Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P1910 - Adapting an Endoscopic HeliX Tacking System to Serve as Fiducial Markers in Esophageal Malignancy
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- EH
Erik Holzwanger, MD, ABOM-D
Center for Advanced Endoscopy, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Erik Holzwanger, MD, ABOM-D1, Sultan Mahmood, MD2, Samuel Igbinedion, MD1, Douglas Pleskow, MD, FACG3, Mandeep Sawhney, MD, MS2, Moamen Gabr, MD, MSc,2, Claire Fung, MD, MS4, Tyler Berzin, MD, FACG2
1Center for Advanced Endoscopy, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 2Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA; 3BIDMC, Boston, MA; 4BIDMC, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Introduction: Fiducial placement for esophageal malignancy can assist with radiotherapy mapping. It may be difficult for certain ulcerated lesions. The Endoscopic HeliX Tacking System (Apollo Endosurgery, Inc.) is a TTS suture-based device that has been gaining popularity in defect closure. There has been off-label use as well with stent fixation, such as with esophageal and duodenal stents. We present a case of a severely ulcerated squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the esophagus in which the X-tack device was modified to serve as fiducial markers.
Case Description/Methods: A 69-year-old-woman with history of breast cancer presented with dysphagia and was found to have a severely ulcerated esophagus with a dominant stricture in the mid esophagus with biopsies revealing esophageal SCC. She was referred for fiducial placement. The esophageal lesion was evaluated with EUS and measured nearly 10cm in length with a .38cm depth. It involved the muscularis propria, however no clear invasion past this level, and thus T2 staging was suspected.
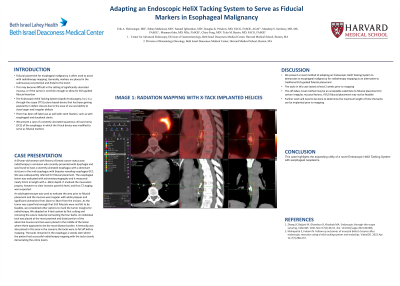
An adult gastroscope was used to evaluate the area prior to fiducial placement and the mucosa was irregular with white plaques and significant ulcerations from 24cm to 34cm from the incisors. As the tumor was superficial enough that EUS fiducials were not felt to be feasible, we considered other options to mark the tumor margins for radiotherapy. We adapted an X-tack system by first cutting and removing the suture material connecting the four barbs. An individual tack was placed at the most proximal and distal portion of the abnormal mucosa and two were placed in the middle of the lesion where there appeared to be the most disease burden. A hemoclip was also placed in this area in the scenario the tacks were to fall off before mapping. The tacks remained in the esophagus 2 weeks later where the patient had successful radiotherapy mapping with the tacks clearly demarcating the entire lesion.
Discussion: We present a novel method of adapting an Endoscopic HeliX Tacking System to demarcate an esophageal malignancy for radiotherapy mapping as an alternative to traditional EUS-guided fiducial placement. The tacks in this case lasted at least 2 weeks prior to mapping. This off-label, novel method may be an acceptable substitute to fiducial placement for certain irregular, mucosal lesions, if EUS fiducial placement may not be feasible. Further work will need to be done to determine the maximum length of time the barbs can be implanted prior to mapping.

Disclosures:
Erik Holzwanger, MD, ABOM-D1, Sultan Mahmood, MD2, Samuel Igbinedion, MD1, Douglas Pleskow, MD, FACG3, Mandeep Sawhney, MD, MS2, Moamen Gabr, MD, MSc,2, Claire Fung, MD, MS4, Tyler Berzin, MD, FACG2. P1910 - Adapting an Endoscopic HeliX Tacking System to Serve as Fiducial Markers in Esophageal Malignancy, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Erik Holzwanger, MD, ABOM-D1, Sultan Mahmood, MD2, Samuel Igbinedion, MD1, Douglas Pleskow, MD, FACG3, Mandeep Sawhney, MD, MS2, Moamen Gabr, MD, MSc,2, Claire Fung, MD, MS4, Tyler Berzin, MD, FACG2
1Center for Advanced Endoscopy, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 2Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA; 3BIDMC, Boston, MA; 4BIDMC, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Introduction: Fiducial placement for esophageal malignancy can assist with radiotherapy mapping. It may be difficult for certain ulcerated lesions. The Endoscopic HeliX Tacking System (Apollo Endosurgery, Inc.) is a TTS suture-based device that has been gaining popularity in defect closure. There has been off-label use as well with stent fixation, such as with esophageal and duodenal stents. We present a case of a severely ulcerated squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the esophagus in which the X-tack device was modified to serve as fiducial markers.
Case Description/Methods: A 69-year-old-woman with history of breast cancer presented with dysphagia and was found to have a severely ulcerated esophagus with a dominant stricture in the mid esophagus with biopsies revealing esophageal SCC. She was referred for fiducial placement. The esophageal lesion was evaluated with EUS and measured nearly 10cm in length with a .38cm depth. It involved the muscularis propria, however no clear invasion past this level, and thus T2 staging was suspected.
An adult gastroscope was used to evaluate the area prior to fiducial placement and the mucosa was irregular with white plaques and significant ulcerations from 24cm to 34cm from the incisors. As the tumor was superficial enough that EUS fiducials were not felt to be feasible, we considered other options to mark the tumor margins for radiotherapy. We adapted an X-tack system by first cutting and removing the suture material connecting the four barbs. An individual tack was placed at the most proximal and distal portion of the abnormal mucosa and two were placed in the middle of the lesion where there appeared to be the most disease burden. A hemoclip was also placed in this area in the scenario the tacks were to fall off before mapping. The tacks remained in the esophagus 2 weeks later where the patient had successful radiotherapy mapping with the tacks clearly demarcating the entire lesion.
Discussion: We present a novel method of adapting an Endoscopic HeliX Tacking System to demarcate an esophageal malignancy for radiotherapy mapping as an alternative to traditional EUS-guided fiducial placement. The tacks in this case lasted at least 2 weeks prior to mapping. This off-label, novel method may be an acceptable substitute to fiducial placement for certain irregular, mucosal lesions, if EUS fiducial placement may not be feasible. Further work will need to be done to determine the maximum length of time the barbs can be implanted prior to mapping.

Figure: Radiation mapping with X-tack implanted helices
Disclosures:
Erik Holzwanger indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sultan Mahmood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samuel Igbinedion indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Douglas Pleskow: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Fuji – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant.
Mandeep Sawhney: Allurion – Stock Options. Immunovia Inc. – Consultant. Marlborough, MA – Consultant.
Moamen Gabr: Adaptive Endo – Consultant. Boston Scientific – Consultant. ConMed – Consultant. Fuji – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant.
Claire Fung indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tyler Berzin: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Fuji – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant.
Erik Holzwanger, MD, ABOM-D1, Sultan Mahmood, MD2, Samuel Igbinedion, MD1, Douglas Pleskow, MD, FACG3, Mandeep Sawhney, MD, MS2, Moamen Gabr, MD, MSc,2, Claire Fung, MD, MS4, Tyler Berzin, MD, FACG2. P1910 - Adapting an Endoscopic HeliX Tacking System to Serve as Fiducial Markers in Esophageal Malignancy, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

