Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3804 - Vaccine-Preventable Illness in Liver Transplant Recipients: Analysis of 170,650 Hospitalizations
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Shivam Kalra, MBBS
Trident Medical Center
North Charleston, SC
Presenting Author(s)
Isha Kohli, MBBS, CPH, MPH1, Aalam Sohal, MD2, Hunza Chaudhry, MD3, Ishandeep Singh, MBBS4, Shivam Kalra, MBBS5, Kirti Arora, MBBS4, Dino Dukovic, BS6, Kanwal Bains, MBBS, CNSC7, Marina Roytman, MD8
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 2Liver Institute Northwest, Seattle, WA; 3University of California San Francisco, Fresno, CA; 4Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India; 5Trident Medical Center, Charleston, SC; 6Ross University School of Medicine, Maramar, FL; 7University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ; 8UCSF Fresno, Fresno, CA
Introduction: Liver transplant (LT) recipients and patients with chronic liver disease (CLD) are at an increased risk of infections. It has been reported that vaccine preventable illness (VPIs) may be more common or severe in these patients due to immunosuppression. The objective of our study was to assess the incidence, mortality, and impact of VPIs on outcomes in LT recipients.
Methods: NIS 2016-2020 was used to identify adult (age >18), hospitalized LT recipients using ICD-10 codes. Information was collected on patient demographics, hospital characteristics, etiology of liver disease, decompensations and outcomes. Patients with missing demographics or mortality were excluded. Patients were stratified into two groups based on the presence or absence of VPI. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to identify the association between VPI and outcomes after adjusting for patient demographics, hospital characteristics, etiology, decompensations, and Elixhauser comorbidities.
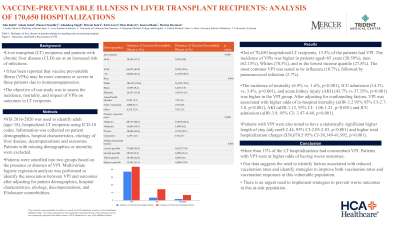
Results: Out of 70,650 hospitalized LT recipients, 13.5% of the patients had VPI. The incidence of VPIs was higher in patients aged >65 years (50.59%), men (62.15%), Whites (70.5%), and in the lowest income quartile (27.8%). The most common VPI was noted to be influenza (10.7%), followed by pneumococcal infection (2.7%). The incidence of mortality (6.9% vs. 1.6%, p< 0.001), ICU admission (14.3% vs. 3.4%, p< 0.001), and acute kidney injury (AKI) (43.7% vs 37.35%, p< 0.001) was higher in the VPI group. After adjusting for confounding factors, VPI was associated with higher odds of in-hospital mortality (aOR-3.2 95% 95% CI-2.7-3.8, p< 0.001), AKI (aOR-1.13, 95% CI- 1.06-1.21, p< 0.001) and ICU admission (aOR-3.9, 95% CI- 3.47-4.40, p< 0.001). Patients with VPI were also noted to have a statistically significant higher length of stay (adj coeff-2.44, 95% CI-2.05-2.83, p< 0.001) and higher total hospitalization charges ($36,070.5 95% CI-30,149-41,992, p< 0.001).
Discussion: More than 13% of the LT hospitalizations had concomitant VPI. Patients with VPI were at higher odds of having worse outcomes. Our data suggest the need to identify factors associated with reduced vaccination rates and identify strategies to improve both vaccination rates and vaccination responses in this vulnerable population There is an urgent need to implement strategies to prevent worse outcomes in this at-risk population.

Disclosures:
Isha Kohli, MBBS, CPH, MPH1, Aalam Sohal, MD2, Hunza Chaudhry, MD3, Ishandeep Singh, MBBS4, Shivam Kalra, MBBS5, Kirti Arora, MBBS4, Dino Dukovic, BS6, Kanwal Bains, MBBS, CNSC7, Marina Roytman, MD8. P3804 - Vaccine-Preventable Illness in Liver Transplant Recipients: Analysis of 170,650 Hospitalizations, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 2Liver Institute Northwest, Seattle, WA; 3University of California San Francisco, Fresno, CA; 4Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India; 5Trident Medical Center, Charleston, SC; 6Ross University School of Medicine, Maramar, FL; 7University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ; 8UCSF Fresno, Fresno, CA
Introduction: Liver transplant (LT) recipients and patients with chronic liver disease (CLD) are at an increased risk of infections. It has been reported that vaccine preventable illness (VPIs) may be more common or severe in these patients due to immunosuppression. The objective of our study was to assess the incidence, mortality, and impact of VPIs on outcomes in LT recipients.
Methods: NIS 2016-2020 was used to identify adult (age >18), hospitalized LT recipients using ICD-10 codes. Information was collected on patient demographics, hospital characteristics, etiology of liver disease, decompensations and outcomes. Patients with missing demographics or mortality were excluded. Patients were stratified into two groups based on the presence or absence of VPI. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to identify the association between VPI and outcomes after adjusting for patient demographics, hospital characteristics, etiology, decompensations, and Elixhauser comorbidities.
Results: Out of 70,650 hospitalized LT recipients, 13.5% of the patients had VPI. The incidence of VPIs was higher in patients aged >65 years (50.59%), men (62.15%), Whites (70.5%), and in the lowest income quartile (27.8%). The most common VPI was noted to be influenza (10.7%), followed by pneumococcal infection (2.7%). The incidence of mortality (6.9% vs. 1.6%, p< 0.001), ICU admission (14.3% vs. 3.4%, p< 0.001), and acute kidney injury (AKI) (43.7% vs 37.35%, p< 0.001) was higher in the VPI group. After adjusting for confounding factors, VPI was associated with higher odds of in-hospital mortality (aOR-3.2 95% 95% CI-2.7-3.8, p< 0.001), AKI (aOR-1.13, 95% CI- 1.06-1.21, p< 0.001) and ICU admission (aOR-3.9, 95% CI- 3.47-4.40, p< 0.001). Patients with VPI were also noted to have a statistically significant higher length of stay (adj coeff-2.44, 95% CI-2.05-2.83, p< 0.001) and higher total hospitalization charges ($36,070.5 95% CI-30,149-41,992, p< 0.001).
Discussion: More than 13% of the LT hospitalizations had concomitant VPI. Patients with VPI were at higher odds of having worse outcomes. Our data suggest the need to identify factors associated with reduced vaccination rates and identify strategies to improve both vaccination rates and vaccination responses in this vulnerable population There is an urgent need to implement strategies to prevent worse outcomes in this at-risk population.

Figure: Figure 1- Outcomes, in patients of Liver Transplant stratified by the presence of VPI.
Disclosures:
Isha Kohli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aalam Sohal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hunza Chaudhry indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ishandeep Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shivam Kalra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kirti Arora indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dino Dukovic indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kanwal Bains indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marina Roytman: Gilead – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Intercept – Advisor or Review Panel Member. VBI – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Isha Kohli, MBBS, CPH, MPH1, Aalam Sohal, MD2, Hunza Chaudhry, MD3, Ishandeep Singh, MBBS4, Shivam Kalra, MBBS5, Kirti Arora, MBBS4, Dino Dukovic, BS6, Kanwal Bains, MBBS, CNSC7, Marina Roytman, MD8. P3804 - Vaccine-Preventable Illness in Liver Transplant Recipients: Analysis of 170,650 Hospitalizations, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
