Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2246 - Rash and Remedy: Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis Associated With Adalimumab Therapy in Crohn's Disease
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Scott Weismiller, DO, MS
Penn State Milton S Hershey Medical Center
Presenting Author(s)
Scott Weismiller, DO, MS1, Arsh Momin, MD1, Maylenid Oyola, MD1, Nabeel Akhtar, MD2
1Penn State Milton S Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA; 2Penn State University, Hershey, PA
Introduction: Adalimumab and other tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α inhibitors are commonly used in the treatment of moderate to severe Crohn's disease (CD). This class of medications has several associated adverse cutaneous reactions, the rarest of which is leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV). We report a case of LCV in a patient with CD on adalimumab.
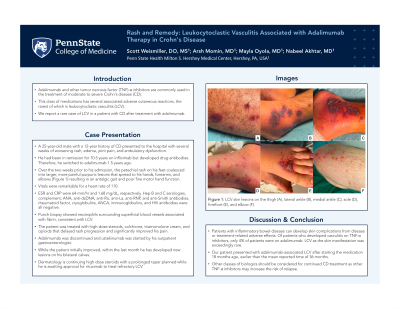
Case Description/Methods: A 25-year-old male with a 12-year history of CD presented to the hospital with several weeks of worsening rash, edema, joint pain, and ambulatory dysfunction. His CD had been in remission for around 10.5 years on infliximab, but developed drug antibodies and switched to adalimumab 1.5 years ago. Two weeks prior to admission, he was prescribed doxycycline for presumed Rocky Mountain spotted fever, which did not improve his symptoms. The petechial rash on his feet had coalesced into larger, more painful purpuric lesions and spread to his hands, forearms, and elbows, causing an antalgic gait and poor fine motor hand function (Figure 1).
Vitals showed a heart rate of 110. ESR and CRP were 64 mm/hr and 1.68 mg/dL, respectively. Expanded infectious and autoimmune workup was negative. Dermatology performed a punch biopsy, which showed neutrophils surrounding superficial blood vessels associated with fibrin, consistent with LCV. Dermatology and gastroenterology agreed this was due to adalimumab, which was discontinued. The patient was treated with high-dose steroids, colchicine, triamcinolone cream, and opioids. Gastroenterology discussed switching the patient to ustekinumab outpatient. After improving, he was discharged on a prolonged prednisone taper.
Discussion: Adalimumab and other TNF-α inhibitors are widely utilized for both induction and maintenance therapy for moderate to severe CD. Skin lesions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease on TNF-α inhibitors have been reported to occur in about 30% of patients, but LCV is exceedingly rare. Our patient presented with adalimumab-associated LCV after starting the medication 18 months ago, earlier than the mean reported time of 36 months.
Healthcare providers should be aware that LCV is a potential complication of TNF-α inhibitors. Treatment of LCV should involve discontinuing the offending agent, supportive care, and anti-inflammatory medical therapies. There should be further discussion about deciding which biologic therapy to switch to based on side effect profiles.

Disclosures:
Scott Weismiller, DO, MS1, Arsh Momin, MD1, Maylenid Oyola, MD1, Nabeel Akhtar, MD2. P2246 - Rash and Remedy: Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis Associated With Adalimumab Therapy in Crohn's Disease, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Penn State Milton S Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA; 2Penn State University, Hershey, PA
Introduction: Adalimumab and other tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α inhibitors are commonly used in the treatment of moderate to severe Crohn's disease (CD). This class of medications has several associated adverse cutaneous reactions, the rarest of which is leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV). We report a case of LCV in a patient with CD on adalimumab.
Case Description/Methods: A 25-year-old male with a 12-year history of CD presented to the hospital with several weeks of worsening rash, edema, joint pain, and ambulatory dysfunction. His CD had been in remission for around 10.5 years on infliximab, but developed drug antibodies and switched to adalimumab 1.5 years ago. Two weeks prior to admission, he was prescribed doxycycline for presumed Rocky Mountain spotted fever, which did not improve his symptoms. The petechial rash on his feet had coalesced into larger, more painful purpuric lesions and spread to his hands, forearms, and elbows, causing an antalgic gait and poor fine motor hand function (Figure 1).
Vitals showed a heart rate of 110. ESR and CRP were 64 mm/hr and 1.68 mg/dL, respectively. Expanded infectious and autoimmune workup was negative. Dermatology performed a punch biopsy, which showed neutrophils surrounding superficial blood vessels associated with fibrin, consistent with LCV. Dermatology and gastroenterology agreed this was due to adalimumab, which was discontinued. The patient was treated with high-dose steroids, colchicine, triamcinolone cream, and opioids. Gastroenterology discussed switching the patient to ustekinumab outpatient. After improving, he was discharged on a prolonged prednisone taper.
Discussion: Adalimumab and other TNF-α inhibitors are widely utilized for both induction and maintenance therapy for moderate to severe CD. Skin lesions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease on TNF-α inhibitors have been reported to occur in about 30% of patients, but LCV is exceedingly rare. Our patient presented with adalimumab-associated LCV after starting the medication 18 months ago, earlier than the mean reported time of 36 months.
Healthcare providers should be aware that LCV is a potential complication of TNF-α inhibitors. Treatment of LCV should involve discontinuing the offending agent, supportive care, and anti-inflammatory medical therapies. There should be further discussion about deciding which biologic therapy to switch to based on side effect profiles.

Figure: Figure 1: Images of skin lesions on thigh (A), lateral ankle (B), medial ankle (C), sole (D), forefoot (E), and elbow (F).
Disclosures:
Scott Weismiller indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arsh Momin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maylenid Oyola indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nabeel Akhtar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Scott Weismiller, DO, MS1, Arsh Momin, MD1, Maylenid Oyola, MD1, Nabeel Akhtar, MD2. P2246 - Rash and Remedy: Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis Associated With Adalimumab Therapy in Crohn's Disease, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
