Sunday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P1257 - Duodenal Polyp Surveillance in Familial Adenomatous Polyposis: Long-Term Follow Up at a Single Tertiary Care Center
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- DS
Daniel Schupack, MD
Mayo Clinic
Rochester, MN
Presenting Author(s)
Daniel Schupack, MD, Shubham Sood, MBBS, Fnu Deepali, MBBS, Nayantara Coelho-Prabhu, MBBS, Lisa Boardman, MD
Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: The Spigelman classification aims to stratify patients with Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) into stages enabling selection of appropriate follow up interval for upper endoscopy with goal to reduce risk of duodenal cancer. Our primary objective was to study progression of duodenal polyps on serial upper endoscopies.
Methods: In this retrospective study, data was collected from 2547 endoscopic procedures from 371 patients with FAP who underwent upper gastrointestinal surveillance at our tertiary care center between 1989-2023. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS with Chi-square tests.
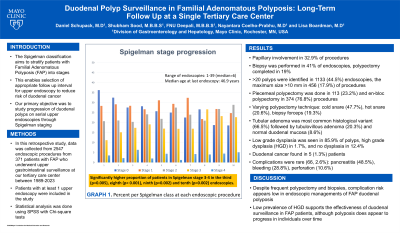
Results: The number of endoscopies per patient ranged from 1-39 (median=6). Median age at last recorded endoscopy was 46.9. Initial endoscopy at our center was normal in 129 patients (34.8%) which decreased to 85 patients (32.5%) and 65 patients (27.5%) by second and third endoscopies. Following longitudinally and comparing to baseline endoscopy at our institution, there was a significantly higher proportion of patients in Spigelman stage 3-4 in the third (p=0.005), eighth (p< 0.001), ninth (p=0.002) and tenth (p=0.002) endoscopies completed. It was common to have >20 polyps in the duodenum (44.5%) and polyps were >10 mm in 17.9% of procedures. Papillary involvement was seen in 32.9% of procedures. Biopsy was performed in 41.0% of endoscopies, while polypectomy was pursued in 19.0%. Polypectomy was completed in piecemeal fashion in 113 (23.2%) and as whole polypectomy in 374 (76.8%) procedures. Polypectomy was mostly done using a cold snare (47.7%) while hot snare (20.6%) and biopsy forceps (19.3%) were also used. Histologically, polyps were predominantly tubular adenoma (66.5%) and tubulovillous adenoma (20.3%), with a small proportion being normal duodenal mucosa (8.6%). Low grade dysplasia was seen in 85.9% of polyps, high grade dysplasia (HGD) in 1.7%, and no dysplasia in 12.4%. Duodenal cancer was found in 5 (1.3%) patients. Complications were rare (66, 2.6%) and included pancreatitis (48.5%), bleeding (28.8%) and perforation (10.6%). Graph 1. shows the Spigelman class progression for patients over their first 10 endoscopies at our institution.
Discussion: We present extensive data on endoscopic follow up for duodenal polyp surveillance in FAP patients. Despite frequent polypectomy and biopsies, complication risk appears low. Furthermore, low prevalence of HGD supports the effectiveness of duodenal surveillance in FAP patients, although polyposis does appear to progress in individuals over time.

Disclosures:
Daniel Schupack, MD, Shubham Sood, MBBS, Fnu Deepali, MBBS, Nayantara Coelho-Prabhu, MBBS, Lisa Boardman, MD. P1257 - Duodenal Polyp Surveillance in Familial Adenomatous Polyposis: Long-Term Follow Up at a Single Tertiary Care Center, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: The Spigelman classification aims to stratify patients with Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) into stages enabling selection of appropriate follow up interval for upper endoscopy with goal to reduce risk of duodenal cancer. Our primary objective was to study progression of duodenal polyps on serial upper endoscopies.
Methods: In this retrospective study, data was collected from 2547 endoscopic procedures from 371 patients with FAP who underwent upper gastrointestinal surveillance at our tertiary care center between 1989-2023. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS with Chi-square tests.
Results: The number of endoscopies per patient ranged from 1-39 (median=6). Median age at last recorded endoscopy was 46.9. Initial endoscopy at our center was normal in 129 patients (34.8%) which decreased to 85 patients (32.5%) and 65 patients (27.5%) by second and third endoscopies. Following longitudinally and comparing to baseline endoscopy at our institution, there was a significantly higher proportion of patients in Spigelman stage 3-4 in the third (p=0.005), eighth (p< 0.001), ninth (p=0.002) and tenth (p=0.002) endoscopies completed. It was common to have >20 polyps in the duodenum (44.5%) and polyps were >10 mm in 17.9% of procedures. Papillary involvement was seen in 32.9% of procedures. Biopsy was performed in 41.0% of endoscopies, while polypectomy was pursued in 19.0%. Polypectomy was completed in piecemeal fashion in 113 (23.2%) and as whole polypectomy in 374 (76.8%) procedures. Polypectomy was mostly done using a cold snare (47.7%) while hot snare (20.6%) and biopsy forceps (19.3%) were also used. Histologically, polyps were predominantly tubular adenoma (66.5%) and tubulovillous adenoma (20.3%), with a small proportion being normal duodenal mucosa (8.6%). Low grade dysplasia was seen in 85.9% of polyps, high grade dysplasia (HGD) in 1.7%, and no dysplasia in 12.4%. Duodenal cancer was found in 5 (1.3%) patients. Complications were rare (66, 2.6%) and included pancreatitis (48.5%), bleeding (28.8%) and perforation (10.6%). Graph 1. shows the Spigelman class progression for patients over their first 10 endoscopies at our institution.
Discussion: We present extensive data on endoscopic follow up for duodenal polyp surveillance in FAP patients. Despite frequent polypectomy and biopsies, complication risk appears low. Furthermore, low prevalence of HGD supports the effectiveness of duodenal surveillance in FAP patients, although polyposis does appear to progress in individuals over time.

Figure: Figure 1. Duodenal polyposis progression over time based on Spigelman score
Disclosures:
Daniel Schupack indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shubham Sood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fnu Deepali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nayantara Coelho-Prabhu: Alexion Pharma – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Iterative Health – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Lisa Boardman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Schupack, MD, Shubham Sood, MBBS, Fnu Deepali, MBBS, Nayantara Coelho-Prabhu, MBBS, Lisa Boardman, MD. P1257 - Duodenal Polyp Surveillance in Familial Adenomatous Polyposis: Long-Term Follow Up at a Single Tertiary Care Center, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
