Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P2423 - Demographics, Outcomes, and Cardiac Complications of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Hospitalizations: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Ankoor Patel, MD
Rutgers-Robert Wood Johnson Medical School
New Brunswick, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Ankoor Patel, MD1, Mina Iskander, MD2, Joel Mintz, MD2, Juan Uribe, MD2, Moises Vasquez, MD2, Juan Quintero-Martínez, MD2, Mohammed Mustafa, MD2, Jose Luna-Alvarez-Amezquita, MD2, Alexander Chen, MD3, Carlos Minacapelli, MD1, Vinod Rustgi, MD, MBA1
1Rutgers-Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ; 2University of Miami/Jackson Memorial Hospital, Miami, FL; 3Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ
Introduction: Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC) is an autoimmune cholestatic liver disease characterized by progressive injury of the intrahepatic biliary ducts and can potentially lead to cirrhosis and liver failure. Data on hospitalizations, outcomes, costs, and cardiac complications in patients with PBC are scarce. Using the National Inpatient sample (NIS), we evaluated mortality, length of stay, costs, and prevalence/trends in cardiac complications among patients with PBC in the USA.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2015-2020. PBC patients were identified using ICD-10 codes. Mortality, LOS, and costs were primary outcomes. Cardiac complications, including CHF, acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, and atrial fibrillation were secondary outcomes.
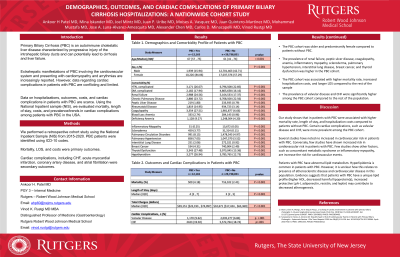
Results: Of the 12,165 hospitalizations included, the majority was female (84.06%). The prevalence of hypertension with complications, DM with complications, renal failure, chronic pulmonary disease, peptic ulcer disease, rheumatoid disease, and anemia were higher among the PBC cohort. Scleroderma, pulmonary hypertension, thyroid dysfunction, breast cancer, and inflammatory myopathy were significantly more common among the PBC cohort compared to the rest of the population (all P < 0.001). The prevalence of valvular disease and CHF were significantly higher among the PBC cohort compared to the rest of the population. The PBC cohort was associated with higher mortality rate, increased hospitalization costs, and longer LOS compared to the rest of the sample.
Discussion: Our study shows the clinical characteristics, outcomes, and prevalence of cardiac complications among patients with PBC in the USA using an inpatient healthcare database. Data on cardiac complications of PBC are scarce. The prevalence of valvular disease and CHF are significantly more common among the PBC cohort. Patients with PBC are associated with higher rate of mortality and significant healthcare utilization and cost burden.
Disclosures:
Ankoor Patel, MD1, Mina Iskander, MD2, Joel Mintz, MD2, Juan Uribe, MD2, Moises Vasquez, MD2, Juan Quintero-Martínez, MD2, Mohammed Mustafa, MD2, Jose Luna-Alvarez-Amezquita, MD2, Alexander Chen, MD3, Carlos Minacapelli, MD1, Vinod Rustgi, MD, MBA1. P2423 - Demographics, Outcomes, and Cardiac Complications of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Hospitalizations: A Nationwide Cohort Study, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Rutgers-Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ; 2University of Miami/Jackson Memorial Hospital, Miami, FL; 3Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ
Introduction: Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC) is an autoimmune cholestatic liver disease characterized by progressive injury of the intrahepatic biliary ducts and can potentially lead to cirrhosis and liver failure. Data on hospitalizations, outcomes, costs, and cardiac complications in patients with PBC are scarce. Using the National Inpatient sample (NIS), we evaluated mortality, length of stay, costs, and prevalence/trends in cardiac complications among patients with PBC in the USA.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2015-2020. PBC patients were identified using ICD-10 codes. Mortality, LOS, and costs were primary outcomes. Cardiac complications, including CHF, acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, and atrial fibrillation were secondary outcomes.
Results: Of the 12,165 hospitalizations included, the majority was female (84.06%). The prevalence of hypertension with complications, DM with complications, renal failure, chronic pulmonary disease, peptic ulcer disease, rheumatoid disease, and anemia were higher among the PBC cohort. Scleroderma, pulmonary hypertension, thyroid dysfunction, breast cancer, and inflammatory myopathy were significantly more common among the PBC cohort compared to the rest of the population (all P < 0.001). The prevalence of valvular disease and CHF were significantly higher among the PBC cohort compared to the rest of the population. The PBC cohort was associated with higher mortality rate, increased hospitalization costs, and longer LOS compared to the rest of the sample.
Discussion: Our study shows the clinical characteristics, outcomes, and prevalence of cardiac complications among patients with PBC in the USA using an inpatient healthcare database. Data on cardiac complications of PBC are scarce. The prevalence of valvular disease and CHF are significantly more common among the PBC cohort. Patients with PBC are associated with higher rate of mortality and significant healthcare utilization and cost burden.
Disclosures:
Ankoor Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mina Iskander indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joel Mintz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Juan Uribe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Moises Vasquez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Juan Quintero-Martínez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Mustafa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jose Luna-Alvarez-Amezquita indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Chen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carlos Minacapelli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vinod Rustgi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ankoor Patel, MD1, Mina Iskander, MD2, Joel Mintz, MD2, Juan Uribe, MD2, Moises Vasquez, MD2, Juan Quintero-Martínez, MD2, Mohammed Mustafa, MD2, Jose Luna-Alvarez-Amezquita, MD2, Alexander Chen, MD3, Carlos Minacapelli, MD1, Vinod Rustgi, MD, MBA1. P2423 - Demographics, Outcomes, and Cardiac Complications of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Hospitalizations: A Nationwide Cohort Study, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
