Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach
P2720 - Genetic Determinants of Biofilm Formation of Helicobacter pylori Using Whole-Genome Sequencing
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- MM
Muhammad Miftahussurur, MD, PhD
Universitas Airlangga
Surabaya, Jawa Timur, Indonesia
Presenting Author(s)
Kartika Afrida Fauzia, MD, PhD1, Hafeza Aftab, MD, PhD2, Muhammad Miftahussurur, MD, PhD3, Langgeng Agung Waskito, MD, PhD3, Vo Phuoc Tuan, MD, PhD4, Ricky Indra Alfaray, MD1, Takashi Matsumoto, MD, PhD1, Michiyuki Yurugi, MD, PhD1, Phawinee Subsomwong, MD, PhD5, Evariste Tshibangu Kabamba, MD, PhD1, Junko Akada, MD, PhD1, Yoshio Yamaoka, MD, PhD1
1Oita University, Yufu, Oita, Japan; 2Dhaka University, Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh; 3Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Jawa Timur, Indonesia; 4Cho Ray Hospital, Ho Chi Minh, Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam; 5Hirosaki University Graduate School of Medicine, Hirosaki, Aomori, Japan
Introduction: Biofilm-forming H. pylori strains have been observed in vivo on the surface of the gastric mucosa. The biofilm is a complex exoolysaccharide structure that protects and maintains life in the presence of external stress. The biofilm also protects bacteria against antibiotics, resulting in a decline in H. pylori eradication therapy. Previous studies reported that high-biofilm formers are likely more resistant to antibiotic exposure. Understanding the mechanism of biofilm formation is essential for improving H. pylori elimination strategies.
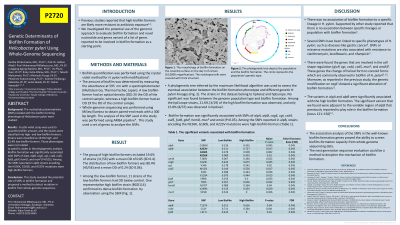
Methods: Fifty-six H. pylori isolate from Bangladeshi patients were included in this cross-sectional study. Crystal violet assay was used to quantify biofilm amount, and the strains were classified into high- and low-biofilm formers. The accessories genes associated with biofilm from whole-genome sequences were extracted and analysed, and SNPs among the previously reported biofilm-related genes were also analysed.
Results: As a result, strains were classified as 19.6% high- and 81.4% low-biofilm formers. These phenotypes were not related to specific clades in the phylogenetic analysis. Biofilm formation was significantly associated with SNPs of alpA, alpB, cagE, cgt, csd4, csd5, futB, gluP, homD, and murF (P< 0.05). Among the SNPs reported in alpB, strains encoding the N156K, G160S, and A223V mutations were high-biofilm formers.
Discussion: The whole-genome sequence data allow researchers to investigate and screen genes and mutations related to biofilm formation. The mutation in the targeted gene, such as 23SrRNA, gyrA and gyrB, was concordant with the antibiotic resistance, and the statistical analysis showed significant results. Therefore, the identification of SNP on the target genes could be informative. We observed a significant association between the SNPs, including alpA, alpB, cagE, and csd4. This could be a method to decipher the mechanism of biofilm formation.
Disclosures:
Kartika Afrida Fauzia, MD, PhD1, Hafeza Aftab, MD, PhD2, Muhammad Miftahussurur, MD, PhD3, Langgeng Agung Waskito, MD, PhD3, Vo Phuoc Tuan, MD, PhD4, Ricky Indra Alfaray, MD1, Takashi Matsumoto, MD, PhD1, Michiyuki Yurugi, MD, PhD1, Phawinee Subsomwong, MD, PhD5, Evariste Tshibangu Kabamba, MD, PhD1, Junko Akada, MD, PhD1, Yoshio Yamaoka, MD, PhD1. P2720 - Genetic Determinants of Biofilm Formation of Helicobacter pylori Using Whole-Genome Sequencing, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Oita University, Yufu, Oita, Japan; 2Dhaka University, Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh; 3Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Jawa Timur, Indonesia; 4Cho Ray Hospital, Ho Chi Minh, Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam; 5Hirosaki University Graduate School of Medicine, Hirosaki, Aomori, Japan
Introduction: Biofilm-forming H. pylori strains have been observed in vivo on the surface of the gastric mucosa. The biofilm is a complex exoolysaccharide structure that protects and maintains life in the presence of external stress. The biofilm also protects bacteria against antibiotics, resulting in a decline in H. pylori eradication therapy. Previous studies reported that high-biofilm formers are likely more resistant to antibiotic exposure. Understanding the mechanism of biofilm formation is essential for improving H. pylori elimination strategies.
Methods: Fifty-six H. pylori isolate from Bangladeshi patients were included in this cross-sectional study. Crystal violet assay was used to quantify biofilm amount, and the strains were classified into high- and low-biofilm formers. The accessories genes associated with biofilm from whole-genome sequences were extracted and analysed, and SNPs among the previously reported biofilm-related genes were also analysed.
Results: As a result, strains were classified as 19.6% high- and 81.4% low-biofilm formers. These phenotypes were not related to specific clades in the phylogenetic analysis. Biofilm formation was significantly associated with SNPs of alpA, alpB, cagE, cgt, csd4, csd5, futB, gluP, homD, and murF (P< 0.05). Among the SNPs reported in alpB, strains encoding the N156K, G160S, and A223V mutations were high-biofilm formers.
Discussion: The whole-genome sequence data allow researchers to investigate and screen genes and mutations related to biofilm formation. The mutation in the targeted gene, such as 23SrRNA, gyrA and gyrB, was concordant with the antibiotic resistance, and the statistical analysis showed significant results. Therefore, the identification of SNP on the target genes could be informative. We observed a significant association between the SNPs, including alpA, alpB, cagE, and csd4. This could be a method to decipher the mechanism of biofilm formation.
Disclosures:
Kartika Afrida Fauzia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hafeza Aftab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Miftahussurur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Langgeng Agung Waskito indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vo Phuoc Tuan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ricky Indra Alfaray indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Takashi Matsumoto indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michiyuki Yurugi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Phawinee Subsomwong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Evariste Tshibangu Kabamba indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Junko Akada indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yoshio Yamaoka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kartika Afrida Fauzia, MD, PhD1, Hafeza Aftab, MD, PhD2, Muhammad Miftahussurur, MD, PhD3, Langgeng Agung Waskito, MD, PhD3, Vo Phuoc Tuan, MD, PhD4, Ricky Indra Alfaray, MD1, Takashi Matsumoto, MD, PhD1, Michiyuki Yurugi, MD, PhD1, Phawinee Subsomwong, MD, PhD5, Evariste Tshibangu Kabamba, MD, PhD1, Junko Akada, MD, PhD1, Yoshio Yamaoka, MD, PhD1. P2720 - Genetic Determinants of Biofilm Formation of Helicobacter pylori Using Whole-Genome Sequencing, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
