Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2224 - SARS-CoV-2 Breakthrough Infections Are Associated with Corticosteroid Use, Waning Anti-Spike IgG Titers, and Reduced T-Cell Clonal Expansion Among Vaccinated Adults with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
.jpeg.jpg)
Angela Mujukian, MD
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Los Angeles, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Viankail Cedillo Castelan, 1, Angela Mujukian, MD1, Dalin Li, PhD1, Michael V.. Chiorean, MD2, Jonathan Braun, MD, PhD1, Dermot McGovern, MD, PhD3, Gil Melmed, MD, MS4
1Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA; 2Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, WA; 3Cedars-Sinai Medical System, Los Angeles, CA; 4Center for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
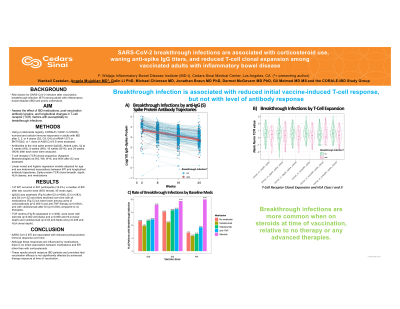
Introduction: Risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection after vaccination (“breakthrough infection” (BTI)) among adults with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are poorly understood. We aimed to assess associations between IBD medications, post-vaccination antibody kinetics, and longitudinal changes in T-cell receptor (TCR) metrics with susceptibility to breakthrough infections.
Methods: We assessed humoral and cellular immune responses in adults with IBD after 2, 3 or 4 doses (D2, D3, D4) of mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2, or 1 dose of Ad26.CoV2.S followed in a nationwide registry (1/2021 to 5/2023). We analyzed antibodies to the viral spike protein [IgG(S), Abbott Labs, IL] at 2 weeks (W2), 8 weeks (W8), 16 weeks (W16), and 24 weeks (W24) after each dose. Additionally, we assessed T-cell receptor (TCR) clonal expansion (Adaptive Biotechnologies) at W2, W8, W16, and W24 after D2. Participants received monthly email reminders to report BTI. We used linear mixed and logistic regression models adjusted for age and sex to analyze associations between BTI and longitudinal antibody trajectories, Spike protein TCR clonal breadth, depth, and HLA classes, and medications.
Results: Overall, 147 BTI occurred in 897 participants (16.4%), a median of 8W after last vaccine dose. IgG(S) was assessed after D2 (n=808), D3 (n=283), and D4 (n=132) and titers declined over time with all medications but were lower among users of corticosteroids (p< 0.0001) and anti-TNF therapy (p< 0.0001), and with vedolizumab after D3 (p=0.038) compared to no therapies. TCR metrics (assessed in n=256) were lower with steroids (p=0.002 anti-Spike and p=0.008 anti-HLA clonal depth) and vedolizumab (p=0.03 anti-Spike and p=0.038 anti-HLA clonal depth). BTI was associated with quantitative declines in TCR clonal expansion at 2W (anti-Spike clonal depth (p=0.05), class II clonal depth (p=0.04) and class II breadth (p=0.04)) but not with IgG(S) levels (figure). BTI were more common among those on steroids at time of vaccination relative to those on no therapy or any advanced therapies after dose 2(p< 0.001).
Discussion: SARS-CoV-2 BTI are associated with reduced postvaccination immune responses over time. Although these responses are influenced by medications, there is no direct association between medications and BTI other than with corticosteroids. These results should reassure IBD patients and providers that vaccination efficacy is not significantly affected by advanced therapies at the time of vaccination.

