Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P3738 - Diagnosis of Littoral Cell Angioma of the Spleen With Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Abdullah Sagar Aleem, MD
University of Texas Health Science Center
Houston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Abdullah Aleem, MD1, Parvir Aujla, MD2, Blake Purtle, MD3, Maya Sarihan, MD4, Allen Omo-Ogboi, MD2, Srinivas Ramireddy, MD5, Jigar Patel, MD2
1University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, AZ; 2University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX; 3University of Texas Health Science, Houston, TX; 4University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, TX; 5UTH Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, TX
Introduction: Littoral cell angioma (LCA) is a rare primary vascular neoplasm of the spleen that carries a risk of malignant potential. The imaging characteristics of LCA are non-specific as the tumor appears similar to other vascular tumors found in the spleen. For a definitive diagnosis, a biopsy with a histopathologic exam is required. Typically, this was achieved after splenectomy due to uncertainty of the tumor’s malignant potential. Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) of splenic tumors has been approached with caution given the heavy vascularity. We discuss a rare case of Littoral Cell Angioma diagnosed with Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (EUS-FNAB).
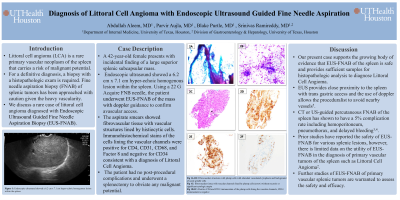
Case Description/Methods: A 42-year-old female with systemic lupus erythematous presents with incidental finding of a large superior splenic subcapsular mass. Endoscopic ultrasound showed a 6.2 cm x 7.1 cm hyper-echoic homogenous lesion within the spleen. Using a 22 G Acquire FNB needle, the patient underwent EUS-FNAB of the mass with doppler guidance to confirm avascular access. The aspirate smears showed fibrovascular tissue with vascular structures lined by histiocytic cells. Immunohistochemical stains of the cells lining the vascular channels were positive for CD4, CD31, CD68, and Factor 8 and negative for CD34 consistent with a diagnosis of Littoral Cell Angioma (Figure 1). The patient had no post-procedural complications and underwent a splenectomy to obviate any malignant potential.
Discussion: Incidental findings of a splenic mass require biopsy and histopathologic analysis to rule out tumors that carry a high risk of malignancy. Our present case supports the growing body of evidence that EUS-FNAB of the spleen is safe and provides sufficient samples for histopathologic analysis to diagnose Littoral Cell Angioma. EUS provides close proximity to the spleen with trans gastric access and the use of doppler allows the proceduralist to avoid nearby vessels. CT or US-guided percutaneous FNAB of the spleen has shown to have a 5% complication rate including hemoperitoneum, pneumothorax, and delayed bleeding. Prior studies have reported the safety of EUS-FNAB for various splenic lesions, however, there is limited data on the utility of EUS-FNAB in the diagnosis of primary vascular tumors of the spleen such as Littoral Cell Angioma.

Disclosures:
Abdullah Aleem, MD1, Parvir Aujla, MD2, Blake Purtle, MD3, Maya Sarihan, MD4, Allen Omo-Ogboi, MD2, Srinivas Ramireddy, MD5, Jigar Patel, MD2. P3738 - Diagnosis of Littoral Cell Angioma of the Spleen With Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, AZ; 2University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX; 3University of Texas Health Science, Houston, TX; 4University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, TX; 5UTH Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, TX
Introduction: Littoral cell angioma (LCA) is a rare primary vascular neoplasm of the spleen that carries a risk of malignant potential. The imaging characteristics of LCA are non-specific as the tumor appears similar to other vascular tumors found in the spleen. For a definitive diagnosis, a biopsy with a histopathologic exam is required. Typically, this was achieved after splenectomy due to uncertainty of the tumor’s malignant potential. Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) of splenic tumors has been approached with caution given the heavy vascularity. We discuss a rare case of Littoral Cell Angioma diagnosed with Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (EUS-FNAB).
Case Description/Methods: A 42-year-old female with systemic lupus erythematous presents with incidental finding of a large superior splenic subcapsular mass. Endoscopic ultrasound showed a 6.2 cm x 7.1 cm hyper-echoic homogenous lesion within the spleen. Using a 22 G Acquire FNB needle, the patient underwent EUS-FNAB of the mass with doppler guidance to confirm avascular access. The aspirate smears showed fibrovascular tissue with vascular structures lined by histiocytic cells. Immunohistochemical stains of the cells lining the vascular channels were positive for CD4, CD31, CD68, and Factor 8 and negative for CD34 consistent with a diagnosis of Littoral Cell Angioma (Figure 1). The patient had no post-procedural complications and underwent a splenectomy to obviate any malignant potential.
Discussion: Incidental findings of a splenic mass require biopsy and histopathologic analysis to rule out tumors that carry a high risk of malignancy. Our present case supports the growing body of evidence that EUS-FNAB of the spleen is safe and provides sufficient samples for histopathologic analysis to diagnose Littoral Cell Angioma. EUS provides close proximity to the spleen with trans gastric access and the use of doppler allows the proceduralist to avoid nearby vessels. CT or US-guided percutaneous FNAB of the spleen has shown to have a 5% complication rate including hemoperitoneum, pneumothorax, and delayed bleeding. Prior studies have reported the safety of EUS-FNAB for various splenic lesions, however, there is limited data on the utility of EUS-FNAB in the diagnosis of primary vascular tumors of the spleen such as Littoral Cell Angioma.

Figure: Fig 1A: Smear shows fibrovascular structures with spindle cells and plump cells with abundant vacuolated cytoplasm (Pap stain) x100. Fig 1B: Smear of plump cells with abundant cytoplasm and background of scant spindle cells, higher magnification (Diff-Quik stain) x 200. Fig 1C: Cellblock shows fibrovascular tissue with vascular channels lined by plump cells (arrow) without necrosis or significant cytologic atypia (H&E) x 200. Fig 1D: CD4 immunostain shows positive staining of the plump cells lining the vascular channels (x 200). Fig 1E: CD31 immunostain shows positive staining of the plump cells lining the vascular channels (x 200). Fig 1F: CD34 immunostain is negative in the plump cells lining the vascular channels (x 200)
Disclosures:
Abdullah Aleem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Parvir Aujla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Blake Purtle indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maya Sarihan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allen Omo-Ogboi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Srinivas Ramireddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jigar Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdullah Aleem, MD1, Parvir Aujla, MD2, Blake Purtle, MD3, Maya Sarihan, MD4, Allen Omo-Ogboi, MD2, Srinivas Ramireddy, MD5, Jigar Patel, MD2. P3738 - Diagnosis of Littoral Cell Angioma of the Spleen With Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
