Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1134 - Fulminant Liver Failure Associated With Use of Dietary Weight Loss Supplement
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Tzu-Yu Liu, MD
University of Tennessee Health Science Center/Methodist University
Louisville, KY
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Tzu-Yu Liu, MD1, Dawit Jowhar, MD, PhD2, Anjana Mary Jacob, ARNP3, Nair Satheesh, MD4, Jiten Kothadia, MD5
1University of Tennessee Health Science Center/Methodist University, Louisville, KY; 2University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN; 3Methodist University, Memphis, TN; 4University of Tennessee Health Science Center/Methodist University Hospital, Memphis, TN; 5University of Tennessee Health Science Center/Methodist University, Memphis, TN
Introduction: Herbal and dietary supplements (HDS) use for weight loss has grown in the USA due to aggressive marketing through social media and burgeoning sales through the internet. Okinawa Flat Belly Tonic is a trendy dietary supplement for weight loss. It uses ingredients with reported hepatotoxicity, including grapeseed, turmeric, bitter melon extract, and green tea (Figure 1a). We describe the first fatal case of fulminant liver failure associated with using Okinawa Flat Belly Tonic.
Case Description/Methods: A 63-year-old female with a history of advanced COPD and morbid obesity presented with a week of fatigue, right upper quadrant pain, and anorexia, followed by jaundice. She reported daily usage of Okinawa Flat Belly Tonic for weight loss for the past three months; she stopped taking this two weeks before hospitalization (Figure 1b). She was also prescribed atorvastatin by her primary care provider and had taken it inconsistently for the past four days before hospitalization. She rarely consumed alcohol. She denied illicit drug use, pre-existing liver disease, or a family history of liver disease.
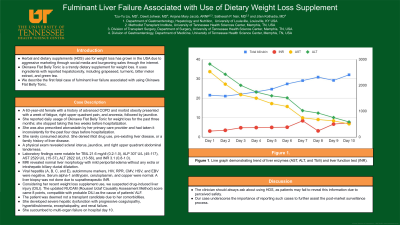
A physical exam revealed sclera icterus, jaundice, and right upper quadrant abdominal tenderness. Laboratory findings were notable for TBIL 21.6 mg/dl (0.2-1.0), ALP 307 U/L (45-117), AST 2529 U/L (15-37), ALT 2822 U/L (13-56), and INR 3.1 (0.8-1.0). Imaging with MRI revealed normal liver morphology with mild periportal edema without any extra or intrahepatic biliary ductal dilatation. Viral hepatitis (A, B, C, and E), autoimmune markers, HIV, RPR, CMV, HSV, and EBV were negative. Serum alpha-1 antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin, and copper were normal. A liver biopsy was not done due to supratherapeutic INR. Considering her recent weight loss supplement use, we suspected drug-induced liver injury (DILI). The updated RUCAM (Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method) score came 8 points, compatible with probable DILI as the cause of the patient's ALF. The patient was deemed not a transplant candidate due to her comorbidities. She developed severe hepatic dysfunction with progressive coagulopathy, hyperbilirubinemia, encephalopathy, and renal failure (Figure 1c). She succumbed to multi-organ failure on hospital day 10.
Discussion: The clinician should always ask about using HDS, as patients may fail to reveal this information due to perceived safety. Our case underscores the importance of reporting such cases to further assist the post-market surveillance process.

Disclosures:
Tzu-Yu Liu, MD1, Dawit Jowhar, MD, PhD2, Anjana Mary Jacob, ARNP3, Nair Satheesh, MD4, Jiten Kothadia, MD5. P1134 - Fulminant Liver Failure Associated With Use of Dietary Weight Loss Supplement, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Tzu-Yu Liu, MD1, Dawit Jowhar, MD, PhD2, Anjana Mary Jacob, ARNP3, Nair Satheesh, MD4, Jiten Kothadia, MD5
1University of Tennessee Health Science Center/Methodist University, Louisville, KY; 2University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN; 3Methodist University, Memphis, TN; 4University of Tennessee Health Science Center/Methodist University Hospital, Memphis, TN; 5University of Tennessee Health Science Center/Methodist University, Memphis, TN
Introduction: Herbal and dietary supplements (HDS) use for weight loss has grown in the USA due to aggressive marketing through social media and burgeoning sales through the internet. Okinawa Flat Belly Tonic is a trendy dietary supplement for weight loss. It uses ingredients with reported hepatotoxicity, including grapeseed, turmeric, bitter melon extract, and green tea (Figure 1a). We describe the first fatal case of fulminant liver failure associated with using Okinawa Flat Belly Tonic.
Case Description/Methods: A 63-year-old female with a history of advanced COPD and morbid obesity presented with a week of fatigue, right upper quadrant pain, and anorexia, followed by jaundice. She reported daily usage of Okinawa Flat Belly Tonic for weight loss for the past three months; she stopped taking this two weeks before hospitalization (Figure 1b). She was also prescribed atorvastatin by her primary care provider and had taken it inconsistently for the past four days before hospitalization. She rarely consumed alcohol. She denied illicit drug use, pre-existing liver disease, or a family history of liver disease.
A physical exam revealed sclera icterus, jaundice, and right upper quadrant abdominal tenderness. Laboratory findings were notable for TBIL 21.6 mg/dl (0.2-1.0), ALP 307 U/L (45-117), AST 2529 U/L (15-37), ALT 2822 U/L (13-56), and INR 3.1 (0.8-1.0). Imaging with MRI revealed normal liver morphology with mild periportal edema without any extra or intrahepatic biliary ductal dilatation. Viral hepatitis (A, B, C, and E), autoimmune markers, HIV, RPR, CMV, HSV, and EBV were negative. Serum alpha-1 antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin, and copper were normal. A liver biopsy was not done due to supratherapeutic INR. Considering her recent weight loss supplement use, we suspected drug-induced liver injury (DILI). The updated RUCAM (Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method) score came 8 points, compatible with probable DILI as the cause of the patient's ALF. The patient was deemed not a transplant candidate due to her comorbidities. She developed severe hepatic dysfunction with progressive coagulopathy, hyperbilirubinemia, encephalopathy, and renal failure (Figure 1c). She succumbed to multi-organ failure on hospital day 10.
Discussion: The clinician should always ask about using HDS, as patients may fail to reveal this information due to perceived safety. Our case underscores the importance of reporting such cases to further assist the post-market surveillance process.

Figure: Figure 1a. Ingredients in Okinawa Flat Belly Tonic b. Okinawa Flat Belly Tonic c. Trend of transaminitis and liver function tests throughout hospital course
Disclosures:
Tzu-Yu Liu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dawit Jowhar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anjana Mary Jacob indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nair Satheesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jiten Kothadia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tzu-Yu Liu, MD1, Dawit Jowhar, MD, PhD2, Anjana Mary Jacob, ARNP3, Nair Satheesh, MD4, Jiten Kothadia, MD5. P1134 - Fulminant Liver Failure Associated With Use of Dietary Weight Loss Supplement, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

