Sunday Poster Session
Category: Obesity
P1167 - Kaplan-Meier Survival Estimates: A Lens into Obesity and GIST Patient Readmission
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Presenting Author(s)
Rajmohan Rammohan, MD, Tulika Saggar, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Sandra Gomez, MD, Saher Sheikh, MD, Rucha Jiyani, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Achal Patel, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most common type of mesenchymal tumors in the gastrointestinal tract, resulting from mutations and overexpression of tyrosine kinase receptors in the interstitial cells of Cajal. In the US, GIST incidence is about 5000 per million, with a median diagnosis age of 66-69. Imatinib transformed GIST treatment, complementing surgical resection, but disease progression is seen even after 2-3 years of therapy. This study is designed to examine how obesity affects the rate of readmission in GIST patients, providing valuable insight for future therapeutic strategies.
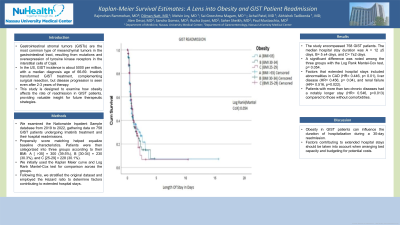
Methods: We examined the Nationwide Inpatient Sample database from 2019 to 2022, gathering data on 758 GIST patients undergoing Imatinib treatment and their hospital readmissions. Propensity score matching helped equalize baseline characteristics. Patients were then categorized into three groups according to their BMI: A [ >35] = 300 (39.5%), B [30-34] = 230 (30.3%), and C [25-29] = 228 (30.1%). We initially used the Kaplan Meier curve and Log Rank Mantel-Cox test for comparison across the groups. Following this, we stratified the original dataset and employed the Hazard ratio to determine factors contributing to extended hospital stays.
Results: The study encompassed 758 GIST patients. The median hospital stay duration was A = 12 ±5 days, B= 5 ±4 days, and C= 7±2 days. A significant difference was noted among the three groups with the Log Rank Mantel-Cox test, p= 0.054. Factors that extended hospital stays included abnormalities in CAD (HR= 0.446, p< 0.01), liver disease (HR= 0.456, p= 0.04), and renal failure (HR= 0.516, p=0.022). Patients with more than two chronic diseases had a notably longer stay (HR= 0.546, p=0.013) compared to those without comorbidities.
Discussion: Obesity in GIST patients can influence the duration of hospitalization during a 30-day readmission. Factors contributing to extended hospital stays should be taken into account when arranging bed capacity and budgeting for potential costs.

Disclosures:
Rajmohan Rammohan, MD, Tulika Saggar, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Sandra Gomez, MD, Saher Sheikh, MD, Rucha Jiyani, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Achal Patel, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA. P1167 - Kaplan-Meier Survival Estimates: A Lens into Obesity and GIST Patient Readmission, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most common type of mesenchymal tumors in the gastrointestinal tract, resulting from mutations and overexpression of tyrosine kinase receptors in the interstitial cells of Cajal. In the US, GIST incidence is about 5000 per million, with a median diagnosis age of 66-69. Imatinib transformed GIST treatment, complementing surgical resection, but disease progression is seen even after 2-3 years of therapy. This study is designed to examine how obesity affects the rate of readmission in GIST patients, providing valuable insight for future therapeutic strategies.
Methods: We examined the Nationwide Inpatient Sample database from 2019 to 2022, gathering data on 758 GIST patients undergoing Imatinib treatment and their hospital readmissions. Propensity score matching helped equalize baseline characteristics. Patients were then categorized into three groups according to their BMI: A [ >35] = 300 (39.5%), B [30-34] = 230 (30.3%), and C [25-29] = 228 (30.1%). We initially used the Kaplan Meier curve and Log Rank Mantel-Cox test for comparison across the groups. Following this, we stratified the original dataset and employed the Hazard ratio to determine factors contributing to extended hospital stays.
Results: The study encompassed 758 GIST patients. The median hospital stay duration was A = 12 ±5 days, B= 5 ±4 days, and C= 7±2 days. A significant difference was noted among the three groups with the Log Rank Mantel-Cox test, p= 0.054. Factors that extended hospital stays included abnormalities in CAD (HR= 0.446, p< 0.01), liver disease (HR= 0.456, p= 0.04), and renal failure (HR= 0.516, p=0.022). Patients with more than two chronic diseases had a notably longer stay (HR= 0.546, p=0.013) compared to those without comorbidities.
Discussion: Obesity in GIST patients can influence the duration of hospitalization during a 30-day readmission. Factors contributing to extended hospital stays should be taken into account when arranging bed capacity and budgeting for potential costs.

Figure: KM model on obesity and GIST
Disclosures:
Rajmohan Rammohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tulika Saggar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Melvin Joy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Greeshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dilman Natt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jiten Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sandra Gomez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saher Sheikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rucha Jiyani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhishek Tadikonda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Achal Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Mustacchia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajmohan Rammohan, MD, Tulika Saggar, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Sandra Gomez, MD, Saher Sheikh, MD, Rucha Jiyani, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Achal Patel, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA. P1167 - Kaplan-Meier Survival Estimates: A Lens into Obesity and GIST Patient Readmission, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

