Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3776 - A Novel Use of Stress Index and Pulse Pressure Change in Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography in Acute Alcohol Associated Hepatitis vs Chronic Liver Disease
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Alessandro Colletta, MD
UMass Chan Medical School
Worcester, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Alessandro Colletta, MD, Katherine M.. Cooper, MD, Deepika Devuni, MD
UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, MA
Introduction: Chronic liver disease (CLD) is characterized by complex hemodynamics. The differences between CLD and acute alcohol associated hepatitis (AAH) in response to hemodynamic stress are poorly understood. We used data from dobutamine stress echocardiography (DSE) to assess hemodynamic parameters in patients with AAH and CLD.
Methods: We analyzed patients who completed inpatient liver transplant evaluation (ILTE) from 10/2017-8/2021. Patients were defined as “AAH” or “CLD” based on LT eligibility. Patients who underwent DSE for cardiac evaluation were included. Patients received dobutamine infusion at doses of 10, 20, 30 and 40 μgr/kg/min to target 85% of the age-predicted maximum heart rate (HR). Parameters of interest included pulse pressure change (∆PP) between after stress and baseline, baseline shock index (BSI), post-stress SI (PSSI) and ratio of SI after stress to baseline (SIratio). ∆PP is systolic blood pressure (SBP) – diastolic blood pressure (DBP), SI is HR/SBP. Post-LT outcomes included ICU and total hospital days post-LT. Relationships were analyzed using linear regression.
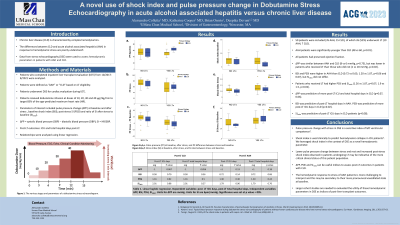
Results: 50 patients were included (35 AAH, 15 CLD), of which 26 (52%) underwent LT (19 AAH, 7 CLD). AAH patients were significantly younger than CLD (48 vs 60, p< 0.01). All patients had preserved ejection fraction. ∆PP was similar between AAH and CLD (8 vs 6 mmHg, p=0.75), but was lower in patients who received LT than did not (1 vs 18 mmHg, p=0.02). BSI and PSSI were higher in AAH than CLD (0.72 vs 0.63; 1.20 vs 1.07, p=0.06 and 0.07), but SIratio did not differ. Patients who received LT had higher PSSI and SIratio (1.26 vs 1.07, p=0.07; 1.9 vs 1.5, p=0.02). ∆PP was predictive of more post-LT ICU and total hospital days in CLD (p=0.07, 0.06). BSI was predictive of post-LT hospital days in AAH. PSSI was predictive of more post-LT ICU days in CLD (p=0.02). SIratio was predictive of post-LT ICU days in CLD patients (p=0.08).
Discussion: Pulse pressure change with stress in DSE is considered a sensitive index of left ventricular competence, while shock index is used clinically to predict hemodynamic collapse in ICU patients. In this abstract, we leveraged shock index in the context of DSE as a novel hemodynamic parameter. We show that ∆PP, PSSI and SIratio can be useful indices to assess post-LT outcomes in patients with CLD. The hemodynamic response to stress of AAH patients is more challenging to interpret and this may be secondary to their more pronounced vasodilated state at baseline.

Disclosures:
Alessandro Colletta, MD, Katherine M.. Cooper, MD, Deepika Devuni, MD. P3776 - A Novel Use of Stress Index and Pulse Pressure Change in Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography in Acute Alcohol Associated Hepatitis vs Chronic Liver Disease, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, MA
Introduction: Chronic liver disease (CLD) is characterized by complex hemodynamics. The differences between CLD and acute alcohol associated hepatitis (AAH) in response to hemodynamic stress are poorly understood. We used data from dobutamine stress echocardiography (DSE) to assess hemodynamic parameters in patients with AAH and CLD.
Methods: We analyzed patients who completed inpatient liver transplant evaluation (ILTE) from 10/2017-8/2021. Patients were defined as “AAH” or “CLD” based on LT eligibility. Patients who underwent DSE for cardiac evaluation were included. Patients received dobutamine infusion at doses of 10, 20, 30 and 40 μgr/kg/min to target 85% of the age-predicted maximum heart rate (HR). Parameters of interest included pulse pressure change (∆PP) between after stress and baseline, baseline shock index (BSI), post-stress SI (PSSI) and ratio of SI after stress to baseline (SIratio). ∆PP is systolic blood pressure (SBP) – diastolic blood pressure (DBP), SI is HR/SBP. Post-LT outcomes included ICU and total hospital days post-LT. Relationships were analyzed using linear regression.
Results: 50 patients were included (35 AAH, 15 CLD), of which 26 (52%) underwent LT (19 AAH, 7 CLD). AAH patients were significantly younger than CLD (48 vs 60, p< 0.01). All patients had preserved ejection fraction. ∆PP was similar between AAH and CLD (8 vs 6 mmHg, p=0.75), but was lower in patients who received LT than did not (1 vs 18 mmHg, p=0.02). BSI and PSSI were higher in AAH than CLD (0.72 vs 0.63; 1.20 vs 1.07, p=0.06 and 0.07), but SIratio did not differ. Patients who received LT had higher PSSI and SIratio (1.26 vs 1.07, p=0.07; 1.9 vs 1.5, p=0.02). ∆PP was predictive of more post-LT ICU and total hospital days in CLD (p=0.07, 0.06). BSI was predictive of post-LT hospital days in AAH. PSSI was predictive of more post-LT ICU days in CLD (p=0.02). SIratio was predictive of post-LT ICU days in CLD patients (p=0.08).
Discussion: Pulse pressure change with stress in DSE is considered a sensitive index of left ventricular competence, while shock index is used clinically to predict hemodynamic collapse in ICU patients. In this abstract, we leveraged shock index in the context of DSE as a novel hemodynamic parameter. We show that ∆PP, PSSI and SIratio can be useful indices to assess post-LT outcomes in patients with CLD. The hemodynamic response to stress of AAH patients is more challenging to interpret and this may be secondary to their more pronounced vasodilated state at baseline.

Figure: Table1. Linear regression analysis of post liver transplant outcomes relative to DSE hemodynamic parameters.
Disclosures:
Alessandro Colletta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Katherine Cooper indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Deepika Devuni: NIAAA (AA017986) – Grant/Research Support. Sequana Medical – Grant/Research Support.
Alessandro Colletta, MD, Katherine M.. Cooper, MD, Deepika Devuni, MD. P3776 - A Novel Use of Stress Index and Pulse Pressure Change in Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography in Acute Alcohol Associated Hepatitis vs Chronic Liver Disease, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
