Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach
P2761 - Effect of Chronic Gastric Electrical Stimulation on Regeneration of Gastric Interstitial Cells of Cajal in Gastroparesis Patients
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Irene Sarosiek, MD
Texas Tech
El Paso, Texas
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Outstanding Research Award in the Stomach Category
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Irene Sarosiek, MD1, Mohammad Bashashati, MD2, Ryan Torelli, BS3, Osvaldo Padilla, MD4, Brian Davis, MD5, Richard McCallum, MD4
1Texas Tech, El Paso, TX; 2University of Texas Austin, Austin, TX; 3PLF School of Medicine, El Paso, TX; 4TTUHSC, El Paso, TX; 5Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX
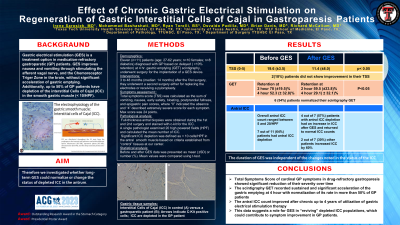
Introduction: Gastric electrical stimulation (GES) is a treatment option in medication-refractory gastroparetic (GP) patients. GES improves nausea and vomiting through stimulating the afferent vagal nerve, and the Chemoreceptor Triger Zone in the brain, without significant acceleration of gastric emptying. Additionally, up to 50% of GP patients have depletion of the interstitial Cells of Cajal (ICC) in the smooth gastric muscle (< 10/HPF). Therefore we investigated whether long-term GES could normalize or change depleted ICC in the antrum.
Methods: Eleven patients (age: 27-62 years; n=10 females; n=8 diabetics) diagnosed with GP based on delayed ( >10% retention) at 4 hr. gastric emptying (GE) scintigraphy, underwent surgery for the implantation of a GES device. Three to 48 months (median: 14 months) after the first surgery, they underwent a second surgery either for replacing the electrodes or receiving a pyloroplasty. Total symptoms score (TSS) was calculated as the sum of vomiting, nausea, early satiety, bloating, postprandial fullness, and epigastric pain scores, where 0 indicated the absence and 4 described extremely severe score for each symptom. Full-thickness antral biopsies were obtained during the 1st and 2nd surgery and stained with c-kit for the ICC. Before and after GES data was presented as mean (±SD) or number (%). Mean values were compared using t-test.
Results: After GES, TSS significantly improved from 19.6±3.5 to 11.4±8.0 (p< 0.05); only 2 patients did not show improvement in their TSS. Before GES, antral ICC count ranged between 5 and 20/HPF; 7 (63.6%) patients had antral ICC depletion at baseline, with a mean of 6.4±1.5 (range 5-8) ICC/HPF. After GES this mean value increased to 8.3±4.1 (range 6-16). Four out of 7 (57%) patients with antral ICC depletion had an increase in ICC after GES, returning to normal in two, while ICC numbers increased by 60% in the 2 other patients. The duration of GES was independent of the changes status of ICC.
Discussion: 1.The mean antral ICC count improved after chronic GES
2. TSS score of GP symptoms in drug-refractory gastroparesis showed significant reduction
3. This data suggests a role for GES in “reviving” depleted ICC populations, which could contribute to symptom improvement in GP patients.
Disclosures:
Irene Sarosiek, MD1, Mohammad Bashashati, MD2, Ryan Torelli, BS3, Osvaldo Padilla, MD4, Brian Davis, MD5, Richard McCallum, MD4. P2761 - Effect of Chronic Gastric Electrical Stimulation on Regeneration of Gastric Interstitial Cells of Cajal in Gastroparesis Patients, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Irene Sarosiek, MD1, Mohammad Bashashati, MD2, Ryan Torelli, BS3, Osvaldo Padilla, MD4, Brian Davis, MD5, Richard McCallum, MD4
1Texas Tech, El Paso, TX; 2University of Texas Austin, Austin, TX; 3PLF School of Medicine, El Paso, TX; 4TTUHSC, El Paso, TX; 5Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX
Introduction: Gastric electrical stimulation (GES) is a treatment option in medication-refractory gastroparetic (GP) patients. GES improves nausea and vomiting through stimulating the afferent vagal nerve, and the Chemoreceptor Triger Zone in the brain, without significant acceleration of gastric emptying. Additionally, up to 50% of GP patients have depletion of the interstitial Cells of Cajal (ICC) in the smooth gastric muscle (< 10/HPF). Therefore we investigated whether long-term GES could normalize or change depleted ICC in the antrum.
Methods: Eleven patients (age: 27-62 years; n=10 females; n=8 diabetics) diagnosed with GP based on delayed ( >10% retention) at 4 hr. gastric emptying (GE) scintigraphy, underwent surgery for the implantation of a GES device. Three to 48 months (median: 14 months) after the first surgery, they underwent a second surgery either for replacing the electrodes or receiving a pyloroplasty. Total symptoms score (TSS) was calculated as the sum of vomiting, nausea, early satiety, bloating, postprandial fullness, and epigastric pain scores, where 0 indicated the absence and 4 described extremely severe score for each symptom. Full-thickness antral biopsies were obtained during the 1st and 2nd surgery and stained with c-kit for the ICC. Before and after GES data was presented as mean (±SD) or number (%). Mean values were compared using t-test.
Results: After GES, TSS significantly improved from 19.6±3.5 to 11.4±8.0 (p< 0.05); only 2 patients did not show improvement in their TSS. Before GES, antral ICC count ranged between 5 and 20/HPF; 7 (63.6%) patients had antral ICC depletion at baseline, with a mean of 6.4±1.5 (range 5-8) ICC/HPF. After GES this mean value increased to 8.3±4.1 (range 6-16). Four out of 7 (57%) patients with antral ICC depletion had an increase in ICC after GES, returning to normal in two, while ICC numbers increased by 60% in the 2 other patients. The duration of GES was independent of the changes status of ICC.
Discussion: 1.The mean antral ICC count improved after chronic GES
2. TSS score of GP symptoms in drug-refractory gastroparesis showed significant reduction
3. This data suggests a role for GES in “reviving” depleted ICC populations, which could contribute to symptom improvement in GP patients.
Disclosures:
Irene Sarosiek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Bashashati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ryan Torelli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Osvaldo Padilla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brian Davis indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Richard McCallum: Evoke Pharma – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Irene Sarosiek, MD1, Mohammad Bashashati, MD2, Ryan Torelli, BS3, Osvaldo Padilla, MD4, Brian Davis, MD5, Richard McCallum, MD4. P2761 - Effect of Chronic Gastric Electrical Stimulation on Regeneration of Gastric Interstitial Cells of Cajal in Gastroparesis Patients, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

