Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3630 - Burden of Hidradenitis Suppurativa on Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop, MD
Piedmont Athens Regional Medical Center
Athens, GA
Presenting Author(s)
Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop, MD1, Kikelomo Olaosebikan, MD1, Arnold Forlemu, MD, MPH2, Vishnu Poojitha Ronda, MD2, Pavani Reddy Garlapati, MD2, Praneeth Bandaru, MD2, Saigopal R. Gujjula, 3, Srilaxmi Gujjula, MD2, Vijay Gayam, MD2, Hamsika Moparty, MD2, Denzil Etienne, MD2, Madhavi Reddy, MD2
1Piedmont Athens Regional Medical Center, Athens, GA; 2Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 3American University of Antigua, Coolidge, Saint John, Antigua and Barbuda
Introduction: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) are two conditions that share common genetic and immunologic features; and have similar gut and skin manifestations including perineal and inguinal sterile abscesses, sinus tract formation and scarring. However, the association between both entities is largely unclear. The goal of this study was to verify an association between both diseases, explore the burden of HS on IBD including in-hospital mortality, length of stay (LOS), total costs and complications, and establish baseline comorbidities of IBD patients with HS.
Methods: We conducted a nationwide study using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database for the years 2016 and 2017. All patients with International Classification of Diseases Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) codes for the diagnosis of Crohn’s disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC) and HS were included. We also obtained ICD-10-CM codes for complications including clostridium difficile infection, osteoporosis, sepsis, intensive care admission, and blood transfusion. Odds ratios (OR) and confidence intervals (CI) are reported. p< 0.05 was set for statistical significance.
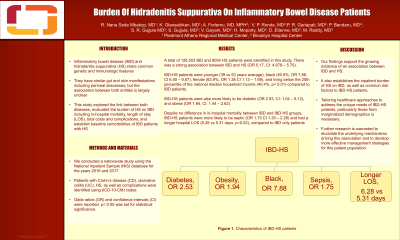
Results: A total of 126,503 IBD and 8054 HS patients were identified in this study. There was a strong association between IBD and HS (OR 5.17, CI: 4.678 – 5.70). IBD-HS patients were younger (39 vs 53 years average), black (50.9%, OR 7.88, CI 6.50 – 9.57), female (63.9%, OR 1.38 CI 1.13 – 1.69), and living below the 25th percentile of the national median household income (40.4%, p< 0.01). IBD-HS patients were also more likely to be diabetic (OR 2.53, CI: 1.04 – 6.12), and obese (OR 1.94, CI: 1.44 – 2.62). Despite no difference in in-hospital mortality between IBD and IBD-HS groups, IBD-HS patients were more likely to be septic (OR 1.75 CI 1.35 – 2.28) and had a longer hospital LOS (6.28 vs 5.31 days, p=0.02), compared to IBD only patients (Table 1).
Discussion: Our findings support the growing evidence of an association between IBD and HS, and establishes the inpatient burden of HS on IBD, as well as common risk factors to IBD-HS patients.
Disclosures:
Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop, MD1, Kikelomo Olaosebikan, MD1, Arnold Forlemu, MD, MPH2, Vishnu Poojitha Ronda, MD2, Pavani Reddy Garlapati, MD2, Praneeth Bandaru, MD2, Saigopal R. Gujjula, 3, Srilaxmi Gujjula, MD2, Vijay Gayam, MD2, Hamsika Moparty, MD2, Denzil Etienne, MD2, Madhavi Reddy, MD2. P3630 - Burden of Hidradenitis Suppurativa on Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Piedmont Athens Regional Medical Center, Athens, GA; 2Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 3American University of Antigua, Coolidge, Saint John, Antigua and Barbuda
Introduction: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) are two conditions that share common genetic and immunologic features; and have similar gut and skin manifestations including perineal and inguinal sterile abscesses, sinus tract formation and scarring. However, the association between both entities is largely unclear. The goal of this study was to verify an association between both diseases, explore the burden of HS on IBD including in-hospital mortality, length of stay (LOS), total costs and complications, and establish baseline comorbidities of IBD patients with HS.
Methods: We conducted a nationwide study using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database for the years 2016 and 2017. All patients with International Classification of Diseases Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) codes for the diagnosis of Crohn’s disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC) and HS were included. We also obtained ICD-10-CM codes for complications including clostridium difficile infection, osteoporosis, sepsis, intensive care admission, and blood transfusion. Odds ratios (OR) and confidence intervals (CI) are reported. p< 0.05 was set for statistical significance.
Results: A total of 126,503 IBD and 8054 HS patients were identified in this study. There was a strong association between IBD and HS (OR 5.17, CI: 4.678 – 5.70). IBD-HS patients were younger (39 vs 53 years average), black (50.9%, OR 7.88, CI 6.50 – 9.57), female (63.9%, OR 1.38 CI 1.13 – 1.69), and living below the 25th percentile of the national median household income (40.4%, p< 0.01). IBD-HS patients were also more likely to be diabetic (OR 2.53, CI: 1.04 – 6.12), and obese (OR 1.94, CI: 1.44 – 2.62). Despite no difference in in-hospital mortality between IBD and IBD-HS groups, IBD-HS patients were more likely to be septic (OR 1.75 CI 1.35 – 2.28) and had a longer hospital LOS (6.28 vs 5.31 days, p=0.02), compared to IBD only patients (Table 1).
Discussion: Our findings support the growing evidence of an association between IBD and HS, and establishes the inpatient burden of HS on IBD, as well as common risk factors to IBD-HS patients.
Disclosures:
Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kikelomo Olaosebikan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arnold Forlemu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vishnu Poojitha Ronda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pavani Reddy Garlapati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Praneeth Bandaru indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saigopal Gujjula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Srilaxmi Gujjula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vijay Gayam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamsika Moparty indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Denzil Etienne indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhavi Reddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop, MD1, Kikelomo Olaosebikan, MD1, Arnold Forlemu, MD, MPH2, Vishnu Poojitha Ronda, MD2, Pavani Reddy Garlapati, MD2, Praneeth Bandaru, MD2, Saigopal R. Gujjula, 3, Srilaxmi Gujjula, MD2, Vijay Gayam, MD2, Hamsika Moparty, MD2, Denzil Etienne, MD2, Madhavi Reddy, MD2. P3630 - Burden of Hidradenitis Suppurativa on Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
