Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P3711 - Efficacy and Safety of Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Refractory Gastroparesis
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
.jpg)
Muhammad Nadeem Nadeem Yousaf, MD
University of Missouri-Columbia
Columbia, MO
Presenting Author(s)
Muhammad Nadeem. Yousaf, MD1, Darian Fard, MD1, Xheni Deda, MD1, Karthik Gangu, MD2, Moafa Ghady, MD1, Sanket Basida, MD1, Alexander K. Malik, MD3, Mustafa Gandhi, MD1, Ahmed I.A. Swi, MD1, Niraj Shah, MD1, Ghassan M. Hammoud, MD1
1University of Missouri-Columbia, Columbia, MO; 2Kansas University Medical Center, Kansas City, KS; 3Summa Health System, Akron, OH
Introduction: Gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) is an emerging third space endoscopic technique for the management of refractory gastroparesis. We sought to determine the efficacy and safety of G-POEM for patients with refractory gastroparesis.
Methods: This is a retrospective, single-center study of consecutive patients with refractory gastroparesis who underwent G-POEM between February 2020 to September 2022. Primary outcome was clinical success defined as improvement in gastroparesis cardinal symptoms index (GCSI) score by 25% and improvement in percent of gastric emptying at 4 hours. Secondary outcomes included technical success rate (defined as successful completion of all procedural steps), rate of adverse events (AE), frequency of hospitalization due to recurrent symptoms after G-POEM and need for additional endoscopic or surgical interventions. Refractory gastroparesis was defined as persistent symptoms despite dietary modifications and pharmacologic therapy.
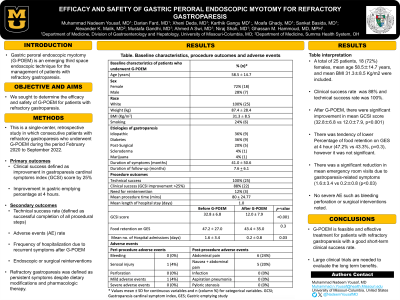
Results: A total of 25 patients, 18 (72%) females, mean age 58.5±14.7 year, and mean BMI 31.3±8.5 Kg/m2 were included. The most common etiology of gastroparesis were idiopathic (36%), diabetes (36%), postsurgical (20%), scleroderma (4%) and marijuana use (4%). Clinical and technical success of procedure were 88% and 100% respectively. The mean duration of symptoms was 41.0±50.6 months. After G-POEM, there were significant improvement in mean GCSI score (32.8±6.8 vs 12.0±7.9, p< 0.001) and tendency of lower percentage of food retention on GES at 4 hours (46.42% vs 44.23%, p=0.3). As per the ASGE severity lexicon, peri-procedural mild AEs were seen in (8%). No patients encountered severe AEs. The common post-procedural AEs were abdominal pain (24%) and nausea (20%). The mean procedure time was 80±24 min and the mean length of hospital stay was 1.0 day. The mean length of follow-up was 7.6±6.1 months. Clinical response was not seen in 3 (12%) patients. Two patients required laparoscopic gastric stimulator placement (one patient had overlap of esophageal dysmotility, and diabetes) and another patient underwent partial gastrectomy for symptoms relief. After G-POEM, there was a significant reduction in mean emergency room visits due to gastroparesis-related symptoms (1.6±3.3 vs 0.2±0.8 (p< 0.03).
Discussion: G-POEM is feasible and effective treatment for refractory gastroparesis with a good short term clinical success rate. Predictive factors of long-term success or failure of G-POEM are yet to be explored on large multicenter studies.
Disclosures:
Muhammad Nadeem. Yousaf, MD1, Darian Fard, MD1, Xheni Deda, MD1, Karthik Gangu, MD2, Moafa Ghady, MD1, Sanket Basida, MD1, Alexander K. Malik, MD3, Mustafa Gandhi, MD1, Ahmed I.A. Swi, MD1, Niraj Shah, MD1, Ghassan M. Hammoud, MD1. P3711 - Efficacy and Safety of Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Refractory Gastroparesis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Missouri-Columbia, Columbia, MO; 2Kansas University Medical Center, Kansas City, KS; 3Summa Health System, Akron, OH
Introduction: Gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) is an emerging third space endoscopic technique for the management of refractory gastroparesis. We sought to determine the efficacy and safety of G-POEM for patients with refractory gastroparesis.
Methods: This is a retrospective, single-center study of consecutive patients with refractory gastroparesis who underwent G-POEM between February 2020 to September 2022. Primary outcome was clinical success defined as improvement in gastroparesis cardinal symptoms index (GCSI) score by 25% and improvement in percent of gastric emptying at 4 hours. Secondary outcomes included technical success rate (defined as successful completion of all procedural steps), rate of adverse events (AE), frequency of hospitalization due to recurrent symptoms after G-POEM and need for additional endoscopic or surgical interventions. Refractory gastroparesis was defined as persistent symptoms despite dietary modifications and pharmacologic therapy.
Results: A total of 25 patients, 18 (72%) females, mean age 58.5±14.7 year, and mean BMI 31.3±8.5 Kg/m2 were included. The most common etiology of gastroparesis were idiopathic (36%), diabetes (36%), postsurgical (20%), scleroderma (4%) and marijuana use (4%). Clinical and technical success of procedure were 88% and 100% respectively. The mean duration of symptoms was 41.0±50.6 months. After G-POEM, there were significant improvement in mean GCSI score (32.8±6.8 vs 12.0±7.9, p< 0.001) and tendency of lower percentage of food retention on GES at 4 hours (46.42% vs 44.23%, p=0.3). As per the ASGE severity lexicon, peri-procedural mild AEs were seen in (8%). No patients encountered severe AEs. The common post-procedural AEs were abdominal pain (24%) and nausea (20%). The mean procedure time was 80±24 min and the mean length of hospital stay was 1.0 day. The mean length of follow-up was 7.6±6.1 months. Clinical response was not seen in 3 (12%) patients. Two patients required laparoscopic gastric stimulator placement (one patient had overlap of esophageal dysmotility, and diabetes) and another patient underwent partial gastrectomy for symptoms relief. After G-POEM, there was a significant reduction in mean emergency room visits due to gastroparesis-related symptoms (1.6±3.3 vs 0.2±0.8 (p< 0.03).
Discussion: G-POEM is feasible and effective treatment for refractory gastroparesis with a good short term clinical success rate. Predictive factors of long-term success or failure of G-POEM are yet to be explored on large multicenter studies.
Disclosures:
Muhammad Yousaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Darian Fard indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Xheni Deda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karthik Gangu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Moafa Ghady indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sanket Basida indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mustafa Gandhi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Swi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Niraj Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ghassan Hammoud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Nadeem. Yousaf, MD1, Darian Fard, MD1, Xheni Deda, MD1, Karthik Gangu, MD2, Moafa Ghady, MD1, Sanket Basida, MD1, Alexander K. Malik, MD3, Mustafa Gandhi, MD1, Ahmed I.A. Swi, MD1, Niraj Shah, MD1, Ghassan M. Hammoud, MD1. P3711 - Efficacy and Safety of Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Refractory Gastroparesis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

