Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3821 - From Coast to Coast: State-Wise Analysis of Acute Hepatitis Cases in the United States from 1990 to 2019
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Silpa Choday, MD
Creighton University
Phoenix, Arizona
Presenting Author(s)
Silpa Choday, MD1, Patrick George. Pathappillil, MD1, Gautam Maddineni, MD2, Laura Cicani, MD3, Neil Vyas, MD1
1Creighton University, Phoenix, AZ; 2Florida State University, Cape Coral, FL; 3International University of Health Sciences, Las Vegas, NV
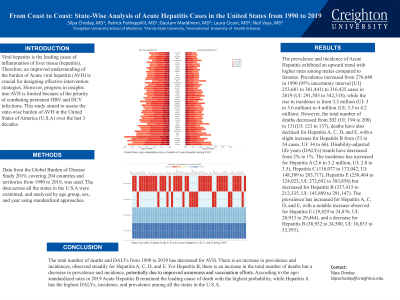
Introduction: Viral hepatitis (A, B, C, D, and E) is the leading cause of liver inflammation. Therefore, an improved understanding of the burden of Acute viral hepatitis (AVH) is crucial for designing not only effective treatment strategies but prevention as well. However, studies of AVH have shown limitations in their progress because of the priority of combating persistent HBV and HCV infections. This study aimed to assess the state-wise burden of AVH in the United States of America (U.S.A).
Methods: From 1990 to 2019 we extrapolated data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019, covering 204 countries and territories. The data across all the states in the U.S.A were examined, and analyzed by age group, sex, and year using standardized approaches.
Results: The prevalence and incidence of Acute Hepatitis exhibited an upward trend with higher rates among males compared to females. Prevalence increased from 276,640 in 1990 (95% uncertainty interval [UI] 253,681 to 301,441) to 316,425 cases in 2019 (UI: 291,585 to 342,318), while the rise in incidence is from 3.3 million (UI: 3 to 3.6 million) to 4 million (UI: 3.5 to 4.2 million). However, the total number of deaths decreased from 202 (UI: 194 to 208) to 131(UI: 123 to 137), deaths have also declined for Hepatitis A, C, and E, with a slight increase for Hepatitis B from (53 to 54 cases, UI: 34 to 66). Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) trends have decreased from 2% to 1%. The incidence has increased for Hepatitis A (2.6 to 3.2 million, UI: 2.8 to 3.5), Hepatitis C (116,077 to 173,042, UI: 148,389 to 203,717), Hepatitis E (258,464 to 324,023, UI: 272,692 to 383,858) but decreased for Hepatitis B (337,413 to 212,335, UI: 145,889 to 291,147). The prevalence has increased for Hepatitis A, C, and E, with a notable increase observed for Hepatitis E (19,829 to 24,876, UI: 20,913 to 29,464), and a decrease for Hepatitis B (38,932 to 24,500, UI: 16,833 to 33,593).
Discussion: The total number of deaths and DALYs from 1990 to 2019 has decreased for AVH. There is an increase in prevalence and incidence, observed steadily for Hepatitis A, C, and E. There is an increase in the total number of deaths but a decrease in the prevalence and incidence of Hepatitis B, potentially due to improved awareness and vaccination efforts. According to the age-standardized rates in 2019, Acute Hepatitis B remained the leading cause of death with the highest probability, while Hepatitis A has the highest DALYs, incidence, and prevalence among all the states in the U.S.A.

Disclosures:
Silpa Choday, MD1, Patrick George. Pathappillil, MD1, Gautam Maddineni, MD2, Laura Cicani, MD3, Neil Vyas, MD1. P3821 - From Coast to Coast: State-Wise Analysis of Acute Hepatitis Cases in the United States from 1990 to 2019, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Creighton University, Phoenix, AZ; 2Florida State University, Cape Coral, FL; 3International University of Health Sciences, Las Vegas, NV
Introduction: Viral hepatitis (A, B, C, D, and E) is the leading cause of liver inflammation. Therefore, an improved understanding of the burden of Acute viral hepatitis (AVH) is crucial for designing not only effective treatment strategies but prevention as well. However, studies of AVH have shown limitations in their progress because of the priority of combating persistent HBV and HCV infections. This study aimed to assess the state-wise burden of AVH in the United States of America (U.S.A).
Methods: From 1990 to 2019 we extrapolated data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019, covering 204 countries and territories. The data across all the states in the U.S.A were examined, and analyzed by age group, sex, and year using standardized approaches.
Results: The prevalence and incidence of Acute Hepatitis exhibited an upward trend with higher rates among males compared to females. Prevalence increased from 276,640 in 1990 (95% uncertainty interval [UI] 253,681 to 301,441) to 316,425 cases in 2019 (UI: 291,585 to 342,318), while the rise in incidence is from 3.3 million (UI: 3 to 3.6 million) to 4 million (UI: 3.5 to 4.2 million). However, the total number of deaths decreased from 202 (UI: 194 to 208) to 131(UI: 123 to 137), deaths have also declined for Hepatitis A, C, and E, with a slight increase for Hepatitis B from (53 to 54 cases, UI: 34 to 66). Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) trends have decreased from 2% to 1%. The incidence has increased for Hepatitis A (2.6 to 3.2 million, UI: 2.8 to 3.5), Hepatitis C (116,077 to 173,042, UI: 148,389 to 203,717), Hepatitis E (258,464 to 324,023, UI: 272,692 to 383,858) but decreased for Hepatitis B (337,413 to 212,335, UI: 145,889 to 291,147). The prevalence has increased for Hepatitis A, C, and E, with a notable increase observed for Hepatitis E (19,829 to 24,876, UI: 20,913 to 29,464), and a decrease for Hepatitis B (38,932 to 24,500, UI: 16,833 to 33,593).
Discussion: The total number of deaths and DALYs from 1990 to 2019 has decreased for AVH. There is an increase in prevalence and incidence, observed steadily for Hepatitis A, C, and E. There is an increase in the total number of deaths but a decrease in the prevalence and incidence of Hepatitis B, potentially due to improved awareness and vaccination efforts. According to the age-standardized rates in 2019, Acute Hepatitis B remained the leading cause of death with the highest probability, while Hepatitis A has the highest DALYs, incidence, and prevalence among all the states in the U.S.A.

Figure: United States Age-standardized ratio of deaths of Acute Hepatitis during 2019
Disclosures:
Silpa Choday indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patrick Pathappillil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gautam Maddineni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laura Cicani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neil Vyas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Silpa Choday, MD1, Patrick George. Pathappillil, MD1, Gautam Maddineni, MD2, Laura Cicani, MD3, Neil Vyas, MD1. P3821 - From Coast to Coast: State-Wise Analysis of Acute Hepatitis Cases in the United States from 1990 to 2019, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
