Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3829 - Medication, Nutrition, Education: A Quality Improvement Initiative to Reduce Readmissions in Patients With Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Sandeep Sikerwar, MD
New York-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center
Poughkeepsie, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Sandeep Sikerwar, MD1, Paul Paik, MD1, Neela Easwar, MD1, Paige Whorley, RD1, Gabrielle Gambino, RD1, Colton Pence, MD1, Russell Rosenblatt, MD, MS2, Arun Jesudian, MD3
1New York-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY; 2New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY; 3Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY
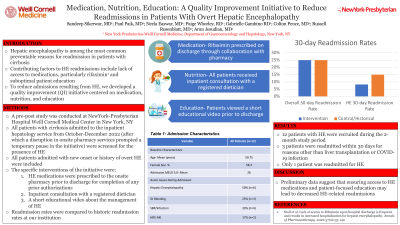
Introduction: Hepatic encephalopathy is among the most common preventable reasons for readmission in patients with cirrhosis. Contributing factors to HE readmissions include lack of access to medications and suboptimal patient education. Rifaximin therapy decreases the risk of HE-related hospitalization; however, insurance and cost barriers prevent access to rifaximin in a subset of patients at risk.1 In an effort to reduce admissions resulting from HE, we developed a quality improvement (QI) initiative to ensure that admitted patients with cirrhosis and HE receive rifaximin, consultation with a registered dietician, and education about HE prior to discharge. Here, we present the initial data from the study.
Methods: A pre-post study was conducted at NewYorkPresbyterian Hospital-Weill Cornell Medical Center in New York, NY. All patients with cirrhosis admitted to the inpatient hepatology service from October-December 2022 (after which a disruption in onsite pharmacy services prompted a temporary pause in the initiative) were screened for the presence of HE. All patients admitted with new onset or history of overt HE were included. The specific interventions of the initiative were: 1) HE medications were prescribed to the onsite pharmacy prior to discharge for completion of any prior authorizations and delivery to bedside 2) Inpatient consultation with a registered dietician, and 3) A short educational video about the management of HE. Readmission rates were compared to historic readmission rates at our institution.
Results: 12 patients with HE were recruited during the 2-month study period, and 3 were readmitted within 30 days for reasons other than liver transplantation or COVID-19 infection, yielding an overall adjusted readmission rate of 25%, which was similar to the historical 30-day readmission rate among patients with cirrhosis at our institution. However, only 1/12 patients was readmitted for HE.
Discussion: The initial results of this QI initiative demonstrate a similar 30-day readmission rate for patients who underwent the intervention compared to historical same center readmissions, although only 1/12 were readmitted for HE. Preliminary data suggest that ensuring access to HE medications as well as patient-focused education on nutrition and disease state may lead to decreased HE-related readmissions.
1. Stoll et al. Lack of access to Rifaximin upon hospital discharge is frequent and results in increased hospitalization for hepatic encephalopathy. Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 2022:57(2)133-140
Disclosures:
Sandeep Sikerwar, MD1, Paul Paik, MD1, Neela Easwar, MD1, Paige Whorley, RD1, Gabrielle Gambino, RD1, Colton Pence, MD1, Russell Rosenblatt, MD, MS2, Arun Jesudian, MD3. P3829 - Medication, Nutrition, Education: A Quality Improvement Initiative to Reduce Readmissions in Patients With Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1New York-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY; 2New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY; 3Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY
Introduction: Hepatic encephalopathy is among the most common preventable reasons for readmission in patients with cirrhosis. Contributing factors to HE readmissions include lack of access to medications and suboptimal patient education. Rifaximin therapy decreases the risk of HE-related hospitalization; however, insurance and cost barriers prevent access to rifaximin in a subset of patients at risk.1 In an effort to reduce admissions resulting from HE, we developed a quality improvement (QI) initiative to ensure that admitted patients with cirrhosis and HE receive rifaximin, consultation with a registered dietician, and education about HE prior to discharge. Here, we present the initial data from the study.
Methods: A pre-post study was conducted at NewYorkPresbyterian Hospital-Weill Cornell Medical Center in New York, NY. All patients with cirrhosis admitted to the inpatient hepatology service from October-December 2022 (after which a disruption in onsite pharmacy services prompted a temporary pause in the initiative) were screened for the presence of HE. All patients admitted with new onset or history of overt HE were included. The specific interventions of the initiative were: 1) HE medications were prescribed to the onsite pharmacy prior to discharge for completion of any prior authorizations and delivery to bedside 2) Inpatient consultation with a registered dietician, and 3) A short educational video about the management of HE. Readmission rates were compared to historic readmission rates at our institution.
Results: 12 patients with HE were recruited during the 2-month study period, and 3 were readmitted within 30 days for reasons other than liver transplantation or COVID-19 infection, yielding an overall adjusted readmission rate of 25%, which was similar to the historical 30-day readmission rate among patients with cirrhosis at our institution. However, only 1/12 patients was readmitted for HE.
Discussion: The initial results of this QI initiative demonstrate a similar 30-day readmission rate for patients who underwent the intervention compared to historical same center readmissions, although only 1/12 were readmitted for HE. Preliminary data suggest that ensuring access to HE medications as well as patient-focused education on nutrition and disease state may lead to decreased HE-related readmissions.
1. Stoll et al. Lack of access to Rifaximin upon hospital discharge is frequent and results in increased hospitalization for hepatic encephalopathy. Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 2022:57(2)133-140
Disclosures:
Sandeep Sikerwar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Paik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neela Easwar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paige Whorley indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gabrielle Gambino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Colton Pence indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Russell Rosenblatt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arun Jesudian: Dynavax Therapeutics – Speakers Bureau. Salix Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Sandeep Sikerwar, MD1, Paul Paik, MD1, Neela Easwar, MD1, Paige Whorley, RD1, Gabrielle Gambino, RD1, Colton Pence, MD1, Russell Rosenblatt, MD, MS2, Arun Jesudian, MD3. P3829 - Medication, Nutrition, Education: A Quality Improvement Initiative to Reduce Readmissions in Patients With Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
