
Case Description/Methods: A 77 year-old Vietnamese male presented to the emergency department with sudden melena and hypotension. On exam, jaundice and fresh blood on rectal exam were noted. Laboratory evaluation showed a total bilirubin of 17 mg/dL, AST 256 U/L, ALT 516 U/L, ALP 78 IU/L, Cr 1.4 mg/dL, hemoglobin 5 g/dL, INR 1.3, lactate 5.4 mmol/L. Fluid resuscitation, PPI infusion and blood transfusions were initiated. CTA abdomen and pelvis showed active intraluminal contrast extravasation into the duodenum which underwent successful IR coil embolization. Upper endoscopy showed 8 mm ulcers with a visible vessel in the second part of the duodenum cauterized and clipped with good hemostasis. Colonoscopy was normal. H. pylori stool antigen, ANA, AMA, AMSA were negative. LFTs normalized after 2 days and patient was discharged home. However, he returned few days later with worsening jaundice and new onset ascites. Paracentesis showed no signs of SBP and SAAG >1.1. Serum immunoglobulins were elevated. Liver MRI depicted cirrhosis and MRCP revealed no biliary ductal dilatation. Liver biopsy showed portal inflammation with increased IgG4-expressing plasma cells. Steroid treatment was started. However, hospital course was complicated by hepatorenal syndrome and heparin induced thrombocytopenia. Bivalirudin was initiated but was stopped shortly after due to GI bleed and shock. After goals of care discussions, patient decided to pursue comfort measures only and was discharge home with hospice.
Discussion: IgG4-RD presentation depends upon disease activity and the distribution of organs involved. The hepatobiliary form of IgG4-RD includes IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and IgG4-related hepatopathy with most patients showing concurrent autoimmune pancreatitis or autoimmune hepatitis, which was not seen in our patient making this case unique. It is necessary to keep high index of suspicion to make an appropriate diagnosis, thereby avoiding unnecessary delays in treatment and the development of irreversible fibrosis and organ failure.

Disclosures:
Wilfor J. Diaz Fernandez, MD. P1048 - IgG-4 Related Disease: The HIT and Run of a Dormant Disease, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
BIDMC, Boston, MA
Introduction: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a chronic, systemic, and autoimmune disease. It may involve various organs and the affected tissues are infiltrated by a large number of lymphocytes, in particular, IgG4-positive plasma cells. The involvement of the hepatobiliary and gastrointestinal tract has been described in prior reports but it is rarely affected. We herein report an interesting case of IgG4-RD manifesting as a duodenal ulcer and decompensated liver disease.
Case Description/Methods: A 77 year-old Vietnamese male presented to the emergency department with sudden melena and hypotension. On exam, jaundice and fresh blood on rectal exam were noted. Laboratory evaluation showed a total bilirubin of 17 mg/dL, AST 256 U/L, ALT 516 U/L, ALP 78 IU/L, Cr 1.4 mg/dL, hemoglobin 5 g/dL, INR 1.3, lactate 5.4 mmol/L. Fluid resuscitation, PPI infusion and blood transfusions were initiated. CTA abdomen and pelvis showed active intraluminal contrast extravasation into the duodenum which underwent successful IR coil embolization. Upper endoscopy showed 8 mm ulcers with a visible vessel in the second part of the duodenum cauterized and clipped with good hemostasis. Colonoscopy was normal. H. pylori stool antigen, ANA, AMA, AMSA were negative. LFTs normalized after 2 days and patient was discharged home. However, he returned few days later with worsening jaundice and new onset ascites. Paracentesis showed no signs of SBP and SAAG >1.1. Serum immunoglobulins were elevated. Liver MRI depicted cirrhosis and MRCP revealed no biliary ductal dilatation. Liver biopsy showed portal inflammation with increased IgG4-expressing plasma cells. Steroid treatment was started. However, hospital course was complicated by hepatorenal syndrome and heparin induced thrombocytopenia. Bivalirudin was initiated but was stopped shortly after due to GI bleed and shock. After goals of care discussions, patient decided to pursue comfort measures only and was discharge home with hospice.
Discussion: IgG4-RD presentation depends upon disease activity and the distribution of organs involved. The hepatobiliary form of IgG4-RD includes IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and IgG4-related hepatopathy with most patients showing concurrent autoimmune pancreatitis or autoimmune hepatitis, which was not seen in our patient making this case unique. It is necessary to keep high index of suspicion to make an appropriate diagnosis, thereby avoiding unnecessary delays in treatment and the development of irreversible fibrosis and organ failure.

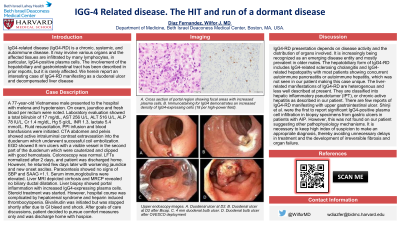
Figure: A. Cross section of portal region showing focal areas with increased plasma cells, B. Immunostaining for IgG4 demonstrates an increased density of IgG4-expressing cells (18 per high-power field).
Disclosures:
Wilfor Diaz Fernandez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wilfor J. Diaz Fernandez, MD. P1048 - IgG-4 Related Disease: The HIT and Run of a Dormant Disease, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

