Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P1857 - Addressing Diagnostic Dilemmas in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Using Esophageal Epithelial Eosinophilic-Derived Neurotoxin
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- YS
Yamen Smadi, MD
Orlando Health Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children
Orlando, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Jessina Thomas, MD1, Puanani Hopson, MD2, Chirajyoti Deb, PhD1, Jeffrey Bornstein, MD1, Devendra Mehta, MD1, Khaled Bittar, MD1, Yamen Smadi, MD1
1Orlando Health Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando, FL; 2Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) is a viable marker of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) disease activity. We studied the utility of measuring EDN from esophageal epithelial brushings for diagnosing EoE, focusing on two scenarios: 1) cases of exclusive distal eosinophilia and 2) cases of discrepancy between endoscopy and histology.
Methods: Records of patients who underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) with EDN measured via esophageal brushings at Orlando Health Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children in Orlando, Florida from January 2014 to October 2018 were retrospectively reviewed. Demographics, clinical, endoscopic, and histologic data were collected. Patients were divided into 2 groups (EoE and controls). EGDs done on EoE patients were further categorized as active or inactive EoE. EGD results were also divided into 4 additional groups based on the distribution of esophageal eosinophilia (PEC ≥15/hpf): >1 level of the esophagus, middle or proximal only, distal only, and no eosinophilia.
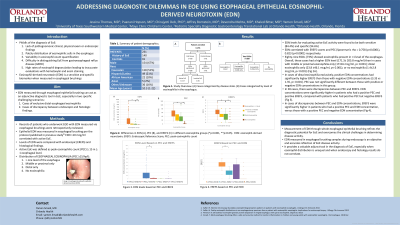
Results: We reviewed 231 patient records (66.7% male, mean age 10.3 years, range 1-22 years). EDN values correlated with endoscopic reference score (EREFS) and peak eosinophil count (PEC) (Spearman’s rho = 0.756 (p< 0.001) and 0.824 (p< 0.001) respectively). Average PEC, EREFS, and EDN concentrations were higher in patients with active EoE than in controls or patients with inactive disease. When grouping patients based on esophageal eosinophilia distribution, EDN mirrored PEC and EREFS. Patients with exclusive distal eosinophilia had lower EDN concentrations than those with eosinophilia in >1 level of the esophagus (23.8 ±46.1 mcg/ml vs 171.3± 205.8 mcg/ml respectively, p< 0.001). EDN values were more consistent with EREFS in cases of discrepancies between endoscopic findings and pathology (p < 0.001).
Discussion: EDN measured in esophageal brushing samples reflects disease activity objectively and accurately. It also offers significant value in cases of exclusive distal esophageal eosinophilia and when discrepancies exist between endoscopy and histology.

Disclosures:
Jessina Thomas, MD1, Puanani Hopson, MD2, Chirajyoti Deb, PhD1, Jeffrey Bornstein, MD1, Devendra Mehta, MD1, Khaled Bittar, MD1, Yamen Smadi, MD1. P1857 - Addressing Diagnostic Dilemmas in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Using Esophageal Epithelial Eosinophilic-Derived Neurotoxin, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Jessina Thomas, MD1, Puanani Hopson, MD2, Chirajyoti Deb, PhD1, Jeffrey Bornstein, MD1, Devendra Mehta, MD1, Khaled Bittar, MD1, Yamen Smadi, MD1
1Orlando Health Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando, FL; 2Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) is a viable marker of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) disease activity. We studied the utility of measuring EDN from esophageal epithelial brushings for diagnosing EoE, focusing on two scenarios: 1) cases of exclusive distal eosinophilia and 2) cases of discrepancy between endoscopy and histology.
Methods: Records of patients who underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) with EDN measured via esophageal brushings at Orlando Health Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children in Orlando, Florida from January 2014 to October 2018 were retrospectively reviewed. Demographics, clinical, endoscopic, and histologic data were collected. Patients were divided into 2 groups (EoE and controls). EGDs done on EoE patients were further categorized as active or inactive EoE. EGD results were also divided into 4 additional groups based on the distribution of esophageal eosinophilia (PEC ≥15/hpf): >1 level of the esophagus, middle or proximal only, distal only, and no eosinophilia.
Results: We reviewed 231 patient records (66.7% male, mean age 10.3 years, range 1-22 years). EDN values correlated with endoscopic reference score (EREFS) and peak eosinophil count (PEC) (Spearman’s rho = 0.756 (p< 0.001) and 0.824 (p< 0.001) respectively). Average PEC, EREFS, and EDN concentrations were higher in patients with active EoE than in controls or patients with inactive disease. When grouping patients based on esophageal eosinophilia distribution, EDN mirrored PEC and EREFS. Patients with exclusive distal eosinophilia had lower EDN concentrations than those with eosinophilia in >1 level of the esophagus (23.8 ±46.1 mcg/ml vs 171.3± 205.8 mcg/ml respectively, p< 0.001). EDN values were more consistent with EREFS in cases of discrepancies between endoscopic findings and pathology (p < 0.001).
Discussion: EDN measured in esophageal brushing samples reflects disease activity objectively and accurately. It also offers significant value in cases of exclusive distal esophageal eosinophilia and when discrepancies exist between endoscopy and histology.

Figure: (A) EDN levels based on PEC and EREFS. (B) EREFS based on PEC and EDN (*p<0.001). EDN: eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. EREFS: Endoscopic Reference Score. PEC: peak eosinophilic count
Disclosures:
Jessina Thomas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Puanani Hopson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chirajyoti Deb indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeffrey Bornstein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Devendra Mehta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khaled Bittar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yamen Smadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jessina Thomas, MD1, Puanani Hopson, MD2, Chirajyoti Deb, PhD1, Jeffrey Bornstein, MD1, Devendra Mehta, MD1, Khaled Bittar, MD1, Yamen Smadi, MD1. P1857 - Addressing Diagnostic Dilemmas in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Using Esophageal Epithelial Eosinophilic-Derived Neurotoxin, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.


