Tuesday Poster Session
Category: General Endoscopy
P3398 - Safety and Outcomes of Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Tube with Jejunal Extension Placement Following Lung Transplantation
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- CP
Christopher Price, MD
University of Alabama at Birmingham
Birmingham, AL
Presenting Author(s)
Christopher Price, MD, Thomas Ruli, MD, Mahmoud Aryan, MD, Shajan Peter, MD
University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL
Introduction: Proper nutrition in patients undergoing lung transplantation (LT) is essential. However, the ability of these patients to meet their oral nutritional requirements after LT can vary. Percutaneous gastrojejunostomy tube (PEG-J) placement is common in patients requiring nutritional support. We examined the utility of PEG-J placement in a LT cohort.
Methods: We performed a retrospective review of patients who underwent LT followed by endoscopic PEG-J placement between 2018-2023 at an academic tertiary medical center. Inclusion criteria consisted of PEG-J placement for enteral nutrition in patients status post-LT. Outcome variables included serum albumin trends, post-procedure complications, mortality, and readmission rates. Descriptive statistics were represented by mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables and frequency percentage for categorical variables.
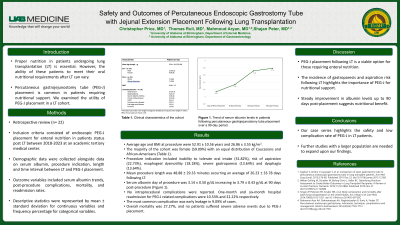
Results: Twenty-two patients underwent LT that subsequently received PEG-J placement. Average age and BMI at procedure were 52.91 ± 10.56 years and 26.86 ± 3.55 kg/m2. The majority of the cohort was female (59.09%) with an equal distribution of Caucasians and African-Americans. Procedure indication included inability to tolerate oral intake (31.82%), risk of aspiration (22.73%), esophageal dysmotility (18.18%), severe gastroparesis (13.64%) and dysphagia (13.64%). Mean procedure length was 48.88 ± 29.33 minutes occurring an average of 26.23 ± 33.78 days following LT. Serum albumin day of procedure was 3.14 ± 0.50 g/dL increasing to 3.79 ± 0.43 g/dL at 90 days post-procedure (Figure 1). Technical success was achieved in 100% of cases with no intraprocedural complications reported. One-month and six-month hospital readmission for PEG-J related complications were 10.53% and 22.22% respectively. The most common complication was early leakage in 9.09% of cases. Overall mortality was 27.27%, and no patients suffered severe adverse events due to PEG-J placement.
Discussion: PEG-J placement following LT is a viable option for those requiring enteral nutrition. Our case series highlights the safety and low complication rate of PEG-J in LT patients. The incidence of gastroparesis and aspiration risk following LT highlights the importance of PEG-J for nutritional support. Steady improvement in albumin levels up to 90 days post-placement suggests nutritional benefit. Further studies with a larger population are needed to expand upon our findings.

Disclosures:
Christopher Price, MD, Thomas Ruli, MD, Mahmoud Aryan, MD, Shajan Peter, MD. P3398 - Safety and Outcomes of Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Tube with Jejunal Extension Placement Following Lung Transplantation, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL
Introduction: Proper nutrition in patients undergoing lung transplantation (LT) is essential. However, the ability of these patients to meet their oral nutritional requirements after LT can vary. Percutaneous gastrojejunostomy tube (PEG-J) placement is common in patients requiring nutritional support. We examined the utility of PEG-J placement in a LT cohort.
Methods: We performed a retrospective review of patients who underwent LT followed by endoscopic PEG-J placement between 2018-2023 at an academic tertiary medical center. Inclusion criteria consisted of PEG-J placement for enteral nutrition in patients status post-LT. Outcome variables included serum albumin trends, post-procedure complications, mortality, and readmission rates. Descriptive statistics were represented by mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables and frequency percentage for categorical variables.
Results: Twenty-two patients underwent LT that subsequently received PEG-J placement. Average age and BMI at procedure were 52.91 ± 10.56 years and 26.86 ± 3.55 kg/m2. The majority of the cohort was female (59.09%) with an equal distribution of Caucasians and African-Americans. Procedure indication included inability to tolerate oral intake (31.82%), risk of aspiration (22.73%), esophageal dysmotility (18.18%), severe gastroparesis (13.64%) and dysphagia (13.64%). Mean procedure length was 48.88 ± 29.33 minutes occurring an average of 26.23 ± 33.78 days following LT. Serum albumin day of procedure was 3.14 ± 0.50 g/dL increasing to 3.79 ± 0.43 g/dL at 90 days post-procedure (Figure 1). Technical success was achieved in 100% of cases with no intraprocedural complications reported. One-month and six-month hospital readmission for PEG-J related complications were 10.53% and 22.22% respectively. The most common complication was early leakage in 9.09% of cases. Overall mortality was 27.27%, and no patients suffered severe adverse events due to PEG-J placement.
Discussion: PEG-J placement following LT is a viable option for those requiring enteral nutrition. Our case series highlights the safety and low complication rate of PEG-J in LT patients. The incidence of gastroparesis and aspiration risk following LT highlights the importance of PEG-J for nutritional support. Steady improvement in albumin levels up to 90 days post-placement suggests nutritional benefit. Further studies with a larger population are needed to expand upon our findings.

Figure: Figure 1. Average Cohort Serum Albumin Trend
Disclosures:
Christopher Price indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas Ruli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahmoud Aryan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shajan Peter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christopher Price, MD, Thomas Ruli, MD, Mahmoud Aryan, MD, Shajan Peter, MD. P3398 - Safety and Outcomes of Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Tube with Jejunal Extension Placement Following Lung Transplantation, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
