Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P2300 - Comparative Analysis of Reoccurrence of Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors Following En Bloc and Piecemeal Endoscopic Resection Therapy
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- BH
Brandon Havranek, BS
Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University
Philadelphia, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Danielle N. Pryor, MPH1, Grace Schiavone, BA2, Brandon Havranek, BS3, Silas J. Buckwalter, 4, Maxwell Berman, BA3, Julietta Gervase, 4, Andrew Palma, BS3, Angela Yang, BA3, Riya Shah, BS5, Chenab Khakh, BS1, Caleb Song, BS3, Blaise Y. O'Malley, MPH3, Alexander Schlachterman, MD1, Christina Tofani, MD6
1Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 2Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 3Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 4Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, PA; 5Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Toms River, NJ; 6Cooper University Health System, Cinnaminson, NJ
Introduction: There has been an increase in diagnoses of gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) in the recent past. Endoscopic techniques such as mucosal resection, submucosal dissection, full thickness resection, and cold forceps removal, can be employed to remove these tumors. This study aims to determine whether en bloc or piecemeal removal influences reoccurrence rate in gastrointestinal NETs.
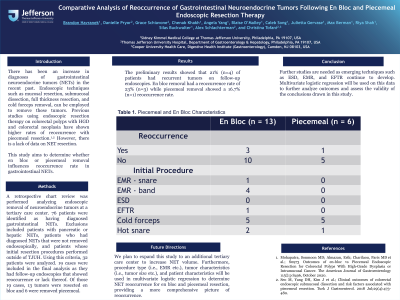
Methods: A retrospective chart review was performed analyzing endoscopic removal of neuroendocrine tumors at a tertiary care center. 76 patients were identified as having diagnosed gastrointestinal NETs. Exclusions included patients with pancreatic or hepatic NETs, patients who had diagnosed NETs that were not removed endoscopically, and patients whose initial resection procedures performed outside of TJUH. Using this criteria, 32 patients were analyzed. 19 cases were included in the final analysis as they had follow-up endoscopies that showed reoccurrence or lack thereof. Of those 19 cases, 13 tumors were resected en bloc and 6 were removed piecemeal.
Results: The preliminary results showed that 21% (n=4) of patients had recurrent tumors on follow-up endoscopies. En bloc removal had a reoccurrence rate of 23% (n=3) while piecemeal removal showed a 16.7% (n=1) reoccurrence rate.
Discussion: Further studies are needed as emerging techniques such as ESD, EMR, and EFTR continue to develop. Multivariate logistic regression will be used on this data to further analyze outcomes and assess the validity of the conclusions drawn in this study.
Disclosures:
Danielle N. Pryor, MPH1, Grace Schiavone, BA2, Brandon Havranek, BS3, Silas J. Buckwalter, 4, Maxwell Berman, BA3, Julietta Gervase, 4, Andrew Palma, BS3, Angela Yang, BA3, Riya Shah, BS5, Chenab Khakh, BS1, Caleb Song, BS3, Blaise Y. O'Malley, MPH3, Alexander Schlachterman, MD1, Christina Tofani, MD6. P2300 - Comparative Analysis of Reoccurrence of Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors Following En Bloc and Piecemeal Endoscopic Resection Therapy, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 2Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 3Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 4Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, PA; 5Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Toms River, NJ; 6Cooper University Health System, Cinnaminson, NJ
Introduction: There has been an increase in diagnoses of gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) in the recent past. Endoscopic techniques such as mucosal resection, submucosal dissection, full thickness resection, and cold forceps removal, can be employed to remove these tumors. This study aims to determine whether en bloc or piecemeal removal influences reoccurrence rate in gastrointestinal NETs.
Methods: A retrospective chart review was performed analyzing endoscopic removal of neuroendocrine tumors at a tertiary care center. 76 patients were identified as having diagnosed gastrointestinal NETs. Exclusions included patients with pancreatic or hepatic NETs, patients who had diagnosed NETs that were not removed endoscopically, and patients whose initial resection procedures performed outside of TJUH. Using this criteria, 32 patients were analyzed. 19 cases were included in the final analysis as they had follow-up endoscopies that showed reoccurrence or lack thereof. Of those 19 cases, 13 tumors were resected en bloc and 6 were removed piecemeal.
Results: The preliminary results showed that 21% (n=4) of patients had recurrent tumors on follow-up endoscopies. En bloc removal had a reoccurrence rate of 23% (n=3) while piecemeal removal showed a 16.7% (n=1) reoccurrence rate.
Discussion: Further studies are needed as emerging techniques such as ESD, EMR, and EFTR continue to develop. Multivariate logistic regression will be used on this data to further analyze outcomes and assess the validity of the conclusions drawn in this study.
Disclosures:
Danielle Pryor indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Grace Schiavone indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brandon Havranek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Silas Buckwalter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maxwell Berman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Julietta Gervase indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Palma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Angela Yang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Riya Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chenab Khakh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Caleb Song indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Blaise O'Malley indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Schlachterman: FujiFilm – Consultant. GI Supply – Consultant. Lumendi – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant.
Christina Tofani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Danielle N. Pryor, MPH1, Grace Schiavone, BA2, Brandon Havranek, BS3, Silas J. Buckwalter, 4, Maxwell Berman, BA3, Julietta Gervase, 4, Andrew Palma, BS3, Angela Yang, BA3, Riya Shah, BS5, Chenab Khakh, BS1, Caleb Song, BS3, Blaise Y. O'Malley, MPH3, Alexander Schlachterman, MD1, Christina Tofani, MD6. P2300 - Comparative Analysis of Reoccurrence of Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors Following En Bloc and Piecemeal Endoscopic Resection Therapy, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
