Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1074 - Nafcillin-Induced Liver Injury: Idiosyncratic vs Intrinsic?
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Denisse Camille Dayto, MD
HCA Florida Citrus Hospital
Inverness, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Denisse Camille Dayto, MD1, Sean-Patrick Prince, MD, MPH2, Qitan Huang, DO1, Andrew Sephien, MD1, Varun Patel, MD3
1HCA Healthcare/USF Morsani GME Consortium: HCA Florida Citrus Hospital, Inverness, FL; 2University of Miami/Holy Cross Hospital, Pompano Beach, FL; 3HCA Florida Citrus Hospital, Inverness, FL
Introduction:
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) can present as elevated transaminases, acute hepatitis, or be as severe as acute liver failure. DILI is a diagnosis of exclusion and can occur at supratherapeutic levels of the medication (intrinsic), or at therapeutic levels of the medication (idiosyncratic). We present the case of Nafcillin-induced liver injury in a 53- year-old male for treatment of MSSA bacteremia.
Case Description/Methods:
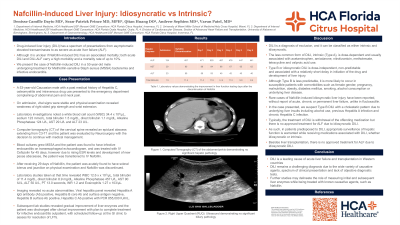
A 53-year-old Caucasian male with history of hepatitis C and intravenous drug use presented with complaints of abdominal and neck pain. Vital signs on admission were significant for a heart rate of 140 beats per minute and blood pressure of 100/65 mmHg. Physical examination revealed weakness of right sided grip strength and wrist extension. Labs showed white blood cell count 34.4 x 103/μL, sodium 123 mmol/L, total bilirubin 1.5 mg/dL, 1.1 mg/dL direct bilirubin, ALP 124 U/L, AST 29 IU/L, ALT 23U/L. CT of the cervical spine revealed an epidural from C3-T1. The patient was started on Cefazolin, Gentamicin and Dexamethasone due to MSSA bacteremia. The patient received 45 days of IV Cefazolin and was transitioned to Nafcillin.
After receiving 29 days of Nafcillin, the patient developed scleral icterus and jaundice. Repeat labs showed total bilirubin 11.4 mg/dL, direct bilirubin 8.9 mg/dL, ALP 469 U/L, AST 64 IU/L, ALT 47 U/L, PT 13.0 seconds, INR 1.2 and eosinophils 1.27 x 103/μL. Right-upper quadrant ultrasound showed normal liver echogenicity and biliary ducts. Further imaging revealed a contracted gallbladder with pericholecystic fluid vs gallbladder wall edema, no stones, choledocholithiasis or biliary dilatation. Hepatitis panel was positive for Hepatitis A antibody, Hepatitis B surface antibody, Hepatitis C antibody, Hepatitis C RNA 855000 IU/mL, but was negative for Hepatitis B core antibody.
Nafcillin was discontinued and the patient was switched to IV Vancomycin and subsequent labs showed gradual improvement of liver enzymes. The patient was discharged after clinical improvement and completing treatment for infective endocarditis.
Discussion:
DILI is a leading cause of acute liver failure and transplantation in Western countries and remains a challenging diagnosis due to a wide variety of causes, clinical presentation, and lack of objective diagnostic tests.
Due to its unpredictability and high associated morbidity and mortality; further studies
may delineate the role of measuring initial and subsequent liver enzymes while being treated with known causative agents.
Disclosures:
Denisse Camille Dayto, MD1, Sean-Patrick Prince, MD, MPH2, Qitan Huang, DO1, Andrew Sephien, MD1, Varun Patel, MD3. P1074 - Nafcillin-Induced Liver Injury: Idiosyncratic vs Intrinsic?, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1HCA Healthcare/USF Morsani GME Consortium: HCA Florida Citrus Hospital, Inverness, FL; 2University of Miami/Holy Cross Hospital, Pompano Beach, FL; 3HCA Florida Citrus Hospital, Inverness, FL
Introduction:
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) can present as elevated transaminases, acute hepatitis, or be as severe as acute liver failure. DILI is a diagnosis of exclusion and can occur at supratherapeutic levels of the medication (intrinsic), or at therapeutic levels of the medication (idiosyncratic). We present the case of Nafcillin-induced liver injury in a 53- year-old male for treatment of MSSA bacteremia.
Case Description/Methods:
A 53-year-old Caucasian male with history of hepatitis C and intravenous drug use presented with complaints of abdominal and neck pain. Vital signs on admission were significant for a heart rate of 140 beats per minute and blood pressure of 100/65 mmHg. Physical examination revealed weakness of right sided grip strength and wrist extension. Labs showed white blood cell count 34.4 x 103/μL, sodium 123 mmol/L, total bilirubin 1.5 mg/dL, 1.1 mg/dL direct bilirubin, ALP 124 U/L, AST 29 IU/L, ALT 23U/L. CT of the cervical spine revealed an epidural from C3-T1. The patient was started on Cefazolin, Gentamicin and Dexamethasone due to MSSA bacteremia. The patient received 45 days of IV Cefazolin and was transitioned to Nafcillin.
After receiving 29 days of Nafcillin, the patient developed scleral icterus and jaundice. Repeat labs showed total bilirubin 11.4 mg/dL, direct bilirubin 8.9 mg/dL, ALP 469 U/L, AST 64 IU/L, ALT 47 U/L, PT 13.0 seconds, INR 1.2 and eosinophils 1.27 x 103/μL. Right-upper quadrant ultrasound showed normal liver echogenicity and biliary ducts. Further imaging revealed a contracted gallbladder with pericholecystic fluid vs gallbladder wall edema, no stones, choledocholithiasis or biliary dilatation. Hepatitis panel was positive for Hepatitis A antibody, Hepatitis B surface antibody, Hepatitis C antibody, Hepatitis C RNA 855000 IU/mL, but was negative for Hepatitis B core antibody.
Nafcillin was discontinued and the patient was switched to IV Vancomycin and subsequent labs showed gradual improvement of liver enzymes. The patient was discharged after clinical improvement and completing treatment for infective endocarditis.
Discussion:
DILI is a leading cause of acute liver failure and transplantation in Western countries and remains a challenging diagnosis due to a wide variety of causes, clinical presentation, and lack of objective diagnostic tests.
Due to its unpredictability and high associated morbidity and mortality; further studies
may delineate the role of measuring initial and subsequent liver enzymes while being treated with known causative agents.
Disclosures:
Denisse Camille Dayto indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sean-Patrick Prince indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Qitan Huang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Sephien indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Varun Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Denisse Camille Dayto, MD1, Sean-Patrick Prince, MD, MPH2, Qitan Huang, DO1, Andrew Sephien, MD1, Varun Patel, MD3. P1074 - Nafcillin-Induced Liver Injury: Idiosyncratic vs Intrinsic?, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
