Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1508 - Marantic Endocarditis in Case of Newly Diagnosed Advanced Pancreatic Neoplasm
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Abhishek A. Chouthai, MD
Cooper University Hospital at Cooper Medical School at Rowan University
Camden, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Abhishek A. Chouthai, MD1, Rabih Ghazi, MD2, Zachary Walder, DO1, Ayush Tarafder, BS3, Tyler McMillan, MD1
1Cooper University Hospital at Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ; 2Cooper University Hospital at Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Philadelphia, PA; 3Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ
Introduction: Marantic endocarditis, also known as non-bacterial or non-infectious endocarditis (NBTE) is an exceedingly rare form of endocarditis which is associated with hypercoagulable conditions such as malignancy and autoimmune diseases. This form of sterile endocarditis is rare and has been mainly associated with lung adenocarcinoma, with few reports describing its association with pancreatic cancer. We report a case of newly diagnosed advanced pancreatic cancer who was found to have NBTE after having multiple acute strokes.
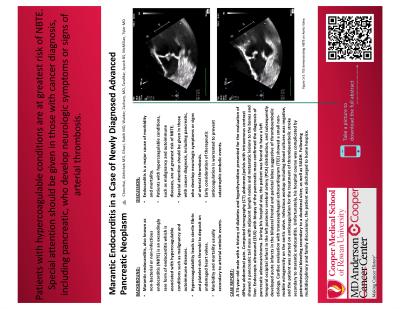
Case Description/Methods: A 74 year old male with a history of diabetes and hypothyroidism presented for the evaluation of diffuse abdominal pain. Computed tomography (CT) abdomen/pelvis with intravenous contrast showed a pancreatic tail mass with adjacent lymph nodes and metastatic lesions to the bones and liver. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) with biopsy of the pancreatic mass confirmed the diagnosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. During his hospital stay, the patient was found to have a left temporal occipital infarct in the left posterior cerebral artery (PCA) distribution, and subsequently developed acute infarcts in the bilateral frontal and parietal lobes suggestive of thromboembolic etiology. Cardiac evaluation with transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) showed a small non-mobile echogenicity on the aortic valve (Figure 1). Infectious workup including blood cultures was negative, and the patient was started on anticoagulation for the treatment of thromboembolic stroke secondary to marantic endocarditis. Unfortunately, his hospital course was complicated by gastrointestinal bleeding secondary to a duodenal ulcer, as well as SIADH. Following multidisciplinary and family discussions, the patient was discharged to home hospice.
Discussion: Endocarditis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. While the majority of cases are infectious, some are found to be non-bacterial. Patients with hypercoagulable conditions, such as malignancy and autoimmune diseases, are at greatest risk of NBTE. Special attention should be given in those with a cancer diagnosis, including pancreatic, who develop neurologic symptoms or signs of arterial thrombosis. In practice, these patients require an infectious workup to rule out bacterial etiology. However, early consideration of therapeutic anticoagulation is warranted to prevent catastrophic embolic events and improve quality of life and survival.

Disclosures:
Abhishek A. Chouthai, MD1, Rabih Ghazi, MD2, Zachary Walder, DO1, Ayush Tarafder, BS3, Tyler McMillan, MD1. P1508 - Marantic Endocarditis in Case of Newly Diagnosed Advanced Pancreatic Neoplasm, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cooper University Hospital at Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ; 2Cooper University Hospital at Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Philadelphia, PA; 3Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ
Introduction: Marantic endocarditis, also known as non-bacterial or non-infectious endocarditis (NBTE) is an exceedingly rare form of endocarditis which is associated with hypercoagulable conditions such as malignancy and autoimmune diseases. This form of sterile endocarditis is rare and has been mainly associated with lung adenocarcinoma, with few reports describing its association with pancreatic cancer. We report a case of newly diagnosed advanced pancreatic cancer who was found to have NBTE after having multiple acute strokes.
Case Description/Methods: A 74 year old male with a history of diabetes and hypothyroidism presented for the evaluation of diffuse abdominal pain. Computed tomography (CT) abdomen/pelvis with intravenous contrast showed a pancreatic tail mass with adjacent lymph nodes and metastatic lesions to the bones and liver. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) with biopsy of the pancreatic mass confirmed the diagnosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. During his hospital stay, the patient was found to have a left temporal occipital infarct in the left posterior cerebral artery (PCA) distribution, and subsequently developed acute infarcts in the bilateral frontal and parietal lobes suggestive of thromboembolic etiology. Cardiac evaluation with transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) showed a small non-mobile echogenicity on the aortic valve (Figure 1). Infectious workup including blood cultures was negative, and the patient was started on anticoagulation for the treatment of thromboembolic stroke secondary to marantic endocarditis. Unfortunately, his hospital course was complicated by gastrointestinal bleeding secondary to a duodenal ulcer, as well as SIADH. Following multidisciplinary and family discussions, the patient was discharged to home hospice.
Discussion: Endocarditis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. While the majority of cases are infectious, some are found to be non-bacterial. Patients with hypercoagulable conditions, such as malignancy and autoimmune diseases, are at greatest risk of NBTE. Special attention should be given in those with a cancer diagnosis, including pancreatic, who develop neurologic symptoms or signs of arterial thrombosis. In practice, these patients require an infectious workup to rule out bacterial etiology. However, early consideration of therapeutic anticoagulation is warranted to prevent catastrophic embolic events and improve quality of life and survival.

Figure: Figure 1: Non-mobile vegetation on the non-coronary cusp of the aortic valve found on TEE.
Disclosures:
Abhishek Chouthai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rabih Ghazi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zachary Walder indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayush Tarafder indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tyler McMillan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhishek A. Chouthai, MD1, Rabih Ghazi, MD2, Zachary Walder, DO1, Ayush Tarafder, BS3, Tyler McMillan, MD1. P1508 - Marantic Endocarditis in Case of Newly Diagnosed Advanced Pancreatic Neoplasm, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