Disclosures:
Viankail Cedillo Castelan, 1, Angela Mujukian, MD1, Dalin Li, PhD1, Michael V.. Chiorean, MD2, Jonathan Braun, MD, PhD1, Dermot McGovern, MD, PhD3, Gil Melmed, MD, MS4. P2224 - SARS-CoV-2 Breakthrough Infections Are Associated with Corticosteroid Use, Waning Anti-Spike IgG Titers, and Reduced T-Cell Clonal Expansion Among Vaccinated Adults with Inflammatory Bowel Disease, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Viankail Cedillo Castelan, 1, Angela Mujukian, MD1, Dalin Li, PhD1, Michael V.. Chiorean, MD2, Jonathan Braun, MD, PhD1, Dermot McGovern, MD, PhD3, Gil Melmed, MD, MS4
1Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA; 2Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, WA; 3Cedars-Sinai Medical System, Los Angeles, CA; 4Center for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: Risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection after vaccination (“breakthrough infection” (BTI)) among adults with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are poorly understood. We aimed to assess associations between IBD medications, post-vaccination antibody kinetics, and longitudinal changes in T-cell receptor (TCR) metrics with susceptibility to breakthrough infections.
Methods: We assessed humoral and cellular immune responses in adults with IBD after 2, 3 or 4 doses (D2, D3, D4) of mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2, or 1 dose of Ad26.CoV2.S followed in a nationwide registry (1/2021 to 5/2023). We analyzed antibodies to the viral spike protein [IgG(S), Abbott Labs, IL] at 2 weeks (W2), 8 weeks (W8), 16 weeks (W16), and 24 weeks (W24) after each dose. Additionally, we assessed T-cell receptor (TCR) clonal expansion (Adaptive Biotechnologies) at W2, W8, W16, and W24 after D2. Participants received monthly email reminders to report BTI. We used linear mixed and logistic regression models adjusted for age and sex to analyze associations between BTI and longitudinal antibody trajectories, Spike protein TCR clonal breadth, depth, and HLA classes, and medications.
Results: Overall, 147 BTI occurred in 897 participants (16.4%), a median of 8W after last vaccine dose. IgG(S) was assessed after D2 (n=808), D3 (n=283), and D4 (n=132) and titers declined over time with all medications but were lower among users of corticosteroids (p< 0.0001) and anti-TNF therapy (p< 0.0001), and with vedolizumab after D3 (p=0.038) compared to no therapies. TCR metrics (assessed in n=256) were lower with steroids (p=0.002 anti-Spike and p=0.008 anti-HLA clonal depth) and vedolizumab (p=0.03 anti-Spike and p=0.038 anti-HLA clonal depth). BTI was associated with quantitative declines in TCR clonal expansion at 2W (anti-Spike clonal depth (p=0.05), class II clonal depth (p=0.04) and class II breadth (p=0.04)) but not with IgG(S) levels (figure). BTI were more common among those on steroids at time of vaccination relative to those on no therapy or any advanced therapies after dose 2(p< 0.001).
Discussion: SARS-CoV-2 BTI are associated with reduced postvaccination immune responses over time. Although these responses are influenced by medications, there is no direct association between medications and BTI other than with corticosteroids. These results should reassure IBD patients and providers that vaccination efficacy is not significantly affected by advanced therapies at the time of vaccination.

Figure: Figure
Disclosures:
Viankail Cedillo Castelan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Angela Mujukian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dalin Li indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Chiorean: AbbVie – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Fuji – Grant/Research Support. Gilead – Grant/Research Support. Janssen – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Novartis – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau.
Jonathan Braun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dermot McGovern: Boehringer-Ingelheim – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. Palatin Technologies – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Consultant, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). Prometheus Laboratories – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant.
Gil Melmed: AbbVie – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant. Arena – Consultant. BI – Consultant. BMS – Consultant. Dieta – Consultant, Owner/Ownership Interest. Eli Lilly – Employee. Ferring – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. Genetech – Consultant. Gilead – Consultant. Janseen – Consultant. Oshi – Consultant, Owner/Ownership Interest. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Prometheus Labs – Consultant. Samsung Bioepis – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Techlab – Consultant. Viatris – Consultant.
Viankail Cedillo Castelan, 1, Angela Mujukian, MD1, Dalin Li, PhD1, Michael V.. Chiorean, MD2, Jonathan Braun, MD, PhD1, Dermot McGovern, MD, PhD3, Gil Melmed, MD, MS4. P2224 - SARS-CoV-2 Breakthrough Infections Are Associated with Corticosteroid Use, Waning Anti-Spike IgG Titers, and Reduced T-Cell Clonal Expansion Among Vaccinated Adults with Inflammatory Bowel Disease, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

