Sunday Poster Session
Category: Practice Management
P1235 - Improving Adequacy of Bowel Preparation With the Aid of Automated Pre-Colonoscopy Text Messaging
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Sean Sileno, MD
Mayo Clinic
Scottsdale, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Sean Sileno, MD1, Lisa R. Anderson, MSN1, Heather Reser, RN2, Todd Aldrich, 1, Tyler Lindhart, 1, Suryakanth Gurudu, MD1, Shabana Pasha, MD3, Francisco Ramirez, MD, MACG1
1Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ; 2Mayo Clinic, Sottsdale, AZ; 3Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Scottsdale, AZ
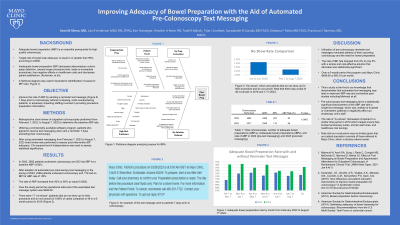
Introduction: Adequate bowel preparation (ABP) is an essential prerequisite for high quality colonoscopy. Target rate of bowel prep adequacy is greater than 90%, however the observed rate is often lower. Inadequate bowel preparation (IBP) decreases adenomatous colonic polyp detection, causes longer procedure time, and leads to incomplete procedures all of which increase healthcare spending. With increasing IBP rates, we implemented a quality improvement project in our outpatient endoscopy unit. We aimed to assess the impact of automated pre-colonoscopy text messaging on bowel preparation quality.
Methods: Retrospective chart review of outpatient colonoscopies at an academic medical center was performed from February 7, 2022 to April 7, 2022 to determine the baseline IBP rate. Data was collected on bowel preparation (BP) quality and completion of the procedure. BP was characterized using the Boston Bowel Preparation Score (BBPS) with a score of six or above being considered adequate. Utilizing a commercially available software program, patients who agreed to receive text messaging were sent a reminder 7 days preceding their colonoscopy. The date and time of their colonoscopy, dietary instructions, and BP instructions were included in the text message. For patients who opted to receive messages on their home phones, voice messages were sent. After using automated messaging from February 7, 2023 to May 7, 2023, chart review was performed to assess post-intervention BP adequacy. Chi-squared test of independence was used to assess statistical significance.
Results: In the spring of 2022, 1439 patients underwent colonoscopy and 109 had an IBP (8%). With the adoption of automated pre-colonoscopy text messaging in the spring of 2023, 1409 patients underwent colonoscopy and 62 had an IBP (4%), effectively cutting the IBP rate by 50%. Thus, the overall rate of ABP increased from 92% to 96% (p-value 0.0002) after implementation of pre-colonoscopy text messaging. Over the study period, a total 41 reminder calls and 1464 text messages were sent to patients for a total cost of $95.58. There may be an unintentional negative impact on the cancellation rates; further data collection and analysis is ongoing.
Discussion: Pre-colonoscopy text messaging led to a statistically significant improvement of the ABP rate without adding significant cost to the practice. Ultimately, lower IBP rates can reduce healthcare costs, result in better outcomes, and improve patient satisfaction.

Disclosures:
Sean Sileno, MD1, Lisa R. Anderson, MSN1, Heather Reser, RN2, Todd Aldrich, 1, Tyler Lindhart, 1, Suryakanth Gurudu, MD1, Shabana Pasha, MD3, Francisco Ramirez, MD, MACG1. P1235 - Improving Adequacy of Bowel Preparation With the Aid of Automated Pre-Colonoscopy Text Messaging, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ; 2Mayo Clinic, Sottsdale, AZ; 3Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Scottsdale, AZ
Introduction: Adequate bowel preparation (ABP) is an essential prerequisite for high quality colonoscopy. Target rate of bowel prep adequacy is greater than 90%, however the observed rate is often lower. Inadequate bowel preparation (IBP) decreases adenomatous colonic polyp detection, causes longer procedure time, and leads to incomplete procedures all of which increase healthcare spending. With increasing IBP rates, we implemented a quality improvement project in our outpatient endoscopy unit. We aimed to assess the impact of automated pre-colonoscopy text messaging on bowel preparation quality.
Methods: Retrospective chart review of outpatient colonoscopies at an academic medical center was performed from February 7, 2022 to April 7, 2022 to determine the baseline IBP rate. Data was collected on bowel preparation (BP) quality and completion of the procedure. BP was characterized using the Boston Bowel Preparation Score (BBPS) with a score of six or above being considered adequate. Utilizing a commercially available software program, patients who agreed to receive text messaging were sent a reminder 7 days preceding their colonoscopy. The date and time of their colonoscopy, dietary instructions, and BP instructions were included in the text message. For patients who opted to receive messages on their home phones, voice messages were sent. After using automated messaging from February 7, 2023 to May 7, 2023, chart review was performed to assess post-intervention BP adequacy. Chi-squared test of independence was used to assess statistical significance.
Results: In the spring of 2022, 1439 patients underwent colonoscopy and 109 had an IBP (8%). With the adoption of automated pre-colonoscopy text messaging in the spring of 2023, 1409 patients underwent colonoscopy and 62 had an IBP (4%), effectively cutting the IBP rate by 50%. Thus, the overall rate of ABP increased from 92% to 96% (p-value 0.0002) after implementation of pre-colonoscopy text messaging. Over the study period, a total 41 reminder calls and 1464 text messages were sent to patients for a total cost of $95.58. There may be an unintentional negative impact on the cancellation rates; further data collection and analysis is ongoing.
Discussion: Pre-colonoscopy text messaging led to a statistically significant improvement of the ABP rate without adding significant cost to the practice. Ultimately, lower IBP rates can reduce healthcare costs, result in better outcomes, and improve patient satisfaction.

Figure: Example of an automated text message sent 7 days before colonoscopy.
Disclosures:
Sean Sileno indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lisa Anderson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Heather Reser indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Todd Aldrich indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tyler Lindhart indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suryakanth Gurudu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shabana Pasha: abbvie – Grant/Research Support. medtronic – Grant/Research Support.
Francisco Ramirez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sean Sileno, MD1, Lisa R. Anderson, MSN1, Heather Reser, RN2, Todd Aldrich, 1, Tyler Lindhart, 1, Suryakanth Gurudu, MD1, Shabana Pasha, MD3, Francisco Ramirez, MD, MACG1. P1235 - Improving Adequacy of Bowel Preparation With the Aid of Automated Pre-Colonoscopy Text Messaging, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
