Monday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P1960 - Safety and Efficacy of Highly Selective 5-HT4 Agonist (Velusetrag, Felcisetrag, Prucalopride) for Diabetic/Idiopathic Gastroparesis - Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Himsikhar Khataniar, MD
Allegheny General Hospital
Pittsburgh, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Parth Patel, MD1, Himsikhar Khataniar, MD2, Priyadarshini Loganathan, MD3, Babu Mohan, MD, MS4
1Ascension Saint Joseph Hospital, Chicago, IL; 2Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA; 3University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX; 4University of Utah Health School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT
Introduction: Gastroparesis continues to significantly affect the quality of life and healthcare expenditure. Effective treatment options are limited and the utility of current prokinetic agents are inhibited by serious adverse effects. There is an unmet need for effective prokinetic agents with acceptable adverse effect profiles. Highly selective 5-HT4 agonists have shown clinical efficacy and safety in randomized controlled trials.
Methods: Multiple databases including Pubmed, Scopus and Embase were screened from inception up until March 2023. Only RCTs that evaluated efficacy and safety of highly selective 5-HT4 agonists for gastroparesis were included. Outcomes of interest were the pooled rates of Gastric Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI) score, gastric emptying (GE) time, and adverse event rate in each group. Standard meta-analysis methodology was followed using the random-effects model, and heterogeneity was assessed by I2 statistics.
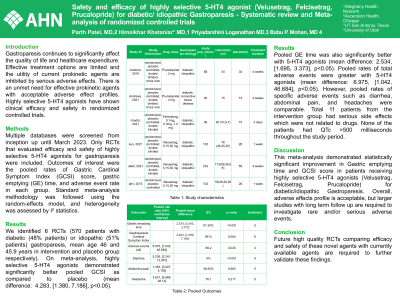
Results: We identified 6 RCTs (570 patients with diabetic (48% patients) or idiopathic (51% patients) gastroparesis, mean age 46 and 45.9 years in intervention and placebo group respectively)
On meta-analysis, highly selective 5-HT4 agonists demonstrated significantly better pooled GCSI as compared to placebo (mean difference: 4.283, [1.380, 7.186], p< 0.05). Pooled GE time was also significantly better with 5-HT4 agonists (mean difference: 2.534, [1.695, 3.373], p< 0.05). Pooled rates of total adverse events were greater with 5-HT4 agonists (mean difference: 6.975, [1.042, 46.684], p< 0.05). However, pooled rates of specific adverse events such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and headaches were comparable. Total 11 patients from the intervention group had serious side effects which were not related to drugs. None of the patients had QTc >500 milliseconds throughout the study period. Results are described in forest plots.
Discussion: This meta-analysis demonstrated statistically significant improvement in Gastric emptying time and GCSI score in patients receiving highly selective 5-HT4 agonists (Velusetrag, Felcisetrag, Prucalopride) for diabetic/idiopathic Gastroparesis. Overall, adverse effects profile is acceptable, but larger studies with long term follow up are required to investigate rare and/or serious adverse events. Future high quality RCTs comparing efficacy and safety of these novel agents with currently available agents are required to validate these findings.

Disclosures:
Parth Patel, MD1, Himsikhar Khataniar, MD2, Priyadarshini Loganathan, MD3, Babu Mohan, MD, MS4. P1960 - Safety and Efficacy of Highly Selective 5-HT4 Agonist (Velusetrag, Felcisetrag, Prucalopride) for Diabetic/Idiopathic Gastroparesis - Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Ascension Saint Joseph Hospital, Chicago, IL; 2Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA; 3University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX; 4University of Utah Health School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT
Introduction: Gastroparesis continues to significantly affect the quality of life and healthcare expenditure. Effective treatment options are limited and the utility of current prokinetic agents are inhibited by serious adverse effects. There is an unmet need for effective prokinetic agents with acceptable adverse effect profiles. Highly selective 5-HT4 agonists have shown clinical efficacy and safety in randomized controlled trials.
Methods: Multiple databases including Pubmed, Scopus and Embase were screened from inception up until March 2023. Only RCTs that evaluated efficacy and safety of highly selective 5-HT4 agonists for gastroparesis were included. Outcomes of interest were the pooled rates of Gastric Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI) score, gastric emptying (GE) time, and adverse event rate in each group. Standard meta-analysis methodology was followed using the random-effects model, and heterogeneity was assessed by I2 statistics.
Results: We identified 6 RCTs (570 patients with diabetic (48% patients) or idiopathic (51% patients) gastroparesis, mean age 46 and 45.9 years in intervention and placebo group respectively)
On meta-analysis, highly selective 5-HT4 agonists demonstrated significantly better pooled GCSI as compared to placebo (mean difference: 4.283, [1.380, 7.186], p< 0.05). Pooled GE time was also significantly better with 5-HT4 agonists (mean difference: 2.534, [1.695, 3.373], p< 0.05). Pooled rates of total adverse events were greater with 5-HT4 agonists (mean difference: 6.975, [1.042, 46.684], p< 0.05). However, pooled rates of specific adverse events such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and headaches were comparable. Total 11 patients from the intervention group had serious side effects which were not related to drugs. None of the patients had QTc >500 milliseconds throughout the study period. Results are described in forest plots.
Discussion: This meta-analysis demonstrated statistically significant improvement in Gastric emptying time and GCSI score in patients receiving highly selective 5-HT4 agonists (Velusetrag, Felcisetrag, Prucalopride) for diabetic/idiopathic Gastroparesis. Overall, adverse effects profile is acceptable, but larger studies with long term follow up are required to investigate rare and/or serious adverse events. Future high quality RCTs comparing efficacy and safety of these novel agents with currently available agents are required to validate these findings.

Figure: Forest plot for studied outcomes.
Disclosures:
Parth Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Himsikhar Khataniar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Priyadarshini Loganathan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Babu Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Parth Patel, MD1, Himsikhar Khataniar, MD2, Priyadarshini Loganathan, MD3, Babu Mohan, MD, MS4. P1960 - Safety and Efficacy of Highly Selective 5-HT4 Agonist (Velusetrag, Felcisetrag, Prucalopride) for Diabetic/Idiopathic Gastroparesis - Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
