Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0284 - Colonic Kaposi Sarcoma in a HIV Negative Patient
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Kinnari Modi, DO
Methodist Dallas Medical Center
Dallas, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Kinnari Modi, DO1, Blake Thompson, MD1, Dillon Drab, 2
1Methodist Dallas Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 2Methodist Dallas, Dallas, TX
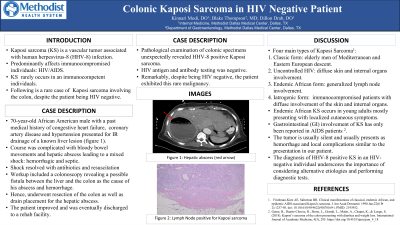
Introduction: Kaposi Sarcoma (KS) is a vascular tumor commonly associated with human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8) infection. It predominantly affects immunocompromised individuals, particularly those with HIV/AIDS. However, KS can rarely occur in immunocompetent individuals. Here we describe a rare case of an African American male who was diagnosed with Kaposi Sarcoma involving the colon, despite being HIV negative.
Case Description/Methods: A 70-year-old African American male with a past medical history of congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease and hypertension presented to the hospital with a large liver cyst. He underwent drainage of the cyst. His course was further complicated with bloody bowel movements leading to hemorrhagic shock and hepatic abscess leading to septic shock. The patient was briefly in the ICU on norepinephrine and improved with antibiotics and blood transfusions. He underwent colonoscopy revealing a possible fistula between the cyst and the colon as the cause of his abscess and hemorrhage. He underwent resection of the colon as well as drain placement for the hepatic abscess. The patient continued to improve and was eventually discharged to a rehab facility.
Prior to discharge, pathological examination of the resected colonic specimens unexpectedly revealed HHV-8 positive Kaposi Sarcoma. His HIV antigen and antibody testing was negative. Remarkably, despite being HIV negative, the patient exhibited this rare malignancy.
Discussion: There are 4 main types of Kaposi Sarcoma: (1) classic form that occurs in elderly men of Mediterranean and Eastern European descent; (2) patients with uncontrolled HIV with diffuse skin and internal organs involvement; (3) endemic African form with generalized lymph node involvement; and (4) iatrogenic form in immunocompromised patients with diffuse involvement of the skin and internal organs. The endemic African Kaposi Sarcoma usually occurs in young adults mostly presenting with localized cutaneous symptoms. Gastrointestinal involvement of KS has only been reported in AIDS patients but is the most common visceral involvement ranging from 40%-60%. The tumor is usually silent and usually presents as hemorrhage and local complications similar to the presentation in our patient. The diagnosis of HHV-8 positive KS in an HIV-negative individual underscores the importance of considering alternative etiologies and performing diagnostic tests.
Disclosures:
Kinnari Modi, DO1, Blake Thompson, MD1, Dillon Drab, 2. P0284 - Colonic Kaposi Sarcoma in a HIV Negative Patient, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Methodist Dallas Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 2Methodist Dallas, Dallas, TX
Introduction: Kaposi Sarcoma (KS) is a vascular tumor commonly associated with human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8) infection. It predominantly affects immunocompromised individuals, particularly those with HIV/AIDS. However, KS can rarely occur in immunocompetent individuals. Here we describe a rare case of an African American male who was diagnosed with Kaposi Sarcoma involving the colon, despite being HIV negative.
Case Description/Methods: A 70-year-old African American male with a past medical history of congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease and hypertension presented to the hospital with a large liver cyst. He underwent drainage of the cyst. His course was further complicated with bloody bowel movements leading to hemorrhagic shock and hepatic abscess leading to septic shock. The patient was briefly in the ICU on norepinephrine and improved with antibiotics and blood transfusions. He underwent colonoscopy revealing a possible fistula between the cyst and the colon as the cause of his abscess and hemorrhage. He underwent resection of the colon as well as drain placement for the hepatic abscess. The patient continued to improve and was eventually discharged to a rehab facility.
Prior to discharge, pathological examination of the resected colonic specimens unexpectedly revealed HHV-8 positive Kaposi Sarcoma. His HIV antigen and antibody testing was negative. Remarkably, despite being HIV negative, the patient exhibited this rare malignancy.
Discussion: There are 4 main types of Kaposi Sarcoma: (1) classic form that occurs in elderly men of Mediterranean and Eastern European descent; (2) patients with uncontrolled HIV with diffuse skin and internal organs involvement; (3) endemic African form with generalized lymph node involvement; and (4) iatrogenic form in immunocompromised patients with diffuse involvement of the skin and internal organs. The endemic African Kaposi Sarcoma usually occurs in young adults mostly presenting with localized cutaneous symptoms. Gastrointestinal involvement of KS has only been reported in AIDS patients but is the most common visceral involvement ranging from 40%-60%. The tumor is usually silent and usually presents as hemorrhage and local complications similar to the presentation in our patient. The diagnosis of HHV-8 positive KS in an HIV-negative individual underscores the importance of considering alternative etiologies and performing diagnostic tests.
Disclosures:
Kinnari Modi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Blake Thompson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dillon Drab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kinnari Modi, DO1, Blake Thompson, MD1, Dillon Drab, 2. P0284 - Colonic Kaposi Sarcoma in a HIV Negative Patient, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
