Monday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P2659 - Application of Cryotherapy on Duodenal Adenoma
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- NS
Neal Shah, DO
Mount Sinai South Nassau
Oceanside, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Neal Shah, DO1, Chandana Lanka, MD2, Andrea Rosen, MD1, Frank Gress, MD, MBA, FACG3
1Mount Sinai South Nassau, Oceanside, NY; 2ISMMS Mt. Sinai South Nassau, Oceanside, NY; 3Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai (ISMMS), Mount Sinai South Nassau (MSSN), Oceanside, NY
Introduction: Duodenal adenomas are early signs of adenocarcinoma and pose challenges for treatment. Cryotherapy has traditionally been used in the management of Barrett's esophagus, palliation of squamous cell carcinoma, gastric antral vascular ectasia, and radiation-induced proctitis. However, there is limited data on its efficacy for duodenal adenoma. We present a case using cryotherapy for treatment of duodenal adenoma refractory to Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA).
Case Description/Methods: 73 year old female with barretts esophagus, referred by general gastroenterology for upper endoscopy with removal of adenomatous duodenal polyp with biopsies suggesting adenoma. Patient underwent three upper endoscopies (EGD) each showing multiple medium-sized non-bleeding sessile polyps in the duodenal bulb with multiple EMR attempts with recurrence of disease. Decision was made to repeat endoscopy and treat area of concern with cryotherapy. Patient had no observed adverse effects post op. In Subsequent EGD’s patient was treated with RFA and cryotherapy respectively with no further adverse effects.
Discussion: Endoscopic polypectomy and EMR, while effective, is technically demanding and associated with a high rate of complications. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), Argon plasma coagulation (APC) therapy, and RFA are three therapeutic options for polyp removal. ESD involves a deep resection into the muscular propria of the luminal wall and carries a high-risk factor for delayed bleeding and/or perforation. While APC ablation only reaches the submucosal layer of lumen wall, it has been associated with recurrence of polyps. Multiple sessions of APC to manage polyp recurrence can potentially increase the risk for bleeding and perforation. Radiofrequency ablation is frequently used for management of Barrett’s esophagus and recently for ampullary polyps however, it is associated with increased risk for stricture formation. Although data is limited, recent case reports and studies suggest cryotherapy therapy ablation of nonpolypoid duodenal adenoma is feasible, with promising safety and efficacy. Further prospective and head-to-head studies comparing cryotherapy and current standard therapy are required to further assess the use of cryotherapy for treatment. Currently, a multicenter prospective non-randomized interventional clinical trial will assess the safety and efficacy of cryoballoon ablation treatment for sporadic and familial nonampullary nonpolypoid duodenal adenomas.

Disclosures:
Neal Shah, DO1, Chandana Lanka, MD2, Andrea Rosen, MD1, Frank Gress, MD, MBA, FACG3. P2659 - Application of Cryotherapy on Duodenal Adenoma, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mount Sinai South Nassau, Oceanside, NY; 2ISMMS Mt. Sinai South Nassau, Oceanside, NY; 3Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai (ISMMS), Mount Sinai South Nassau (MSSN), Oceanside, NY
Introduction: Duodenal adenomas are early signs of adenocarcinoma and pose challenges for treatment. Cryotherapy has traditionally been used in the management of Barrett's esophagus, palliation of squamous cell carcinoma, gastric antral vascular ectasia, and radiation-induced proctitis. However, there is limited data on its efficacy for duodenal adenoma. We present a case using cryotherapy for treatment of duodenal adenoma refractory to Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA).
Case Description/Methods: 73 year old female with barretts esophagus, referred by general gastroenterology for upper endoscopy with removal of adenomatous duodenal polyp with biopsies suggesting adenoma. Patient underwent three upper endoscopies (EGD) each showing multiple medium-sized non-bleeding sessile polyps in the duodenal bulb with multiple EMR attempts with recurrence of disease. Decision was made to repeat endoscopy and treat area of concern with cryotherapy. Patient had no observed adverse effects post op. In Subsequent EGD’s patient was treated with RFA and cryotherapy respectively with no further adverse effects.
Discussion: Endoscopic polypectomy and EMR, while effective, is technically demanding and associated with a high rate of complications. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), Argon plasma coagulation (APC) therapy, and RFA are three therapeutic options for polyp removal. ESD involves a deep resection into the muscular propria of the luminal wall and carries a high-risk factor for delayed bleeding and/or perforation. While APC ablation only reaches the submucosal layer of lumen wall, it has been associated with recurrence of polyps. Multiple sessions of APC to manage polyp recurrence can potentially increase the risk for bleeding and perforation. Radiofrequency ablation is frequently used for management of Barrett’s esophagus and recently for ampullary polyps however, it is associated with increased risk for stricture formation. Although data is limited, recent case reports and studies suggest cryotherapy therapy ablation of nonpolypoid duodenal adenoma is feasible, with promising safety and efficacy. Further prospective and head-to-head studies comparing cryotherapy and current standard therapy are required to further assess the use of cryotherapy for treatment. Currently, a multicenter prospective non-randomized interventional clinical trial will assess the safety and efficacy of cryoballoon ablation treatment for sporadic and familial nonampullary nonpolypoid duodenal adenomas.

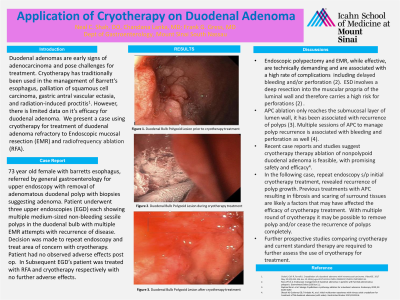
Figure: Images of duodenal polypoid lesion prior to cryotherapy, during cryotherapy, and post cryotherapy treatment
Disclosures:
Neal Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chandana Lanka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrea Rosen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Frank Gress: Salvo Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Stock Options.
Neal Shah, DO1, Chandana Lanka, MD2, Andrea Rosen, MD1, Frank Gress, MD, MBA, FACG3. P2659 - Application of Cryotherapy on Duodenal Adenoma, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
