Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2113 - Efficacy and Safety of Adalimumab in Inducing Clinical Remission in Crohn's Disease: A Meta-Analysis With Subgroup Analysis
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- FA
Feyzullah Aksan, MD
Stony Brook University Hospital
Stony Brook, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Feyzullah Aksan, MD1, Lokman Hekim Tanriverdi, PhD, MD2, Farah Monzur, MD, FACG1
1Stony Brook University Hospital, Stony Brook, NY; 2Inonu University School of Medicine, Malatya, Malatya, Turkey
Introduction: Crohn's disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease characterized by recurrent inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Adalimumab, a tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitor, has shown promise as a treatment option for CD. However, there is a need to consolidate the existing evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to thoroughly assess the efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with CD.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search of Ovid MEDLINE, Web of Science, PubMed, and The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials up until February 20, 2022, to identify relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The systematic review adhered to the guidelines outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Statement. The primary outcome assessed was the induction of clinical remission in patients with moderate to severe CD at week 4. Meta-analyses were performed using random effects models based on inverse variance. Subgroup analyses were conducted to examine the efficacy of adalimumab in patients with prior anti-TNF-α exposure compared to those who were anti-TNF-α naive. The overall risk of bias (RoB) was evaluated using the Cochrane RoB2 too
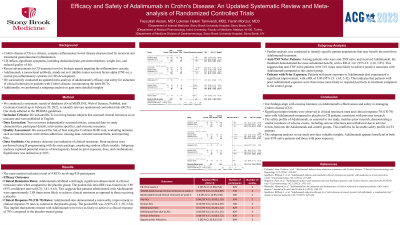
Results: Our meta-analysis of 4 RCTs (n=929) showed adalimumab significantly improved clinical remission (pooled RR=2.89, 95% CI: 1.81-4.61) and CR-70 rates (pooled RR=2, 95% CI: 1.58-2.54) vs. placebo.
Safety outcomes (serious adverse events: pooled RR 0.74 [95% CI, 0.32-1.69]; serious infections: RR 0.48 [95% CI, 0.06-3.72]; withdrawal rate due to adverse events: RR 0.45 [95% CI, 0.17-1.25]; any adverse events: RR 0.96 [95% CI, 0.83-1.10]) were similar between adalimumab and placebo.
In a subgroup analysis, adalimumab showed comparable effectiveness in patients receiving 160/80 mg with anti-TNF-α naïve background (RR 3.61 [95% CI, 2.24-5.85]) and those with prior anti-TNF-α exposure (RR 3.00 [95% CI, 1.65-5.42])
Discussion: This systematic review and meta-analysis provide strong evidence supporting the effectiveness of adalimumab in achieving remission induction and clinical response in patients with moderate to severe Crohn's disease. Adalimumab demonstrates a favorable safety profile during the induction phase. Subgroup analysis reveals comparable efficacy in both anti-TNF-α naive and anti-TNF-α exposed groups. Further research is required to determine the statistical significance of the difference between these subgroups.

Disclosures:
Feyzullah Aksan, MD1, Lokman Hekim Tanriverdi, PhD, MD2, Farah Monzur, MD, FACG1. P2113 - Efficacy and Safety of Adalimumab in Inducing Clinical Remission in Crohn's Disease: A Meta-Analysis With Subgroup Analysis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Stony Brook University Hospital, Stony Brook, NY; 2Inonu University School of Medicine, Malatya, Malatya, Turkey
Introduction: Crohn's disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease characterized by recurrent inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Adalimumab, a tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitor, has shown promise as a treatment option for CD. However, there is a need to consolidate the existing evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to thoroughly assess the efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with CD.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search of Ovid MEDLINE, Web of Science, PubMed, and The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials up until February 20, 2022, to identify relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The systematic review adhered to the guidelines outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Statement. The primary outcome assessed was the induction of clinical remission in patients with moderate to severe CD at week 4. Meta-analyses were performed using random effects models based on inverse variance. Subgroup analyses were conducted to examine the efficacy of adalimumab in patients with prior anti-TNF-α exposure compared to those who were anti-TNF-α naive. The overall risk of bias (RoB) was evaluated using the Cochrane RoB2 too
Results: Our meta-analysis of 4 RCTs (n=929) showed adalimumab significantly improved clinical remission (pooled RR=2.89, 95% CI: 1.81-4.61) and CR-70 rates (pooled RR=2, 95% CI: 1.58-2.54) vs. placebo.
Safety outcomes (serious adverse events: pooled RR 0.74 [95% CI, 0.32-1.69]; serious infections: RR 0.48 [95% CI, 0.06-3.72]; withdrawal rate due to adverse events: RR 0.45 [95% CI, 0.17-1.25]; any adverse events: RR 0.96 [95% CI, 0.83-1.10]) were similar between adalimumab and placebo.
In a subgroup analysis, adalimumab showed comparable effectiveness in patients receiving 160/80 mg with anti-TNF-α naïve background (RR 3.61 [95% CI, 2.24-5.85]) and those with prior anti-TNF-α exposure (RR 3.00 [95% CI, 1.65-5.42])
Discussion: This systematic review and meta-analysis provide strong evidence supporting the effectiveness of adalimumab in achieving remission induction and clinical response in patients with moderate to severe Crohn's disease. Adalimumab demonstrates a favorable safety profile during the induction phase. Subgroup analysis reveals comparable efficacy in both anti-TNF-α naive and anti-TNF-α exposed groups. Further research is required to determine the statistical significance of the difference between these subgroups.

Figure: Figure 1, Forest Plot depicting the Efficacy of Adalimumab in Inducing Remission in Crohn's Disease and Subgroup Analysis based on Prior Anti-TNF Exposure
Disclosures:
Feyzullah Aksan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lokman Hekim Tanriverdi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Farah Monzur: Medtronic (Covidien) – Consultant.
Feyzullah Aksan, MD1, Lokman Hekim Tanriverdi, PhD, MD2, Farah Monzur, MD, FACG1. P2113 - Efficacy and Safety of Adalimumab in Inducing Clinical Remission in Crohn's Disease: A Meta-Analysis With Subgroup Analysis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
