Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P2283 - The Use of Lumen Apposing Metal Stents in Non-Peripancreatic Fluid Collections at a Tertiary Care Oncology Center Between 2017 and 2022
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- DL
Daniel J. Low, MD
MD Anderson Cancer Center
Houston, Texas
Presenting Author(s)
Daniel J. Low, MD1, Iyad S.. Al-Bustami, MD2, Brian R. Weston, MD3, Phillip Ge, MD3, Emmanuel Coronel, MD3, William A Ross, MD3, Ahmad Nakshabandi, MD4, Prateek S. Harne, MBBS, MD5, Jeffrey H. Lee, MD, MPH3
1MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 2University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, TX; 3University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 4UT MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 5University of Texas, Houston, TX
Introduction: Lumen apposing metal stents (LAMS) have been best characterized for management of peripancreatic fluid collections. However, emerging literature has demonstrated its use in gastrointestinal obstruction, cholecystitis, biliary obstruction and altered anatomy (gastric access temporary for endoscopy or GATE). The use of LAMS has been particularly beneficial for patients who are not surgical candidates, including patients with underlying malignancy.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted between 2017 and 2022 at MD Anderson Cancer Center. The inclusion criteria included oncology patients > 18 years of age and patients requiring LAMS placement for various indications. Exclusion criteria included patients requiring LAMS placement for peripancreatic fluid collection management, and patients undergoing procedure for LAMS removal. The primary outcomes of the study were technical success, clinical success, and adverse events.
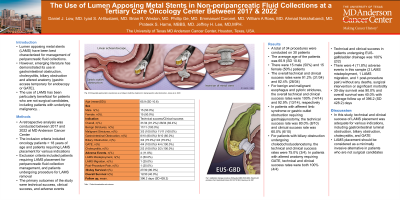
Results: A total of 34 procedures were conducted on 30 patients. The average age of the patients was 65.9 (SD 10.6). There were 15 male (50%) and 15 female (50%) patients. The overall technical and clinical success rates were 91.2% (31/34) and 82.4% (28/34). For benign and malignant esophagus and pyloric strictures, the overall technical and clinical success rates were 100% (14/14) and 92.9% (13/14), respectively. In patients with afferent limb syndrome or gastric outlet obstruction requiring gastrojejunostomy, the technical success rate was 80.0% (8/10) and clinical success rate was 60.0% (6/10). For patients with biliary obstruction undergoing choledochoduodenostomy, the technical and clinical success rates were 75.0% (3/4). In patients with altered anatomy requiring GATE, technical and clinical success rates were both 100% (4/4). Technical and clinical success in patients undergoing EUS-gallbladder drainage was 100% (2/2). There were 4 (11.8%) adverse events in this sample (2 LAMS misdeployment, 1 LAMS migration, and 1 post-procedure pain) without any deaths, surgical intervention or significant morbidity. 30-day survival was 90.0% and overall survival was 40.0% with average follow up of 396.2 (SD 428.2) days.
Discussion: In this study, technical and clinical success of LAMS placement was adequate for various indications, including gastrointestinal luminal obstruction, biliary obstruction, cholecystitis, and GATE. LAMS placement should be considered as a minimally invasive alternative in patients who are not surgical candidates.
Disclosures:
Daniel J. Low, MD1, Iyad S.. Al-Bustami, MD2, Brian R. Weston, MD3, Phillip Ge, MD3, Emmanuel Coronel, MD3, William A Ross, MD3, Ahmad Nakshabandi, MD4, Prateek S. Harne, MBBS, MD5, Jeffrey H. Lee, MD, MPH3. P2283 - The Use of Lumen Apposing Metal Stents in Non-Peripancreatic Fluid Collections at a Tertiary Care Oncology Center Between 2017 and 2022, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 2University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, TX; 3University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 4UT MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 5University of Texas, Houston, TX
Introduction: Lumen apposing metal stents (LAMS) have been best characterized for management of peripancreatic fluid collections. However, emerging literature has demonstrated its use in gastrointestinal obstruction, cholecystitis, biliary obstruction and altered anatomy (gastric access temporary for endoscopy or GATE). The use of LAMS has been particularly beneficial for patients who are not surgical candidates, including patients with underlying malignancy.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted between 2017 and 2022 at MD Anderson Cancer Center. The inclusion criteria included oncology patients > 18 years of age and patients requiring LAMS placement for various indications. Exclusion criteria included patients requiring LAMS placement for peripancreatic fluid collection management, and patients undergoing procedure for LAMS removal. The primary outcomes of the study were technical success, clinical success, and adverse events.
Results: A total of 34 procedures were conducted on 30 patients. The average age of the patients was 65.9 (SD 10.6). There were 15 male (50%) and 15 female (50%) patients. The overall technical and clinical success rates were 91.2% (31/34) and 82.4% (28/34). For benign and malignant esophagus and pyloric strictures, the overall technical and clinical success rates were 100% (14/14) and 92.9% (13/14), respectively. In patients with afferent limb syndrome or gastric outlet obstruction requiring gastrojejunostomy, the technical success rate was 80.0% (8/10) and clinical success rate was 60.0% (6/10). For patients with biliary obstruction undergoing choledochoduodenostomy, the technical and clinical success rates were 75.0% (3/4). In patients with altered anatomy requiring GATE, technical and clinical success rates were both 100% (4/4). Technical and clinical success in patients undergoing EUS-gallbladder drainage was 100% (2/2). There were 4 (11.8%) adverse events in this sample (2 LAMS misdeployment, 1 LAMS migration, and 1 post-procedure pain) without any deaths, surgical intervention or significant morbidity. 30-day survival was 90.0% and overall survival was 40.0% with average follow up of 396.2 (SD 428.2) days.
Discussion: In this study, technical and clinical success of LAMS placement was adequate for various indications, including gastrointestinal luminal obstruction, biliary obstruction, cholecystitis, and GATE. LAMS placement should be considered as a minimally invasive alternative in patients who are not surgical candidates.
Disclosures:
Daniel Low indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iyad Al-Bustami indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brian Weston indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Phillip Ge: Alira Health – Consultant. Boston Scientific – Consultant. Neptune Medical – Consultant. Ovesco America – Consultant.
Emmanuel Coronel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
William A Ross indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Nakshabandi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prateek Harne indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeffrey Lee: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Pentax – Consultant.
Daniel J. Low, MD1, Iyad S.. Al-Bustami, MD2, Brian R. Weston, MD3, Phillip Ge, MD3, Emmanuel Coronel, MD3, William A Ross, MD3, Ahmad Nakshabandi, MD4, Prateek S. Harne, MBBS, MD5, Jeffrey H. Lee, MD, MPH3. P2283 - The Use of Lumen Apposing Metal Stents in Non-Peripancreatic Fluid Collections at a Tertiary Care Oncology Center Between 2017 and 2022, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
