Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach
P2799 - Mixed Gastric Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma/Neuroendocrine Tumor in Crohn’s Patient With Newly Diagnosed Hepatic Neuroendocrine Tumor
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- MB
Mohammad I. Bhatti
Weill Cornell Medicine-Qatar
Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar
Presenting Author(s)
Mohammad I. Bhatti, 1, Malik Mushannen, MD2, Safah Khan, 1, Hamza Chaudhry, MD3, Lasha Gogokhia, MD4, Dana Lukin, MD, PhD, FACG5, David Wan, BS, MD6
1Weill Cornell Medicine-Qatar, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 2NYP-Brooklyn Methodist Hospital, Brooklyn, NY; 3Weill Cornell Medical College, Friendswood, TX; 4New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY; 5Jill Roberts Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, New York, NY; 6Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY
Introduction: Mixed neuroendocrine non-neuroendocrine neoplasm (MiNENs) are a rare type of tumor with both neuroendocrine and non-neuroendocrine features in a given lesion. The features of this neoplasm are not well defined and is even less is known in IBD patients. Here, we present the case of a patient with Crohn’s disease with gastric MiNEN.
Case Description/Methods: A 41-year-old-man with Crohn’s disease complicated by protein-losing enteropathy and ileocolic fistula was diagnosed with high grade hepatic neuroendocrine tumor on liver biopsy. MRE at the time also showed gastric antrum thickening. A month later, he was admitted for management of a provoked lower extremity DVT and bilateral PE. During hospitalization, the patient developed melena with acute anemia that required PRBC transfusions. EGD showed a large clean-based gastric ulcer found on the greater curvature of the stomach. Repeat MRE showed concentric irregular mural thickening of the gastric antrum with adjacent enlarged perigastric lymph nodes and/or extramural extension of tumor. Pathology from EGD biopsies revealed an ulcerated mixed adeno-neuroendocrine carcinoma, establishing the diagnosis of primary gastric tumor with metastasis to the liver. Surgical removal of the gastric MiNEN was deferred in favor for chemotherapy, given metastatic disease. He was treated with 6 cycles of cisplatin/etoposide over a 5-month period followed by palliative radiotherapy to improve obstruction. However, follow up studies demonstrated no significant change in tumor burden and worsening liver metastasis.
Discussion: Neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) are very rare in themselves accounting for 1% of malignant GI tumors. MiNENs (previously called Mixed adeno-neuroendocrine carcinoma), have by definition at least 30% of mass contributed by each of the neuroendocrine and the non-neuroendocrine components. They constitute around 7% of all gastric NENs, though they can occur throughout the digestive tract. As such, diagnosis requires histological analysis from suspected lesions, in addition to imaging studies. History of IBD also increases the risk for gastric neoplasms. Treatments for this tumor range from surgical interventions with adjuvant or neoadjuvant therapy with curative intent, or palliative options for advanced disease; however, there is no well-defined guideline for disease management. Our patient had no significant response to combined chemo and radiation therapy and currently he is planned for second-line chemotherapy with a focus on symptom palliation.

Disclosures:
Mohammad I. Bhatti, 1, Malik Mushannen, MD2, Safah Khan, 1, Hamza Chaudhry, MD3, Lasha Gogokhia, MD4, Dana Lukin, MD, PhD, FACG5, David Wan, BS, MD6. P2799 - Mixed Gastric Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma/Neuroendocrine Tumor in Crohn’s Patient With Newly Diagnosed Hepatic Neuroendocrine Tumor, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Weill Cornell Medicine-Qatar, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 2NYP-Brooklyn Methodist Hospital, Brooklyn, NY; 3Weill Cornell Medical College, Friendswood, TX; 4New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY; 5Jill Roberts Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, New York, NY; 6Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY
Introduction: Mixed neuroendocrine non-neuroendocrine neoplasm (MiNENs) are a rare type of tumor with both neuroendocrine and non-neuroendocrine features in a given lesion. The features of this neoplasm are not well defined and is even less is known in IBD patients. Here, we present the case of a patient with Crohn’s disease with gastric MiNEN.
Case Description/Methods: A 41-year-old-man with Crohn’s disease complicated by protein-losing enteropathy and ileocolic fistula was diagnosed with high grade hepatic neuroendocrine tumor on liver biopsy. MRE at the time also showed gastric antrum thickening. A month later, he was admitted for management of a provoked lower extremity DVT and bilateral PE. During hospitalization, the patient developed melena with acute anemia that required PRBC transfusions. EGD showed a large clean-based gastric ulcer found on the greater curvature of the stomach. Repeat MRE showed concentric irregular mural thickening of the gastric antrum with adjacent enlarged perigastric lymph nodes and/or extramural extension of tumor. Pathology from EGD biopsies revealed an ulcerated mixed adeno-neuroendocrine carcinoma, establishing the diagnosis of primary gastric tumor with metastasis to the liver. Surgical removal of the gastric MiNEN was deferred in favor for chemotherapy, given metastatic disease. He was treated with 6 cycles of cisplatin/etoposide over a 5-month period followed by palliative radiotherapy to improve obstruction. However, follow up studies demonstrated no significant change in tumor burden and worsening liver metastasis.
Discussion: Neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) are very rare in themselves accounting for 1% of malignant GI tumors. MiNENs (previously called Mixed adeno-neuroendocrine carcinoma), have by definition at least 30% of mass contributed by each of the neuroendocrine and the non-neuroendocrine components. They constitute around 7% of all gastric NENs, though they can occur throughout the digestive tract. As such, diagnosis requires histological analysis from suspected lesions, in addition to imaging studies. History of IBD also increases the risk for gastric neoplasms. Treatments for this tumor range from surgical interventions with adjuvant or neoadjuvant therapy with curative intent, or palliative options for advanced disease; however, there is no well-defined guideline for disease management. Our patient had no significant response to combined chemo and radiation therapy and currently he is planned for second-line chemotherapy with a focus on symptom palliation.

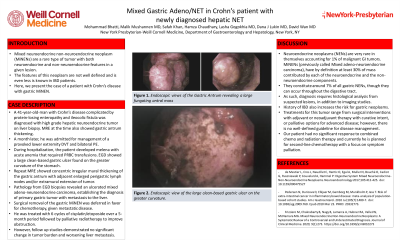
Figure: Figure 1. Endoscopic views of the Gastric Antrum revealing a large fungating antral mass
Figure 2. Endoscopic view of the large clean-based gastric ulcer on the greater curvature
Figure 2. Endoscopic view of the large clean-based gastric ulcer on the greater curvature
Disclosures:
Mohammad Bhatti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Malik Mushannen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Safah Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Chaudhry indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lasha Gogokhia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dana Lukin: Abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Magellan Health – Consultant. Palatin – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant. Prometheus – Consultant. PSI – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support.
David Wan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad I. Bhatti, 1, Malik Mushannen, MD2, Safah Khan, 1, Hamza Chaudhry, MD3, Lasha Gogokhia, MD4, Dana Lukin, MD, PhD, FACG5, David Wan, BS, MD6. P2799 - Mixed Gastric Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma/Neuroendocrine Tumor in Crohn’s Patient With Newly Diagnosed Hepatic Neuroendocrine Tumor, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
